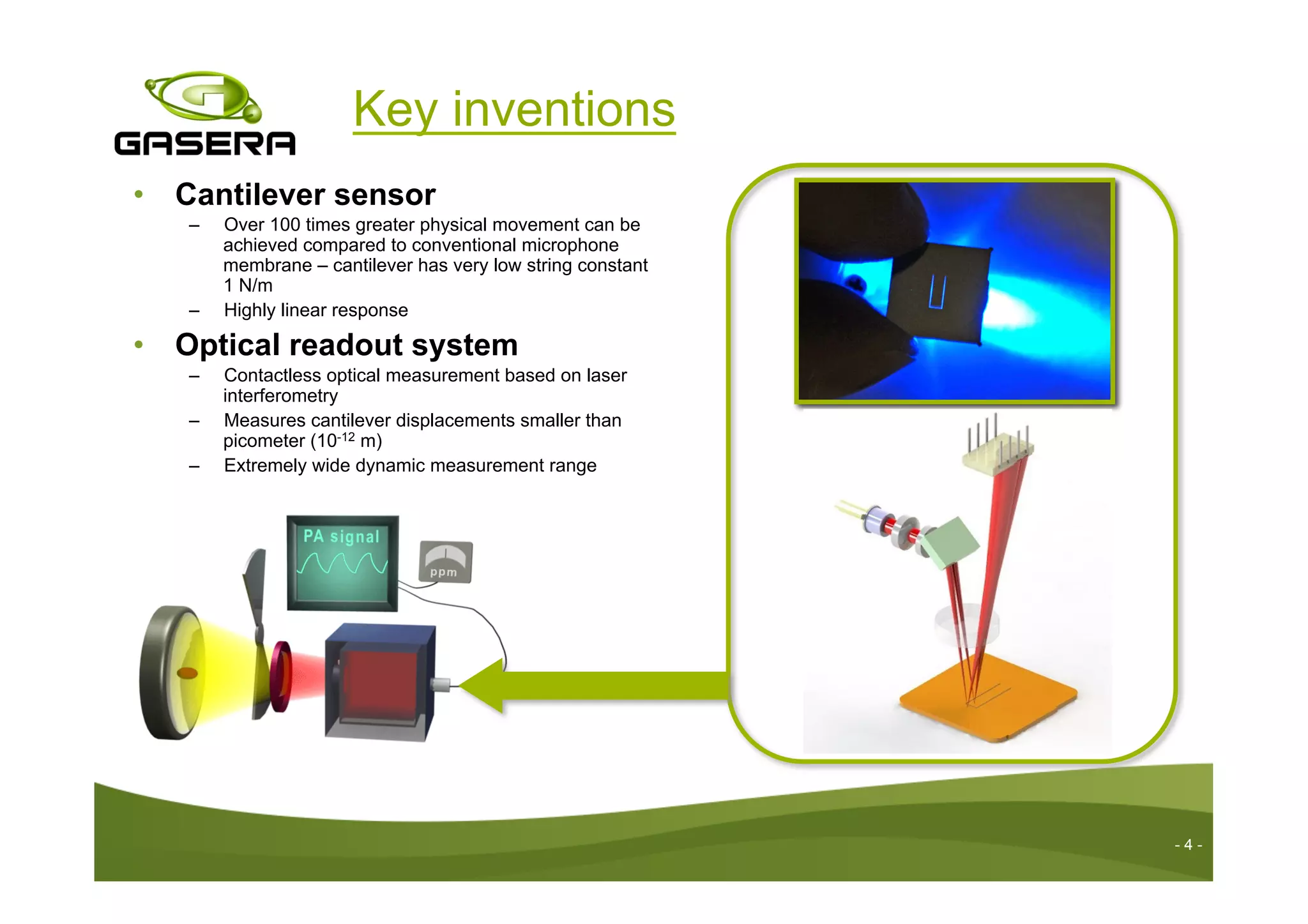
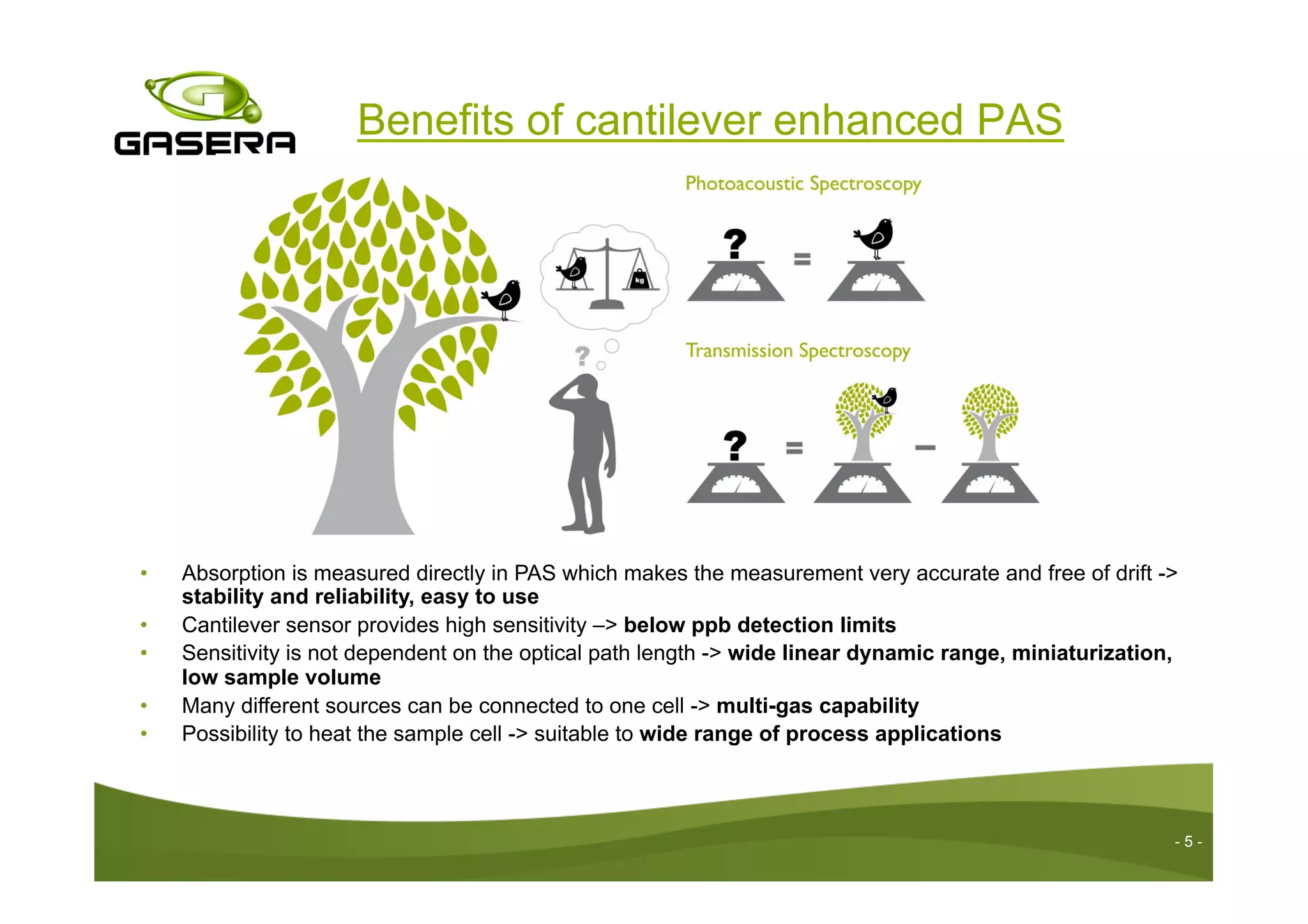
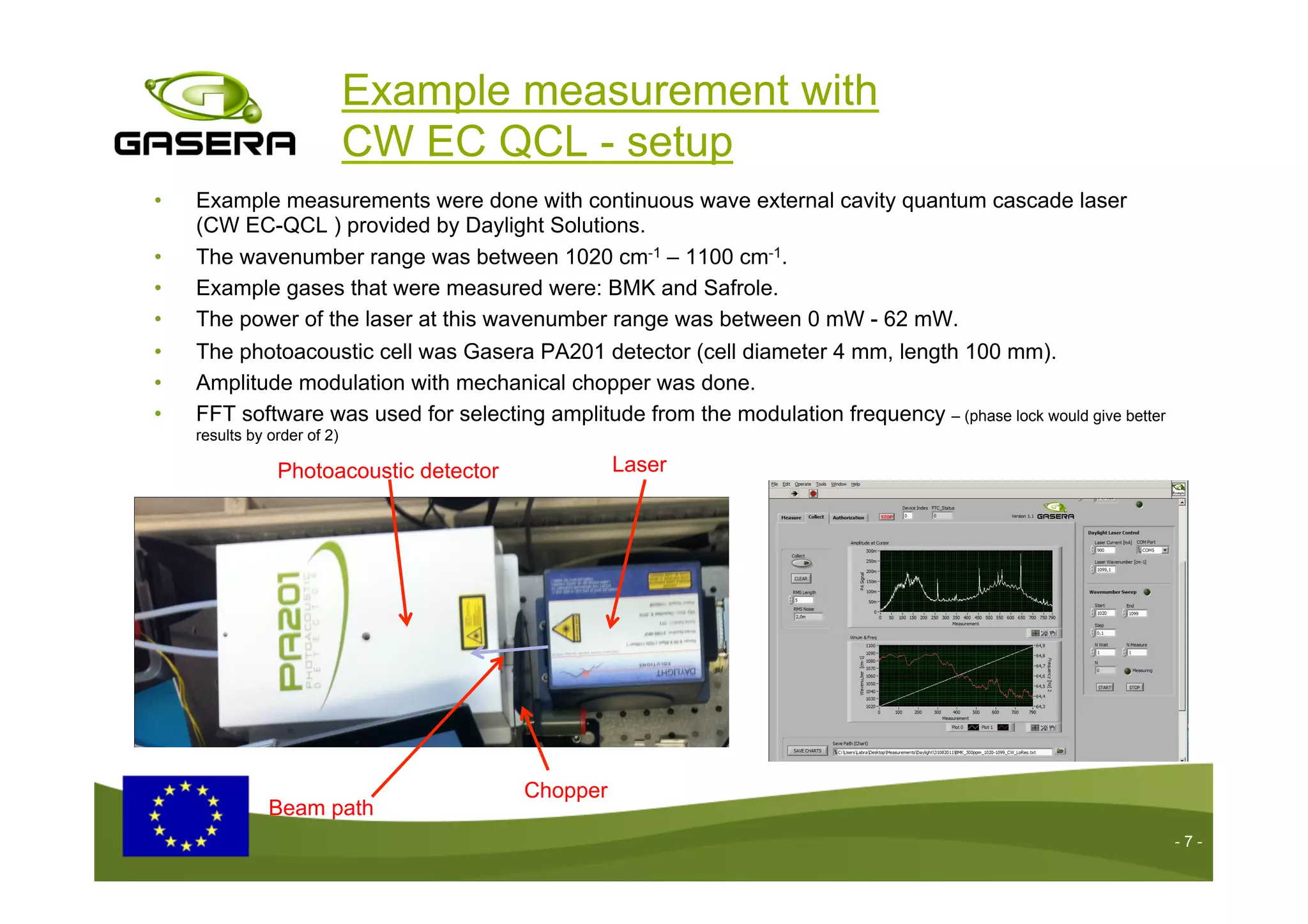
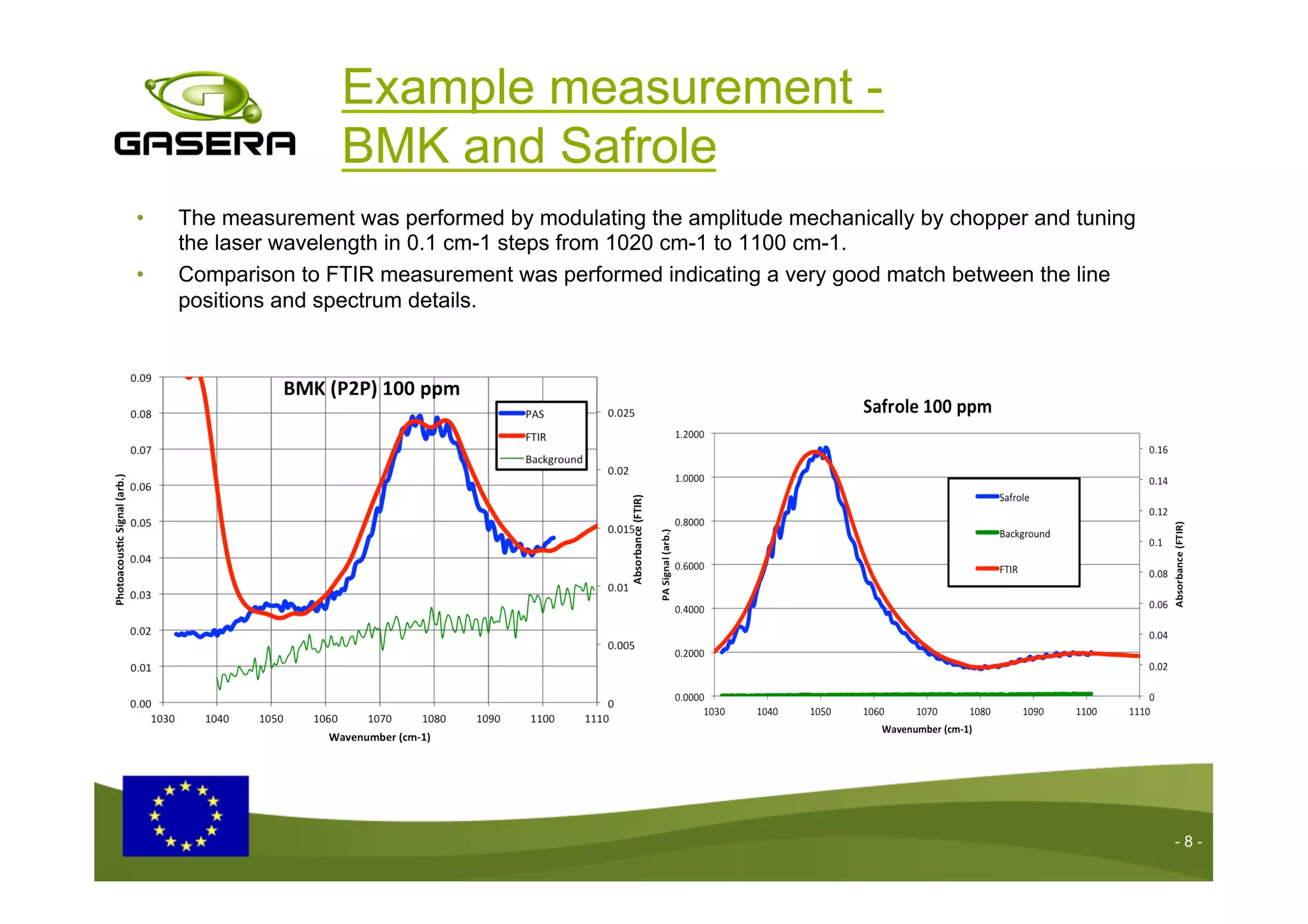
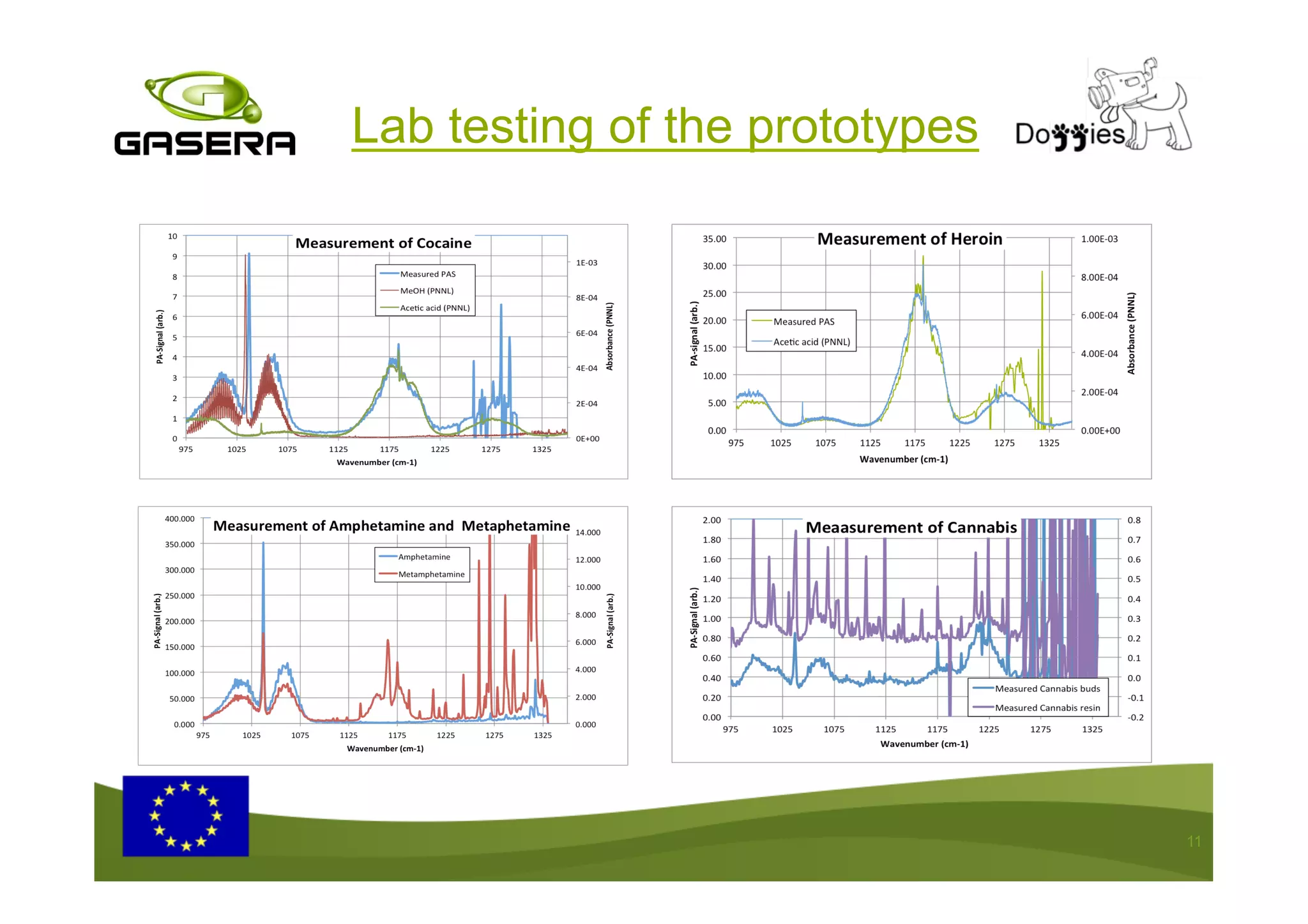
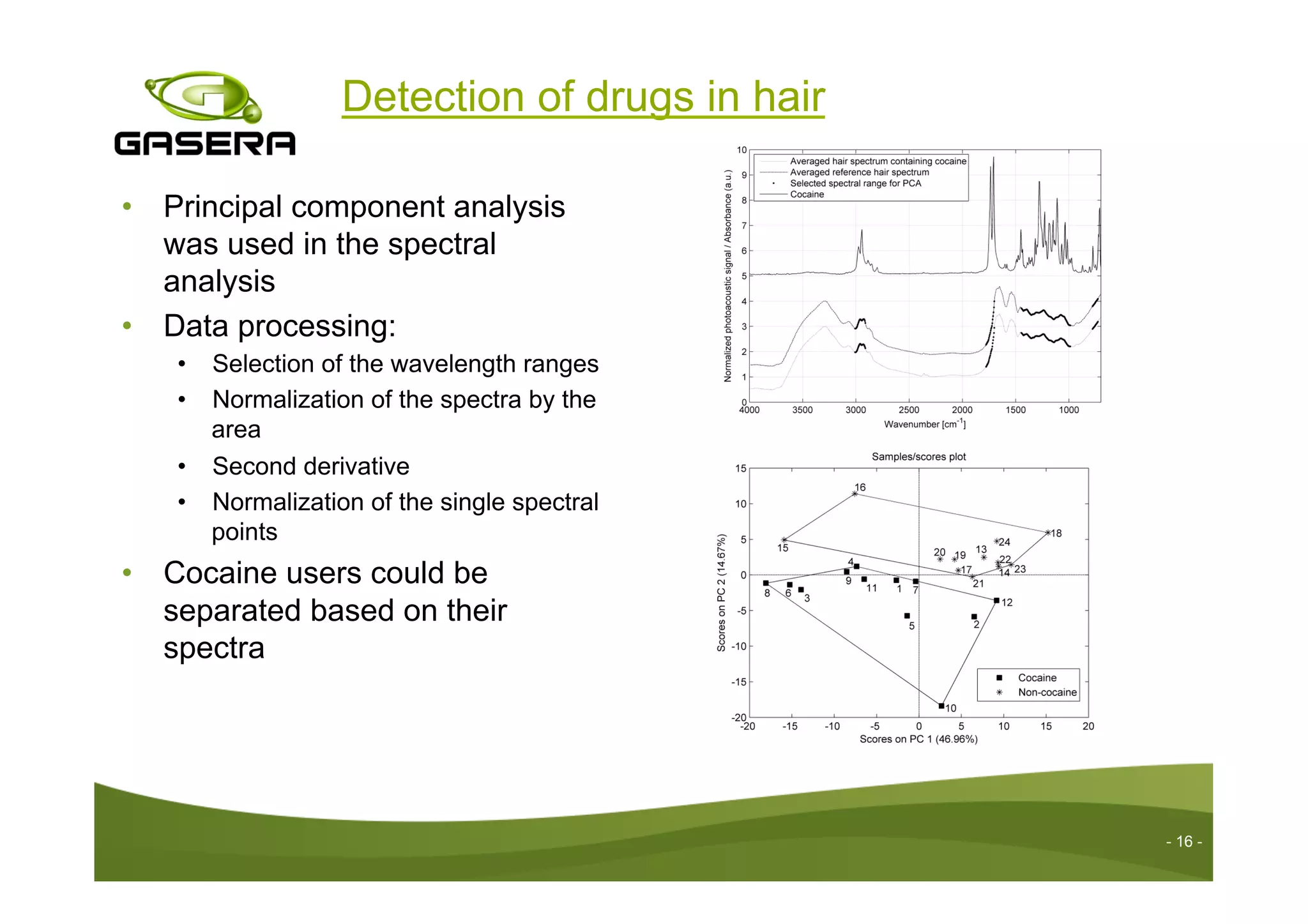
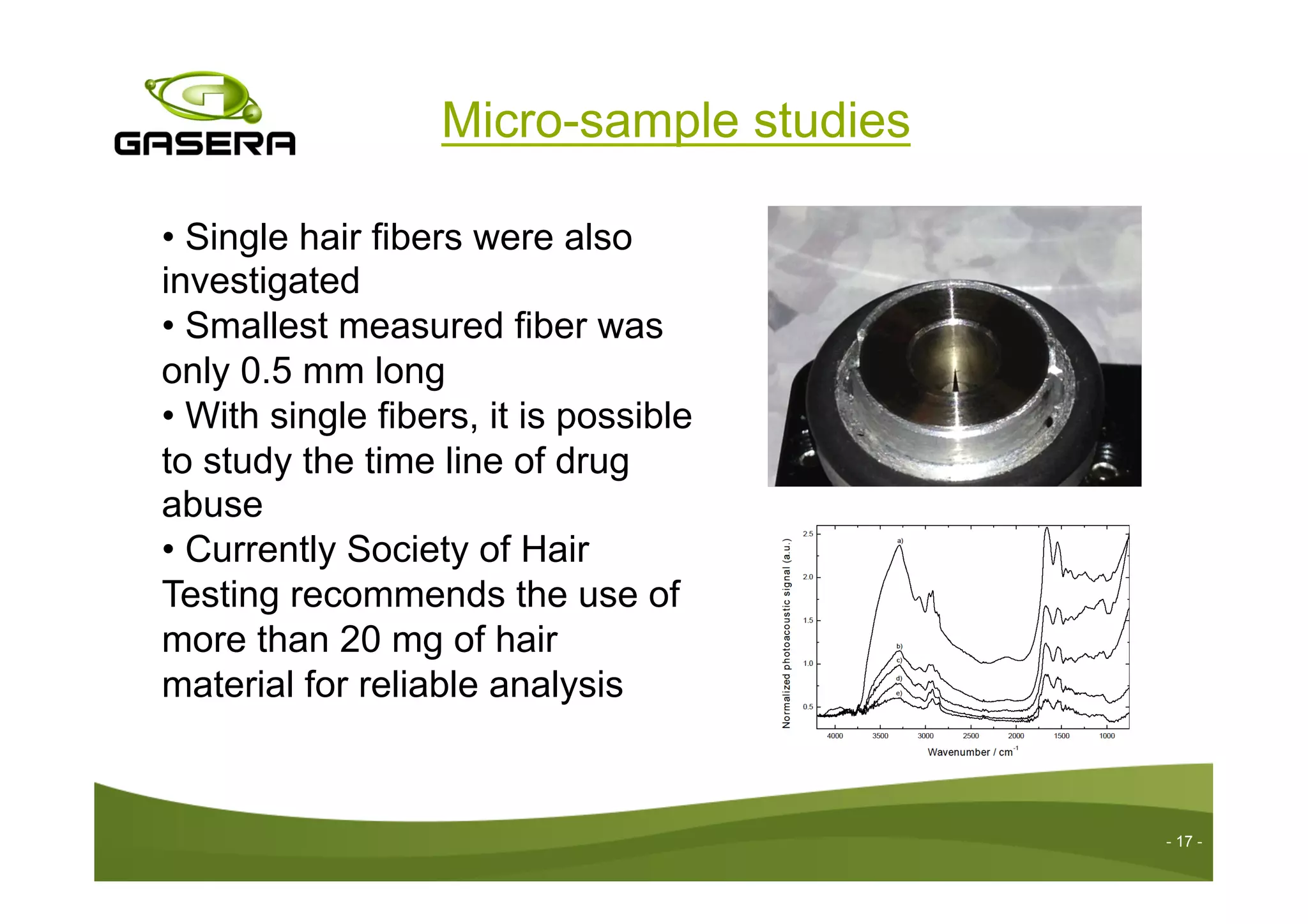
The document discusses the advancements in drug detection using cantilever-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy, highlighting projects funded by the EU that focus on sensing drug precursors and hidden substances. Key technologies include a highly sensitive cantilever sensor and the use of laser photoacoustic detection systems, which have demonstrated low detection limits for various drugs in both vapor and solid forms. Additionally, applications for detecting drugs in hair samples and multi-gas detection capabilities are explored, emphasizing the benefits of miniaturization and non-invasive measurements.