Embed presentation
Download to read offline
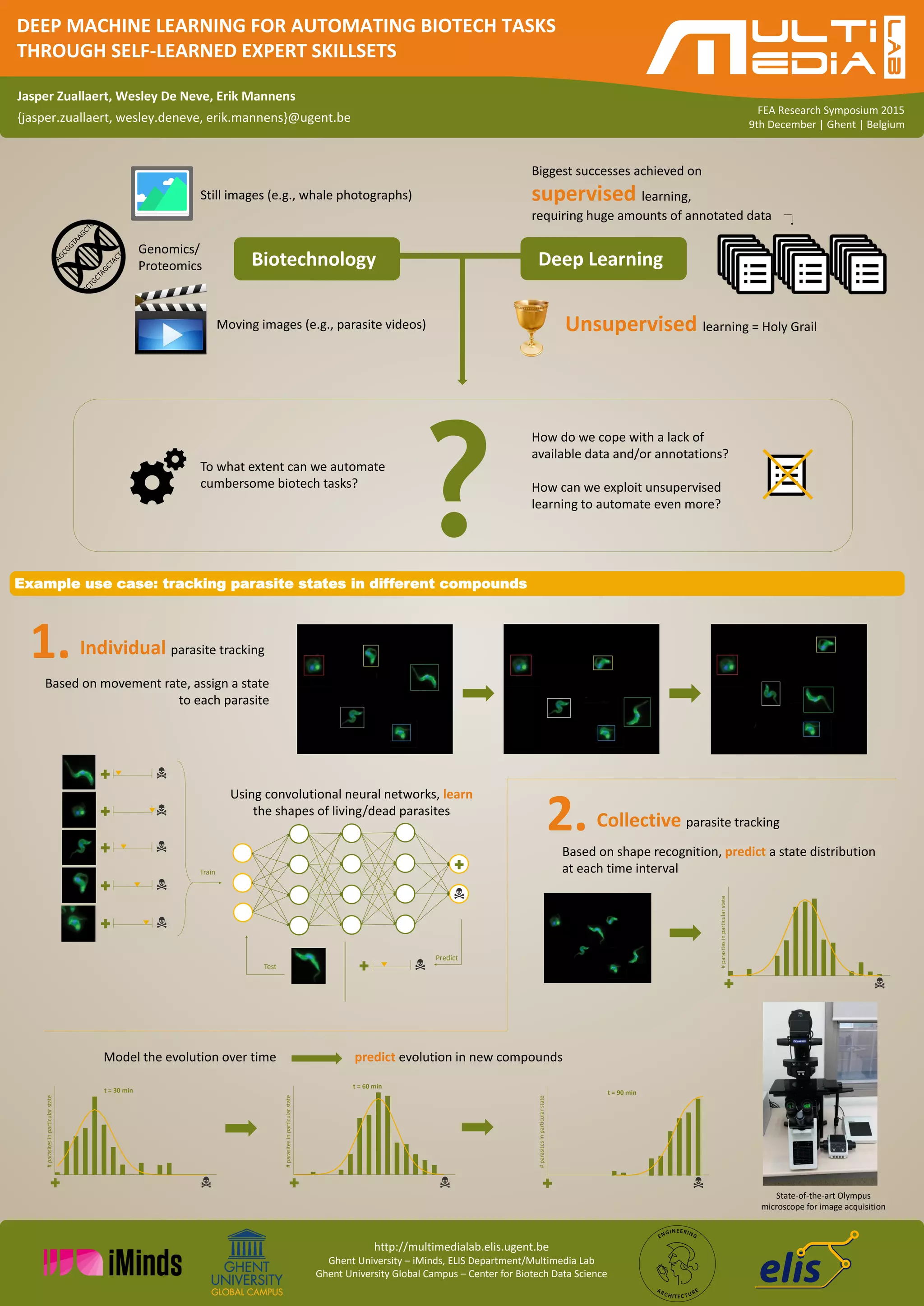

The document discusses the application of deep machine learning in automating biotech tasks, specifically focusing on unsupervised learning methods to compensate for the lack of annotated data. It highlights an example use case involving the tracking of parasite states using convolutional neural networks for individual and collective tracking. The research is presented at the FEA Research Symposium 2015 in Ghent, Belgium.
