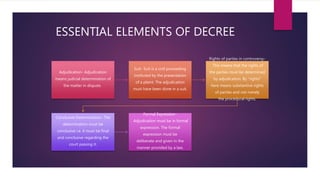
This document defines key terms from the Civil Procedure Code related to decrees. It explains that a decree is the formal expression of an adjudication that conclusively determines the rights of parties in a suit. A decree must be the result of a judicial determination in a suit and formally express the outcome. It can be preliminary and determine further proceedings are needed, or final. Certain decisions like dismissing a case for default are considered orders, not decrees. Decrees are distinguished from judgments and orders. The document outlines the elements of and types of decrees according to Indian civil procedure law.