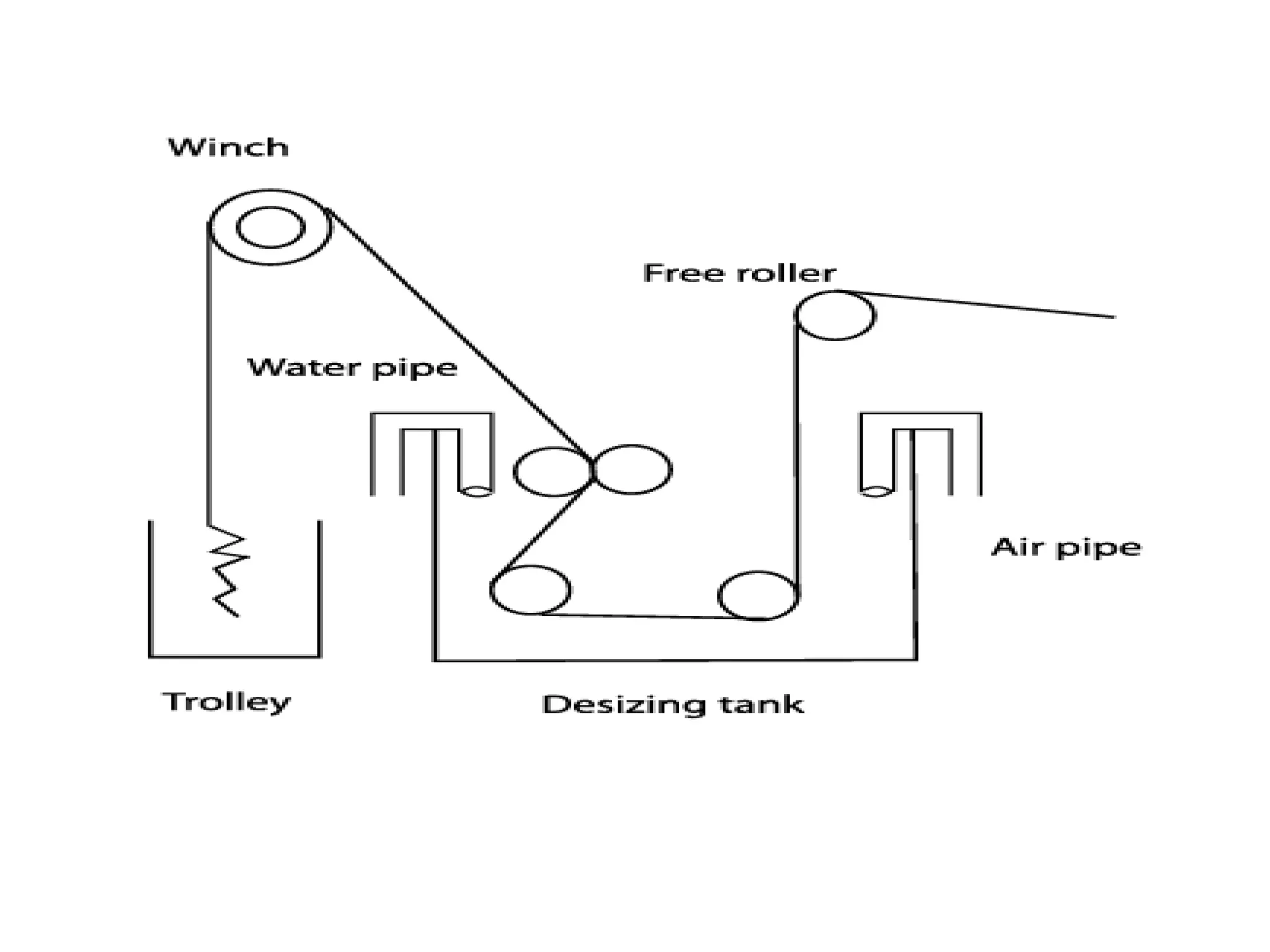
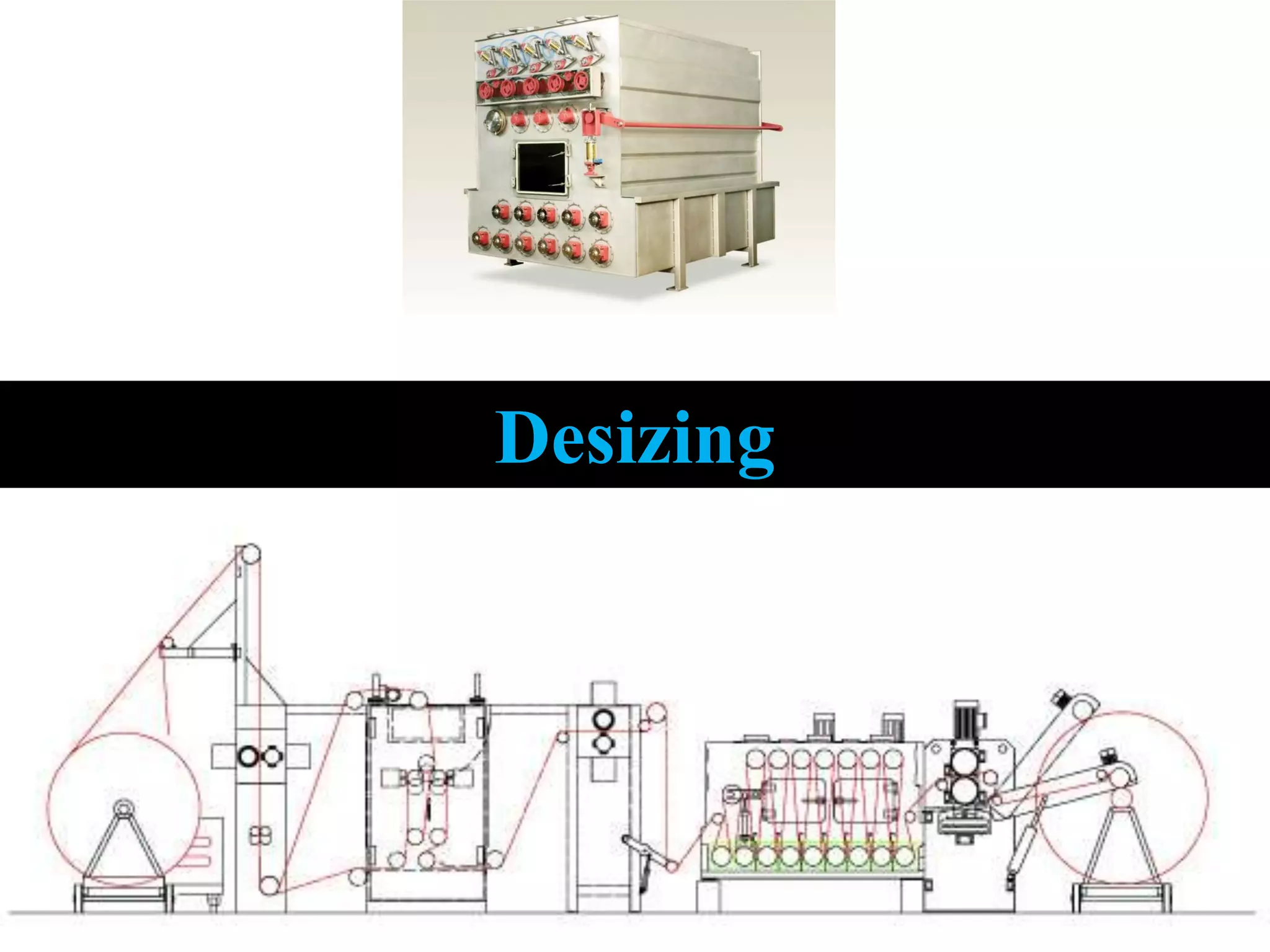
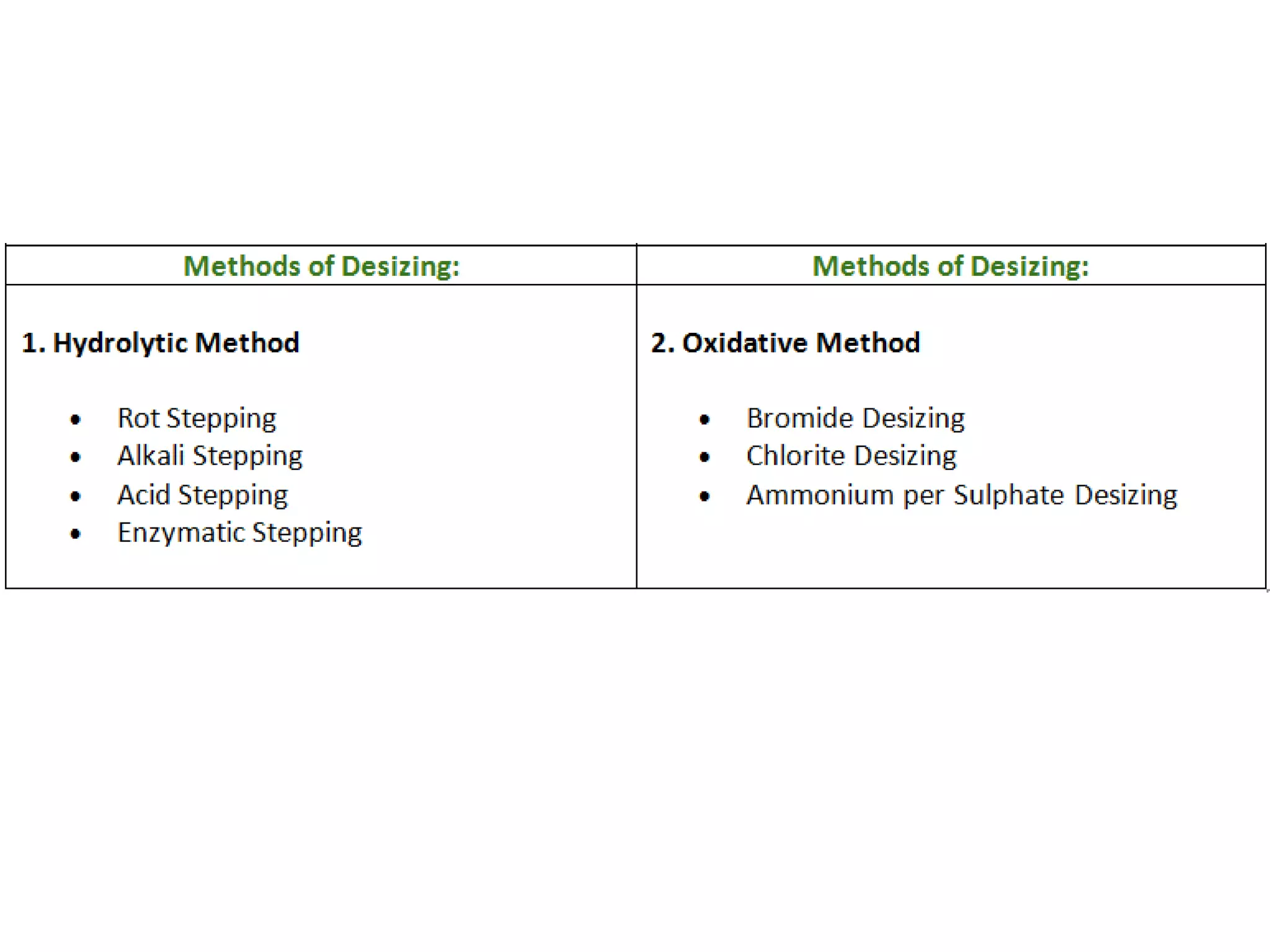
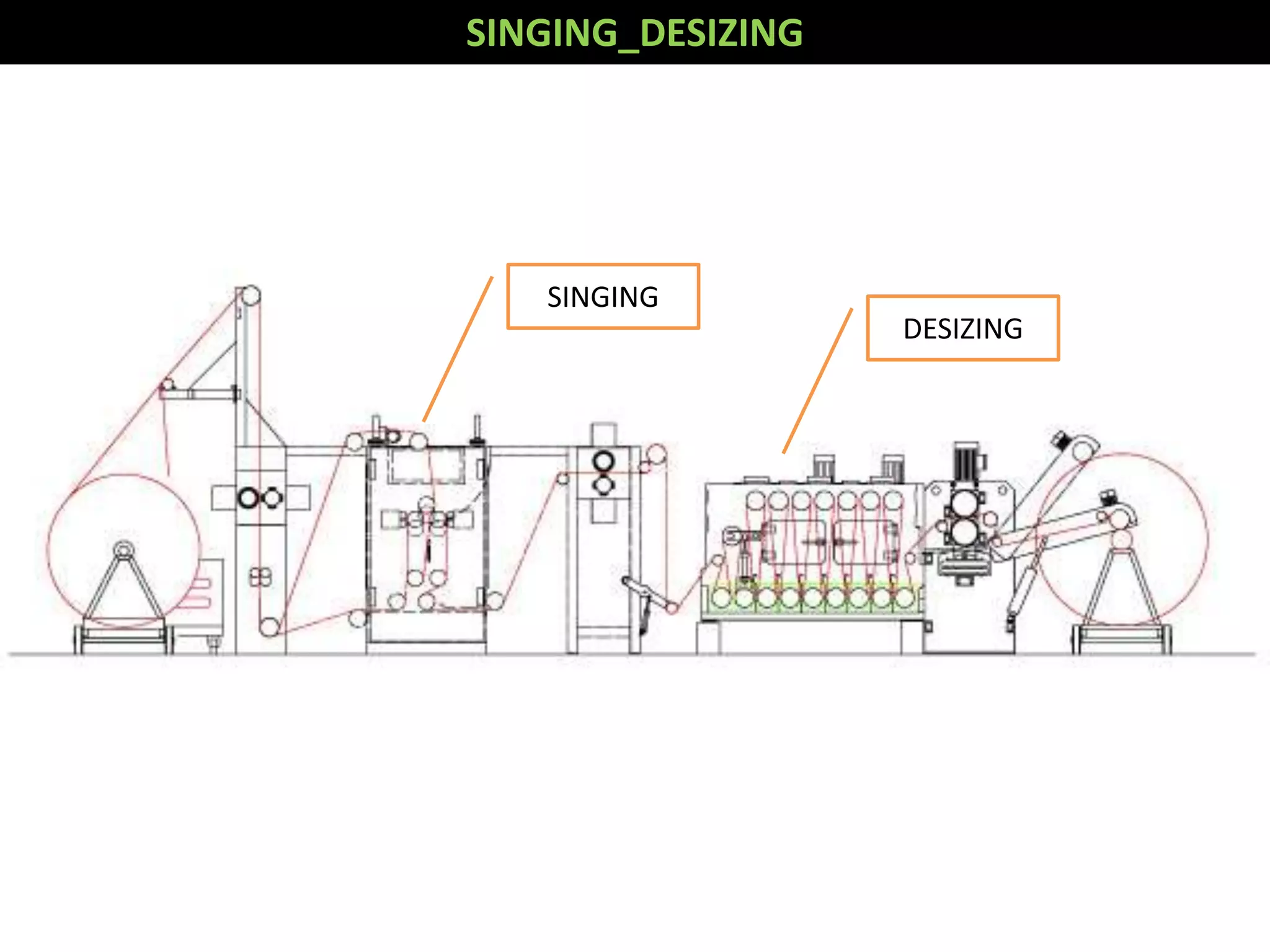
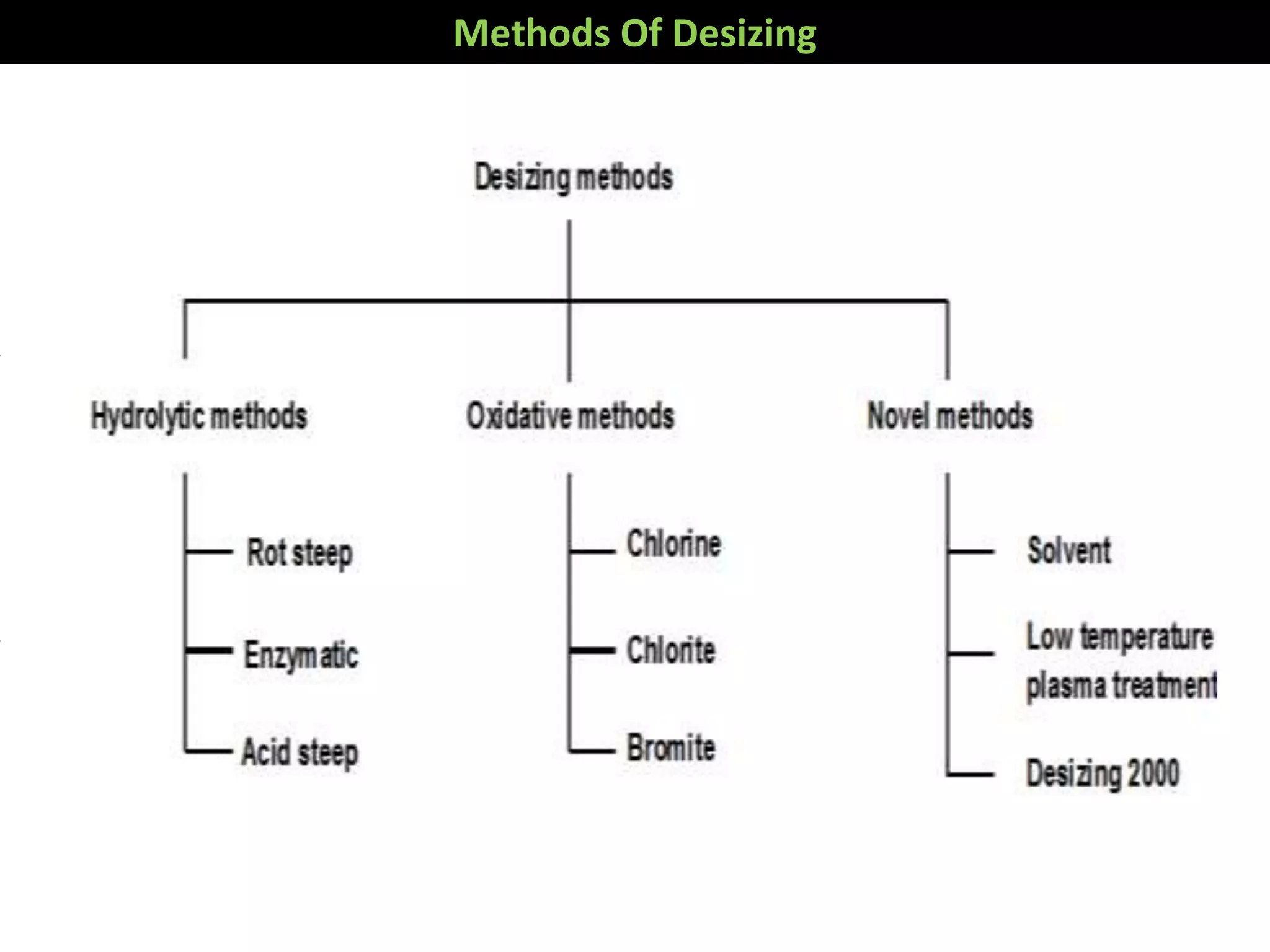
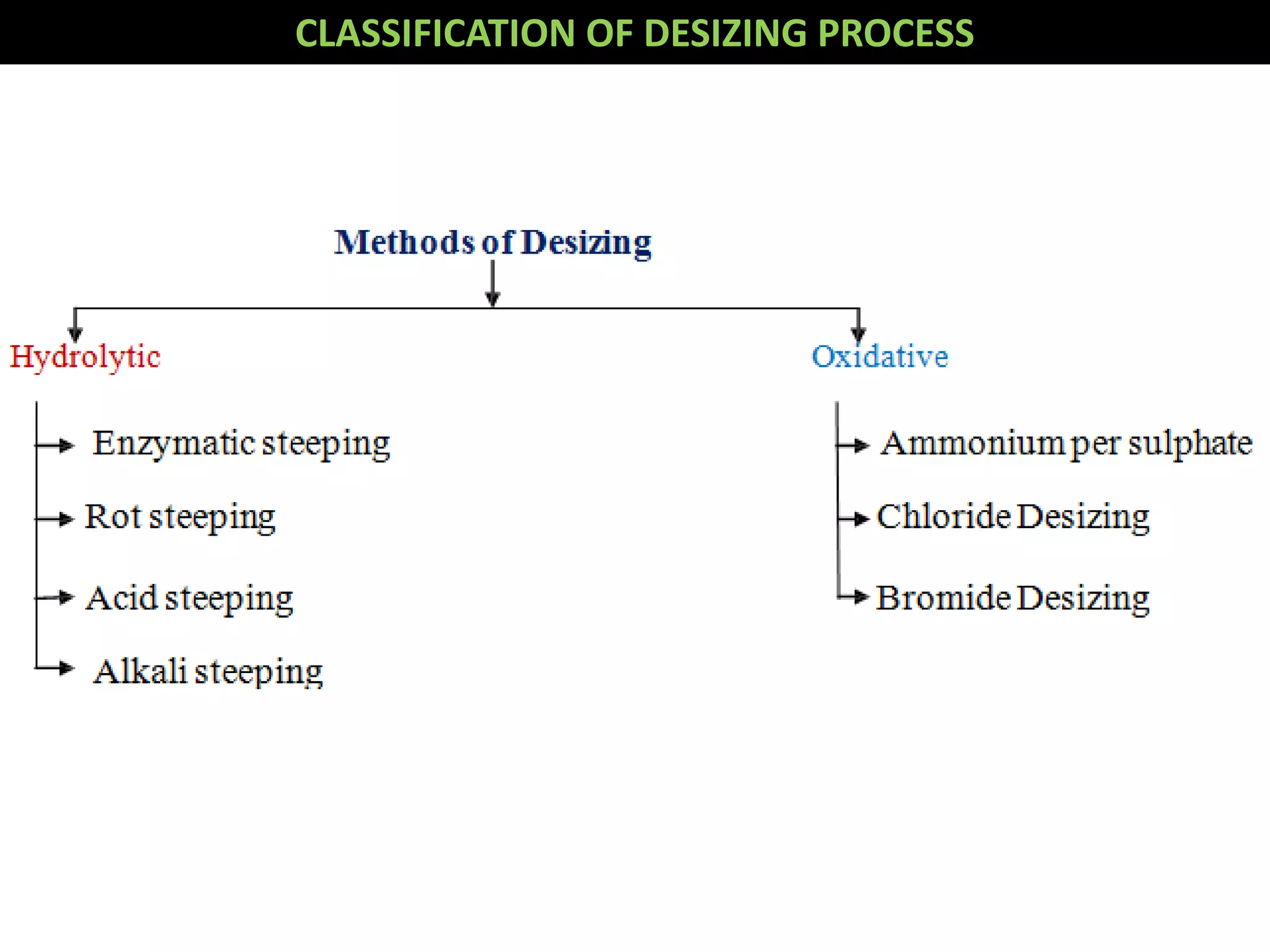
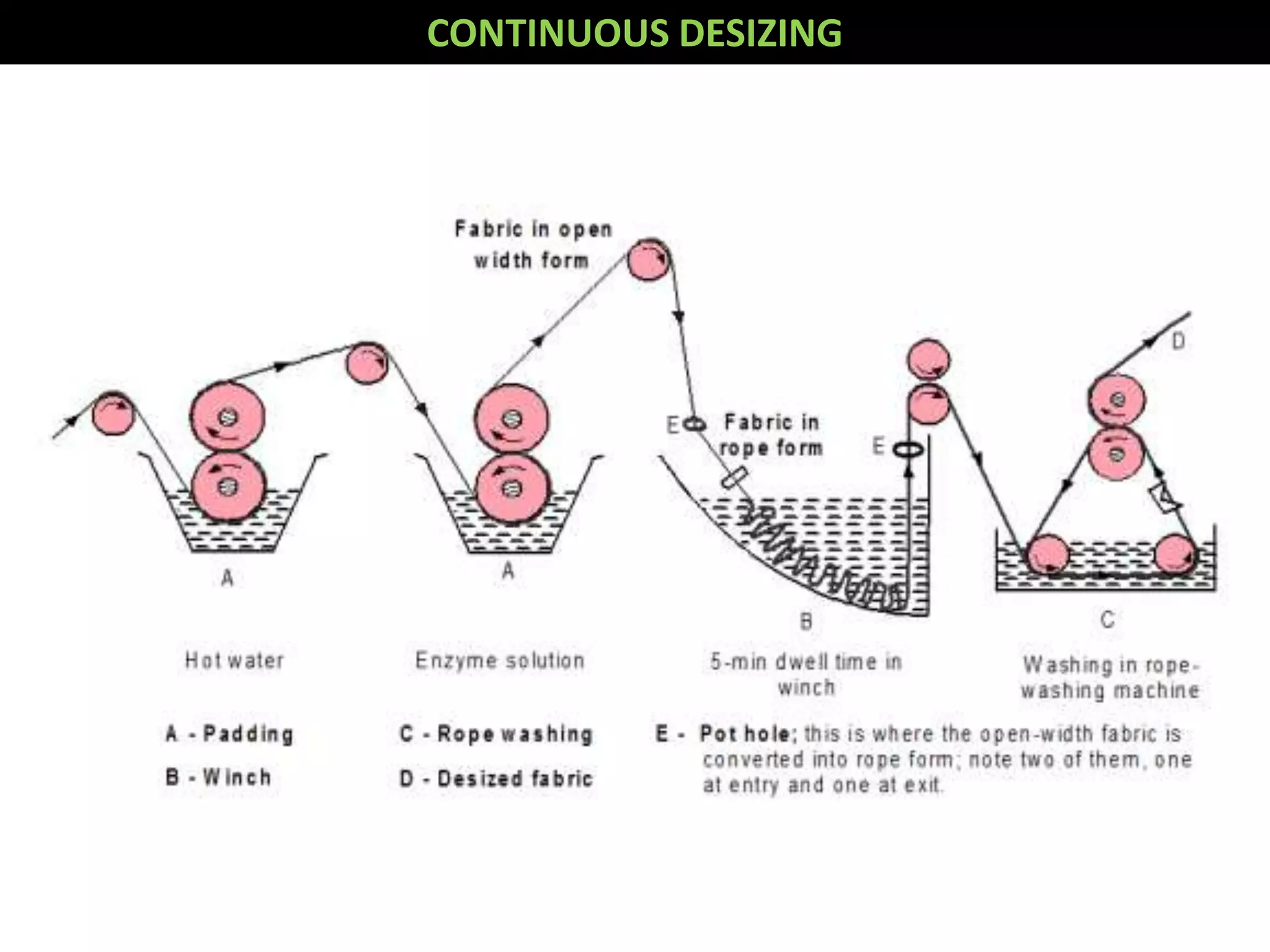
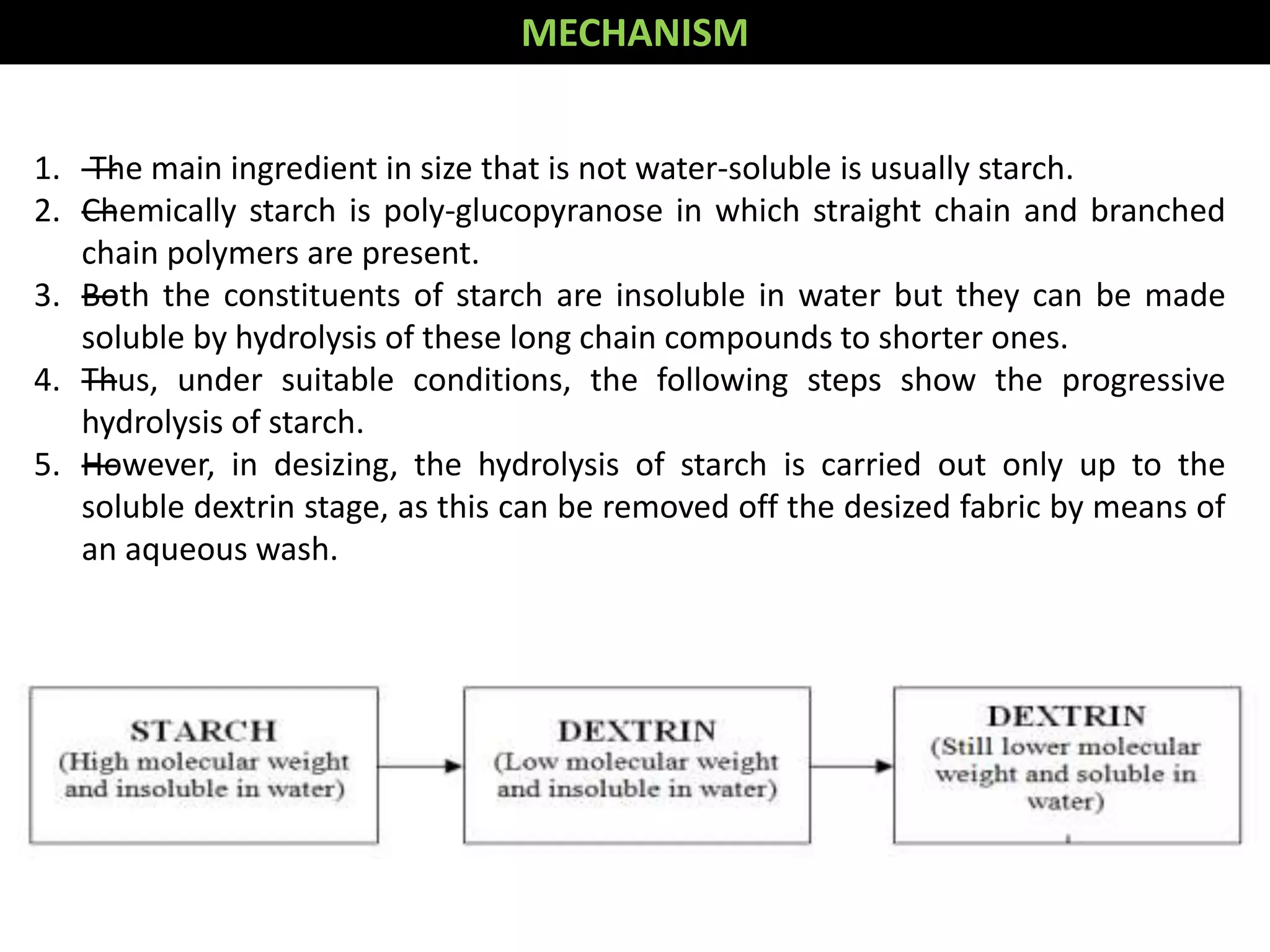
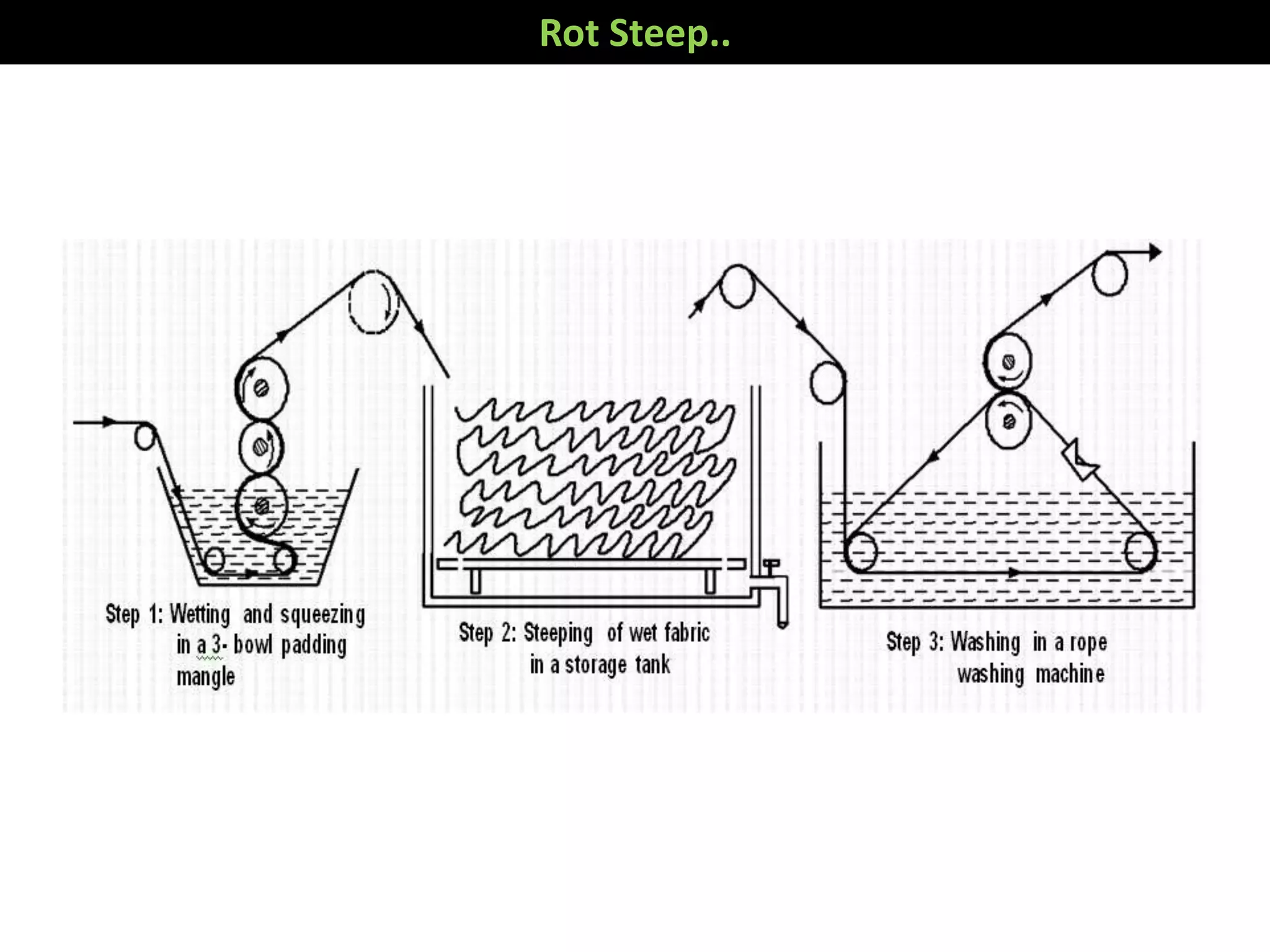
1. The document discusses different methods of desizing fabrics, which is the process of removing starch coatings called "size" that are applied during weaving.
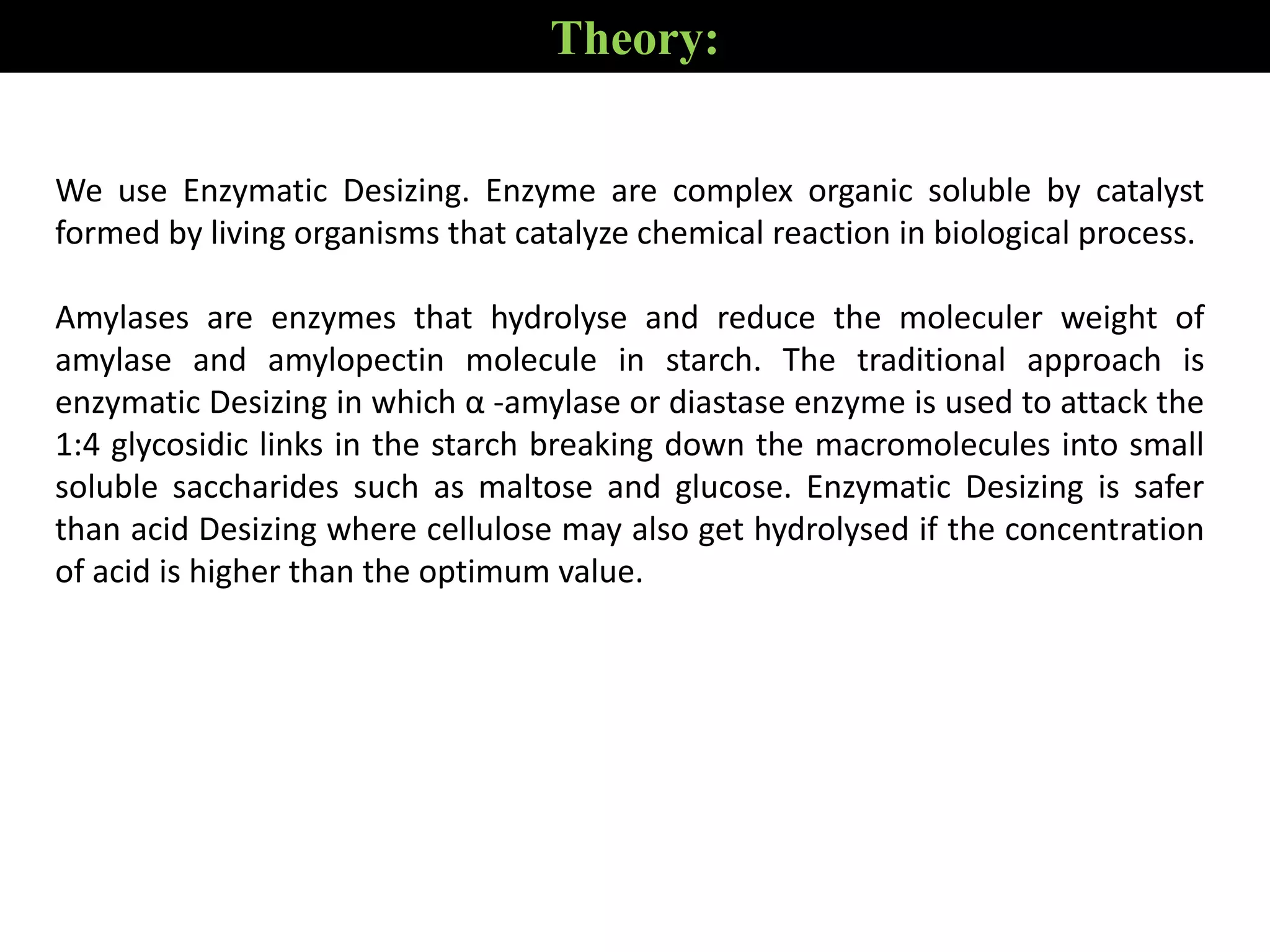
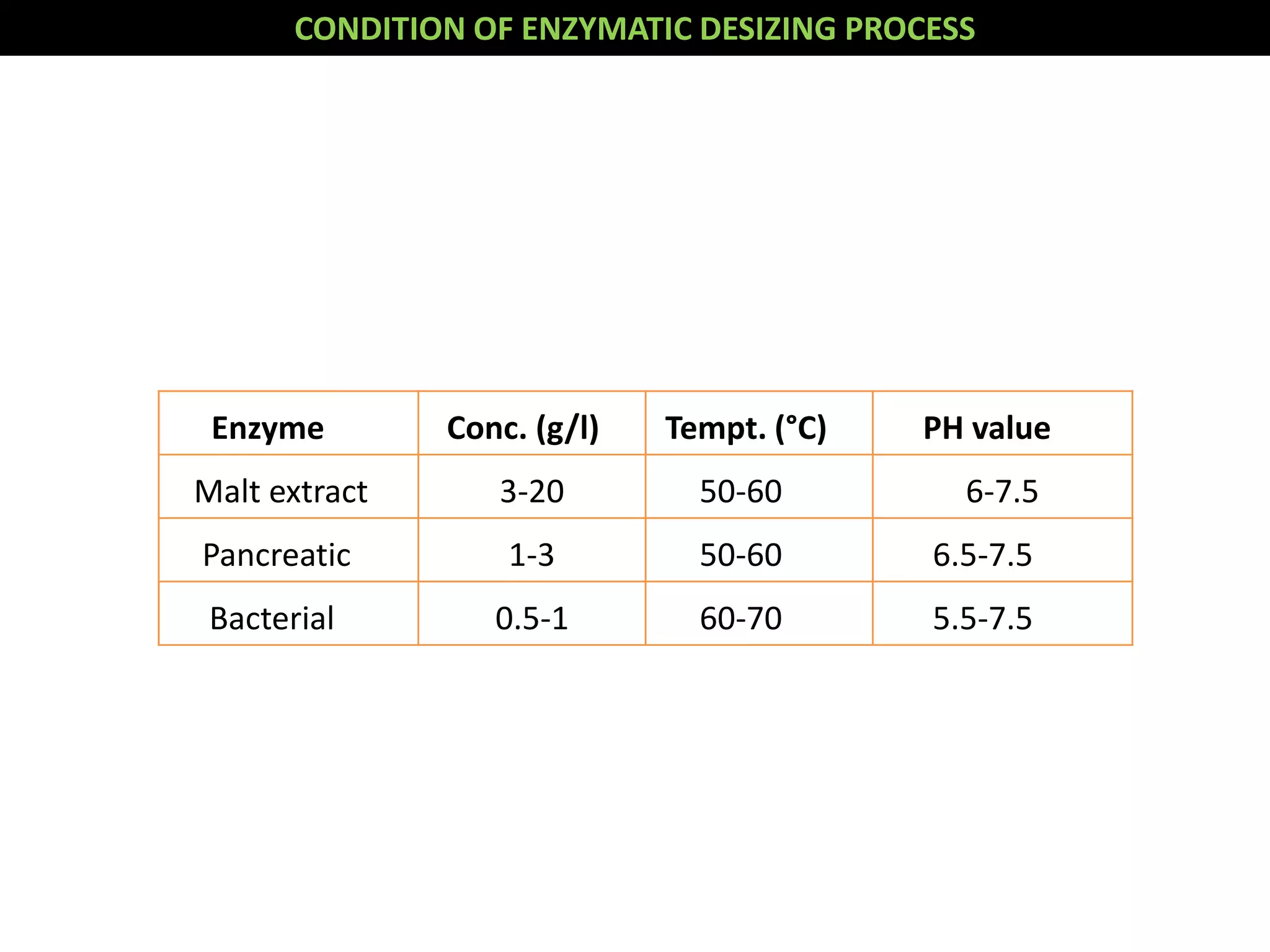
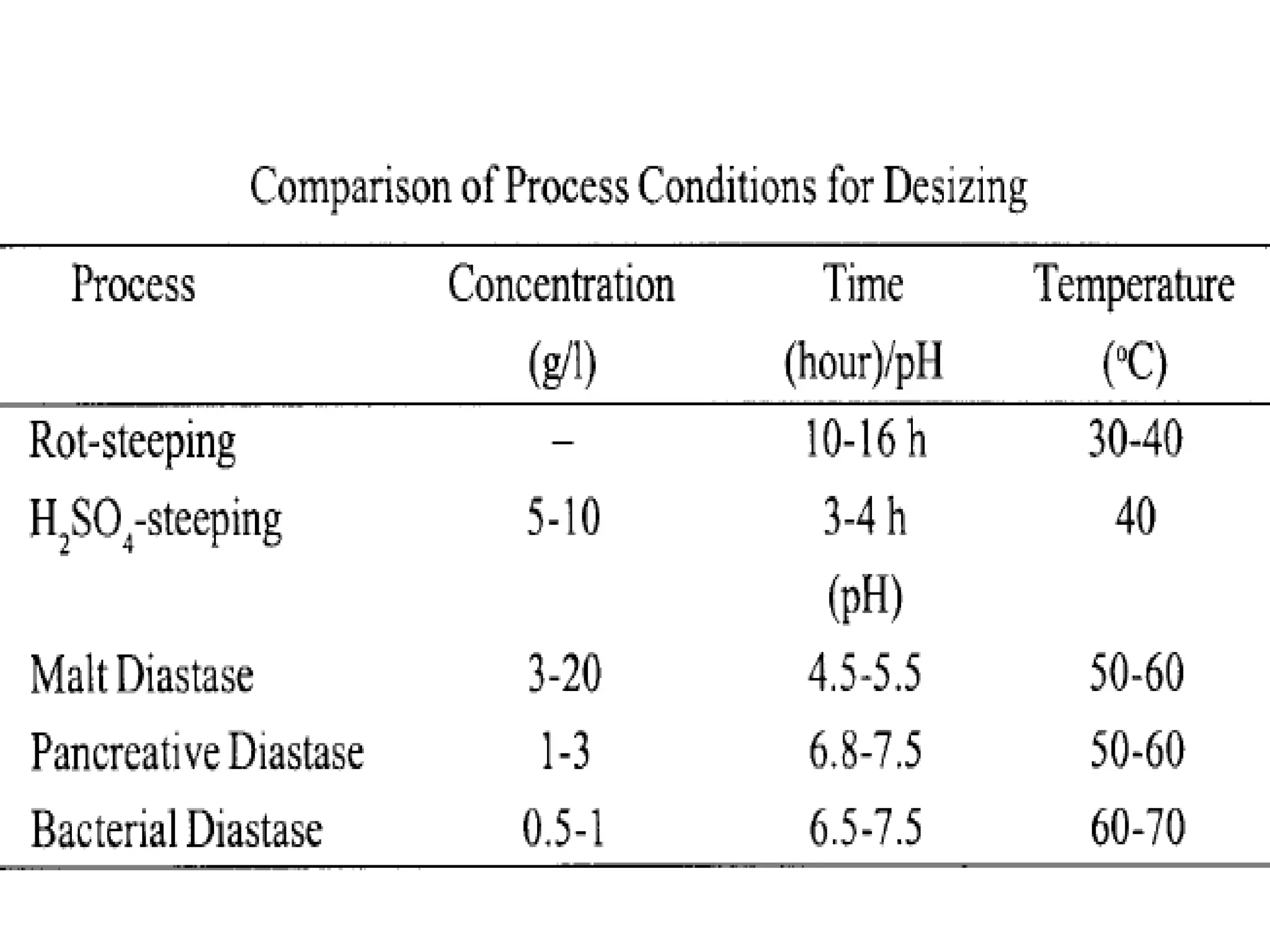
2. Enzymatic desizing using amylase enzymes is the most common method as it can break down starch without damaging cellulose fibers.
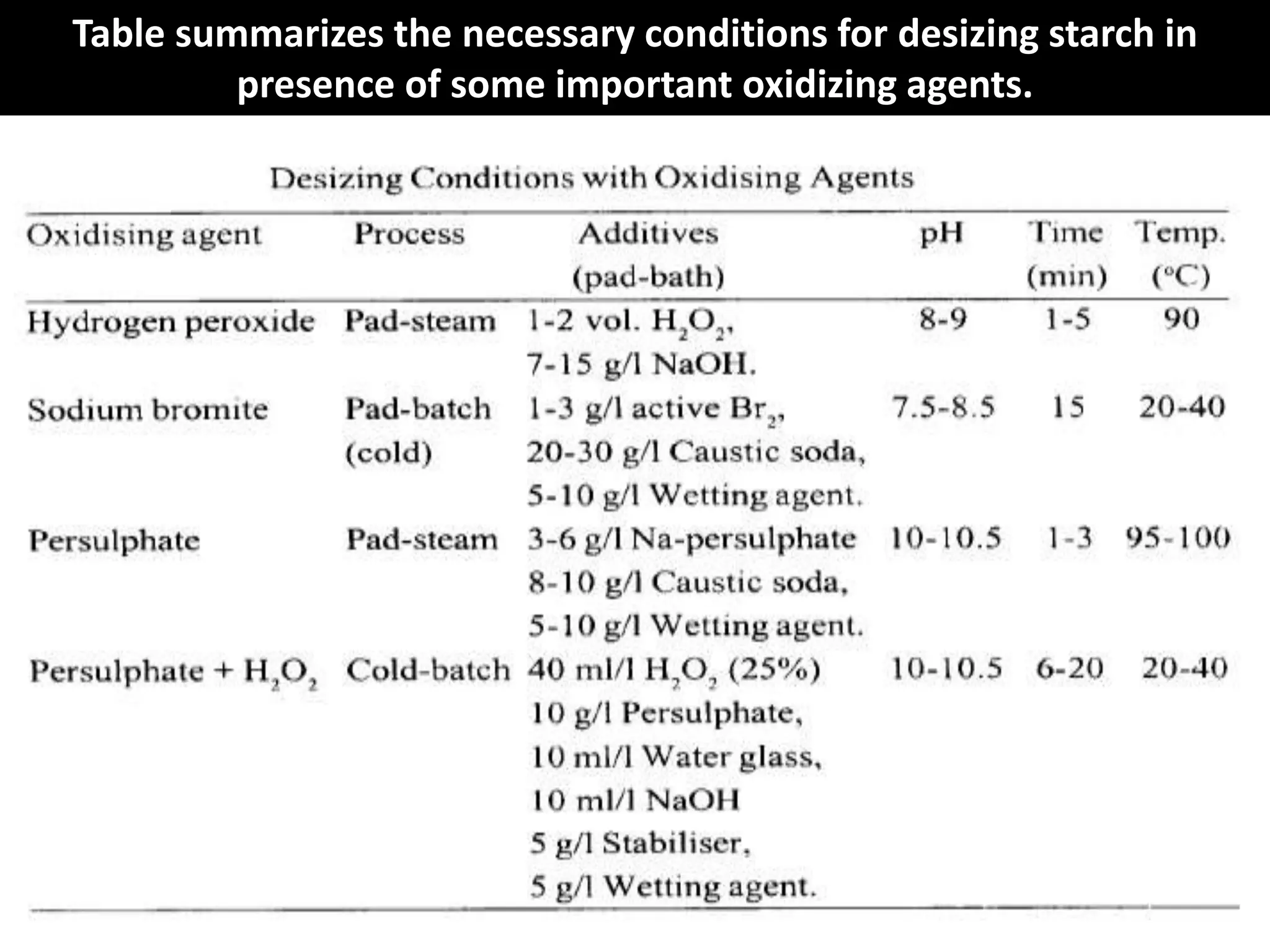
3. Other oxidative methods can also be used to desize fabrics by oxidizing and breaking down starch into soluble products using oxidizing agents like sodium bromite.





















![The performance ofa commercial enzyme wastested and process optimization
trials
were performed. Optimum circumstances obtained were:
0.75% (o.w.f.) enzyme, pH 4.1, 62 °C and a process time of 45 minutes.
Acid consumption of the raw cotton fabric played an important role in pH
adjustments. Similar results were reported using pure amyloglucosidase enzymes
[10]; however, storage and usage properties as well as the availability of pure
enzymes may cause problems when compared to commercial ones. A commercial
enzyme readily used in the food industry was utilized in this study. The sufficiency of
the generated glucose to utilize the desizing liquor for bleaching was tested by
using glucose oxidize enzyme to produce hydrogen peroxide from this glucose.
Bleaching trials were performed with the glucose generated. Compatible whiteness
degrees were attained. Results are reported in the second part of the study.
CONCLUTION](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/desizing-140503101043-phpapp01-140701072516-phpapp02/75/Desizing-140503101043-phpapp01-35-2048.jpg)