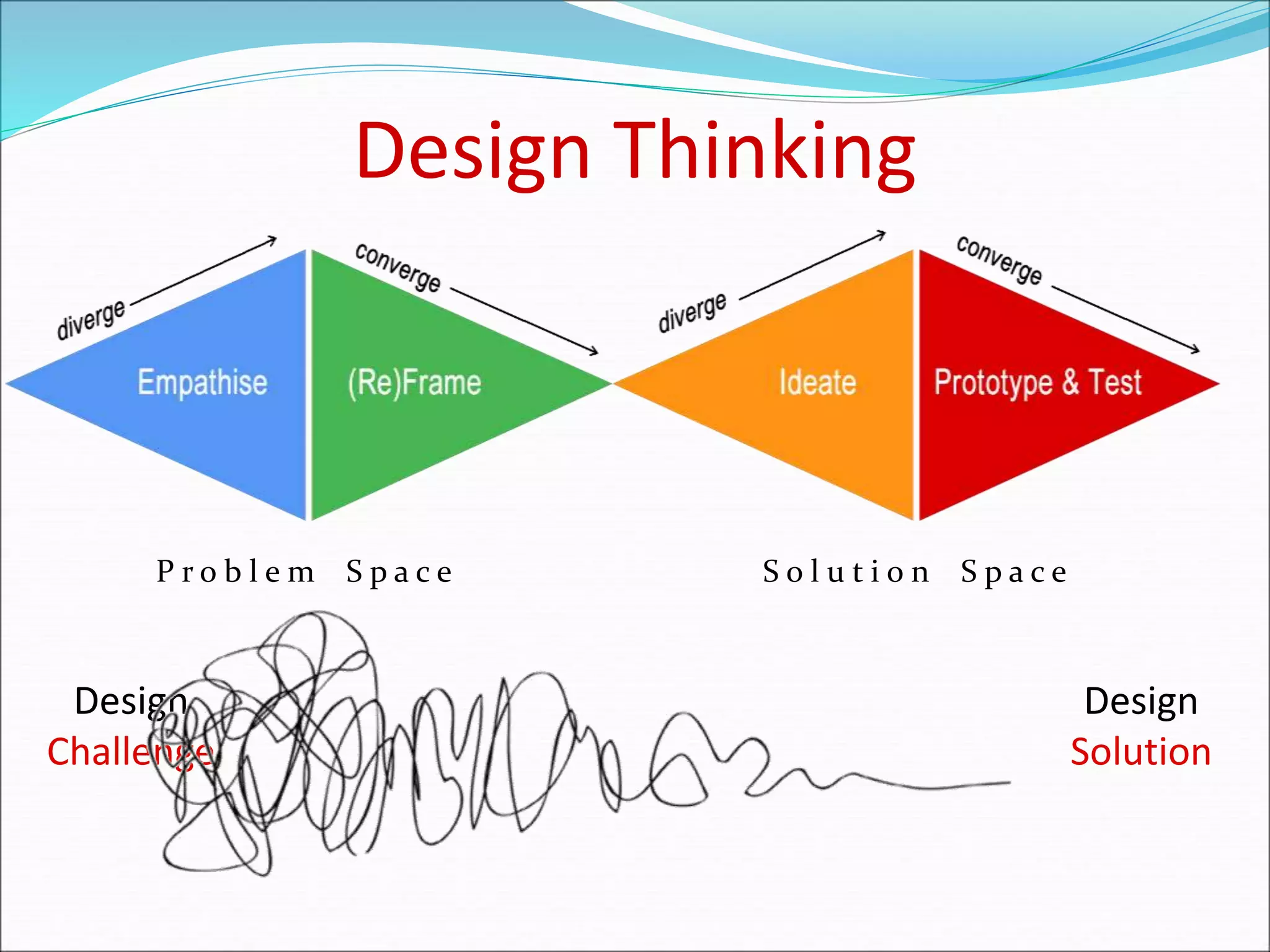
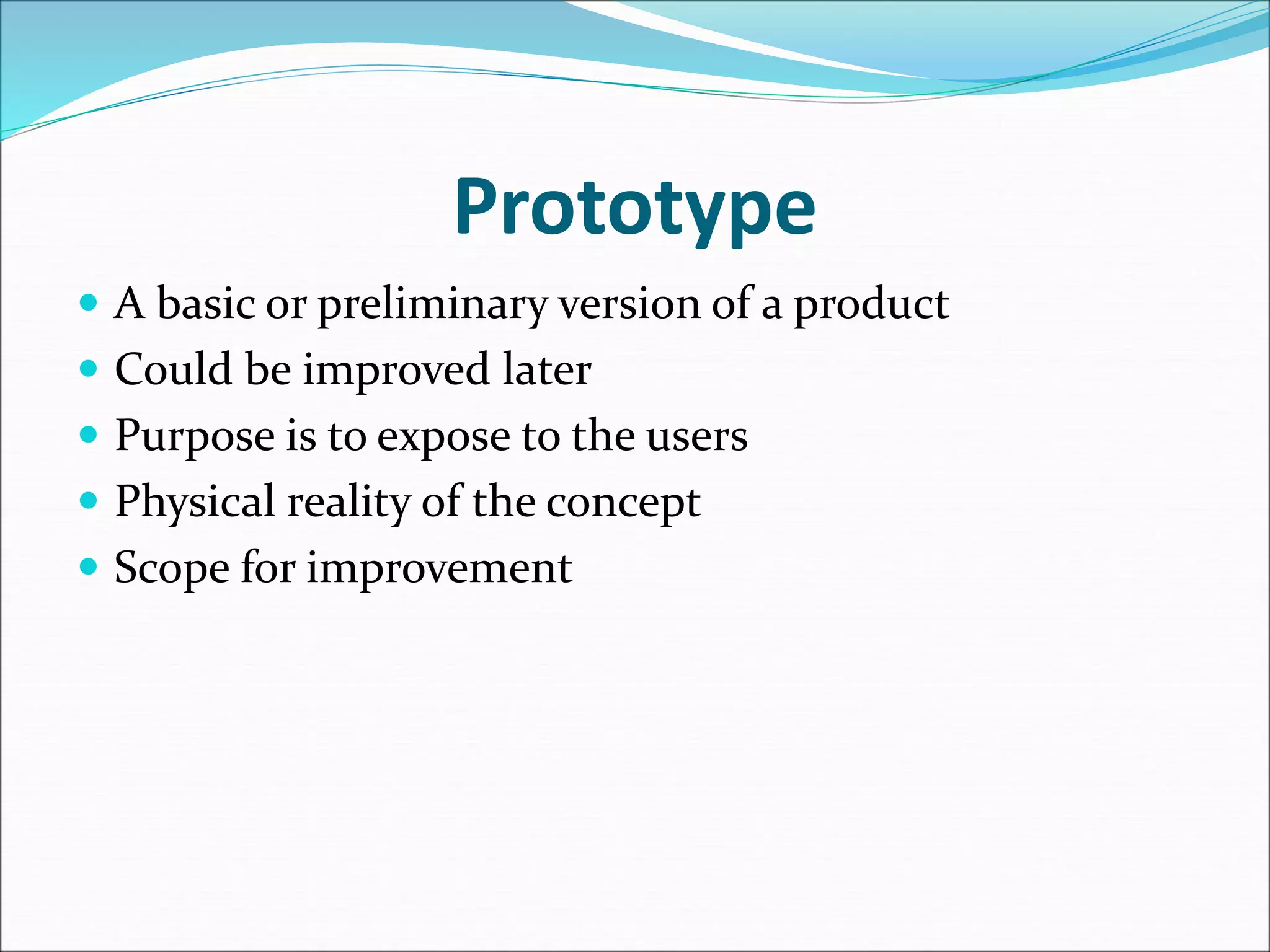
This document introduces design thinking as a philosophy and set of tools to help solve problems creatively from a human-centered perspective. It explains the design thinking process as having 5 steps: empathize, define, ideate, prototype, and test. Empathizing involves understanding problems from the user's perspective without judgment through observation and interaction. Defining involves analyzing insights to develop a precise problem statement focused on user needs. Ideating is about generating many ideas through brainstorming and mind mapping. Prototyping creates a preliminary version of an idea for user testing. The process iterates by taking feedback to improve and retest solutions. An example of redesigning a sleep bag for preterm babies is provided.