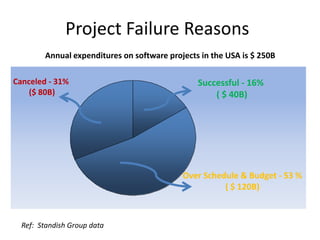
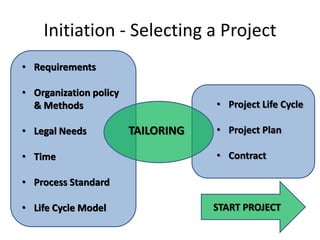
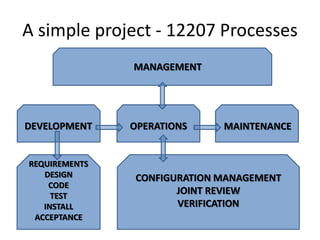
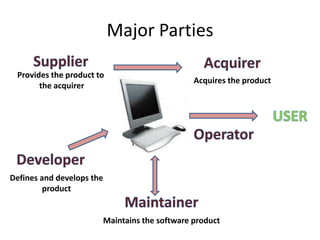
The document discusses the ISO 12207 standard for software development life cycles. It provides an overview of the standard including defining two types of software projects, describing key processes like management, quality assurance, and configuration management. It emphasizes that following the standard and implementing best practices like requirements documentation, risk management, and software metrics can help improve success rates for software projects.