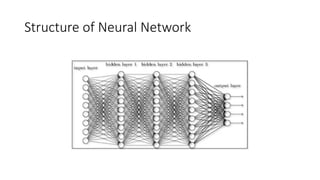
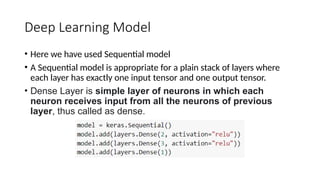
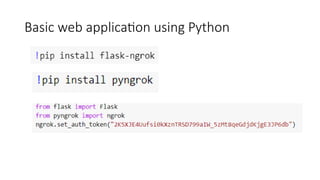
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning utilizing artificial neural networks with multiple layers to extract features from data and requires vast volumes of data for training. It encompasses supervised, semi-supervised, and unsupervised learning methods and is applicable across various industries, including automotive and healthcare. Key tools in deep learning include TensorFlow, for implementing best practices, and Keras, a high-level API that simplifies neural network implementation.