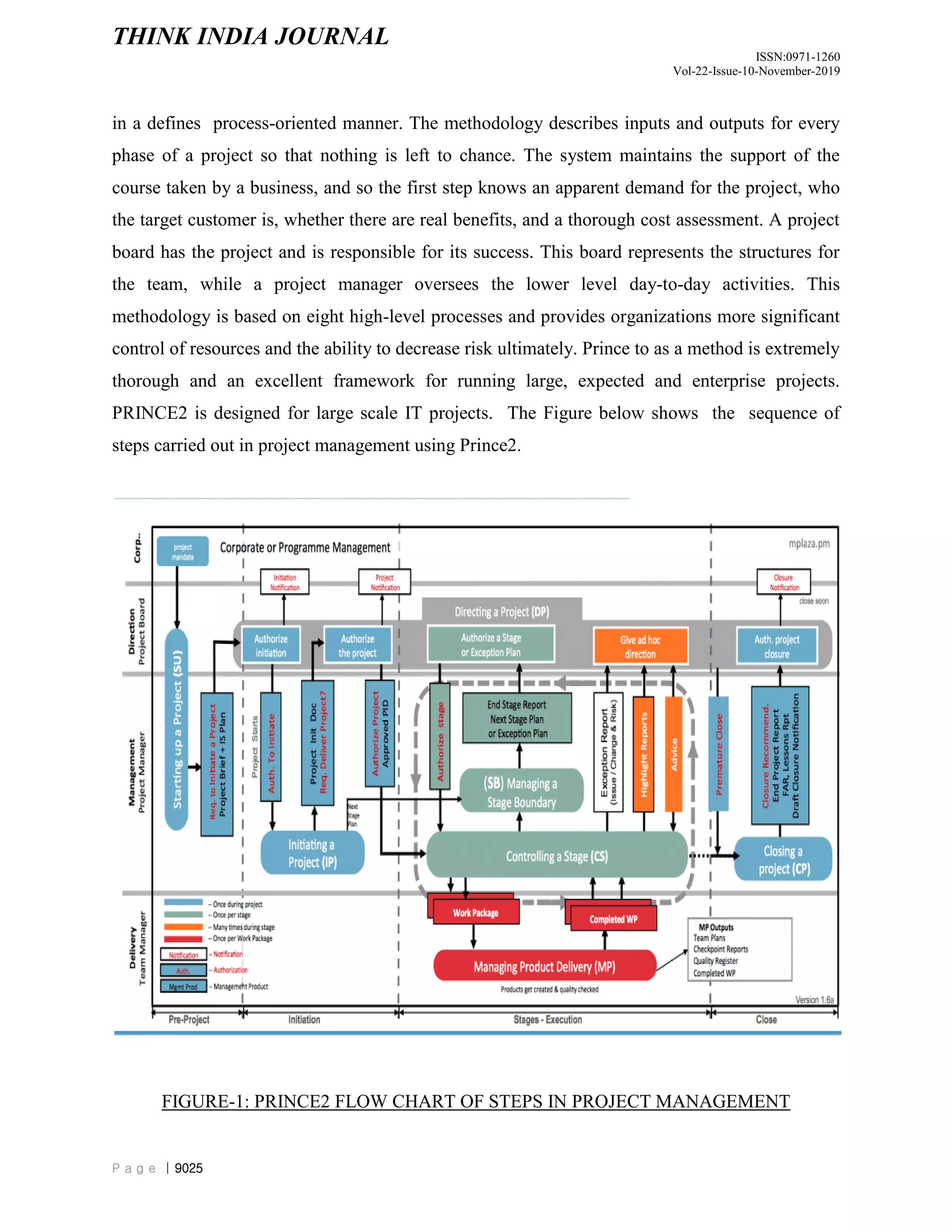
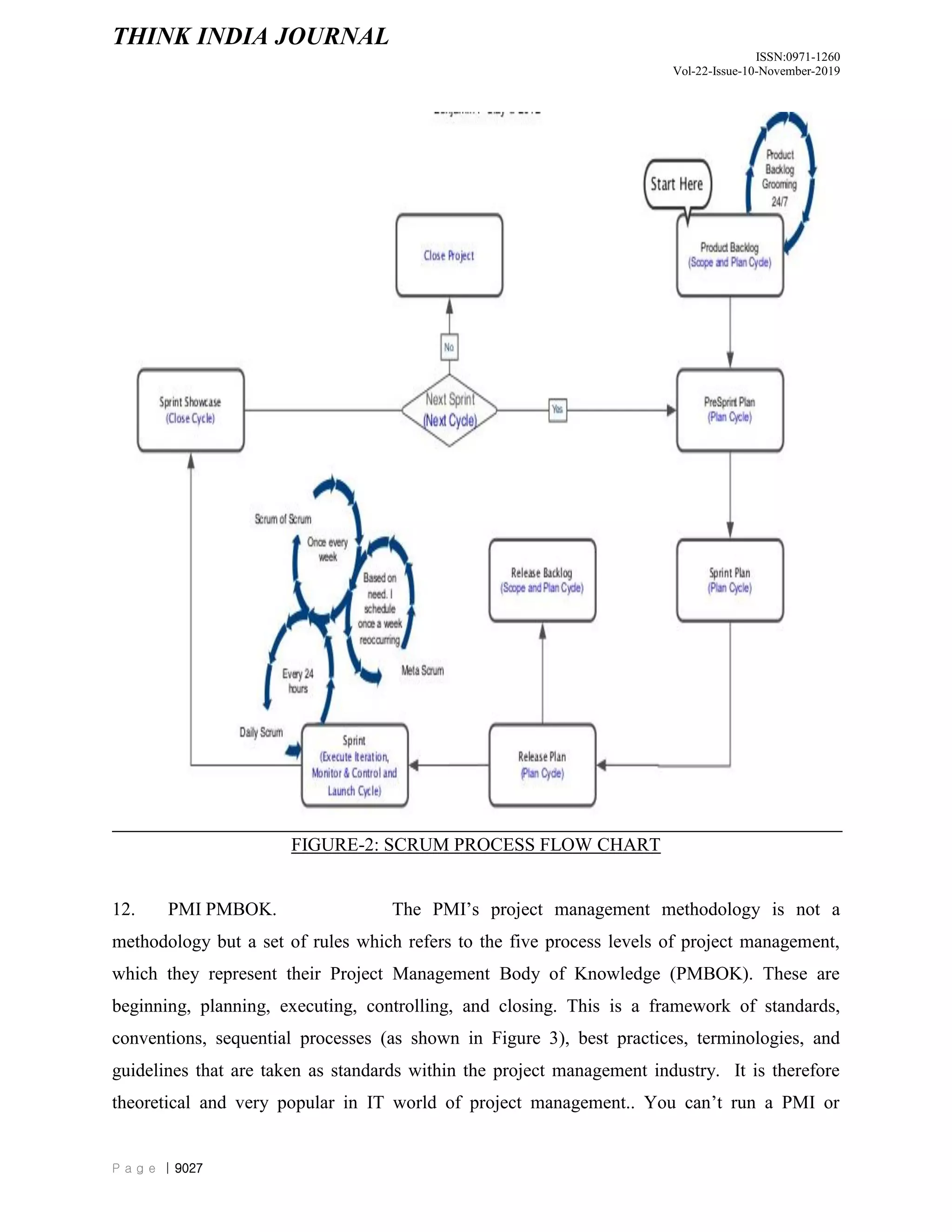
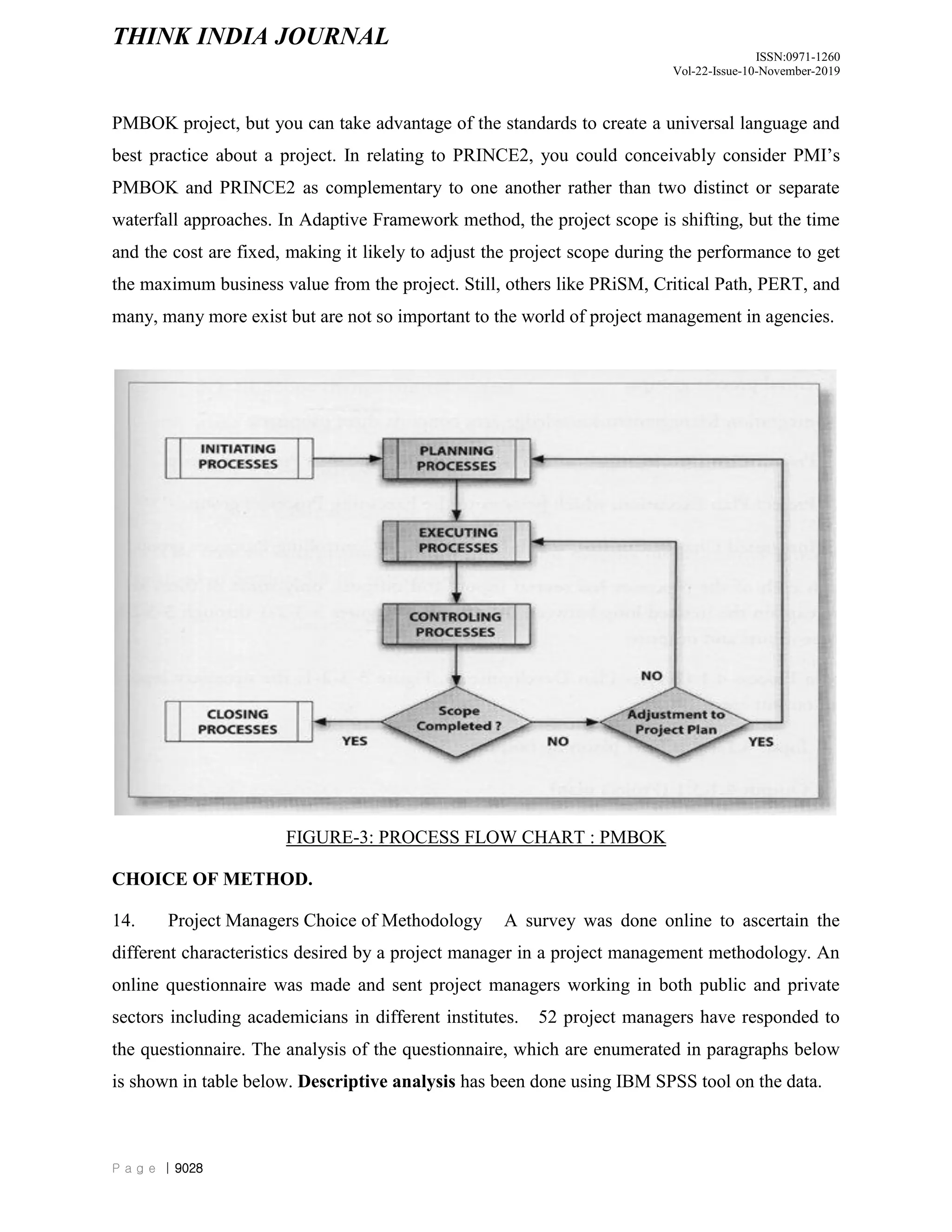
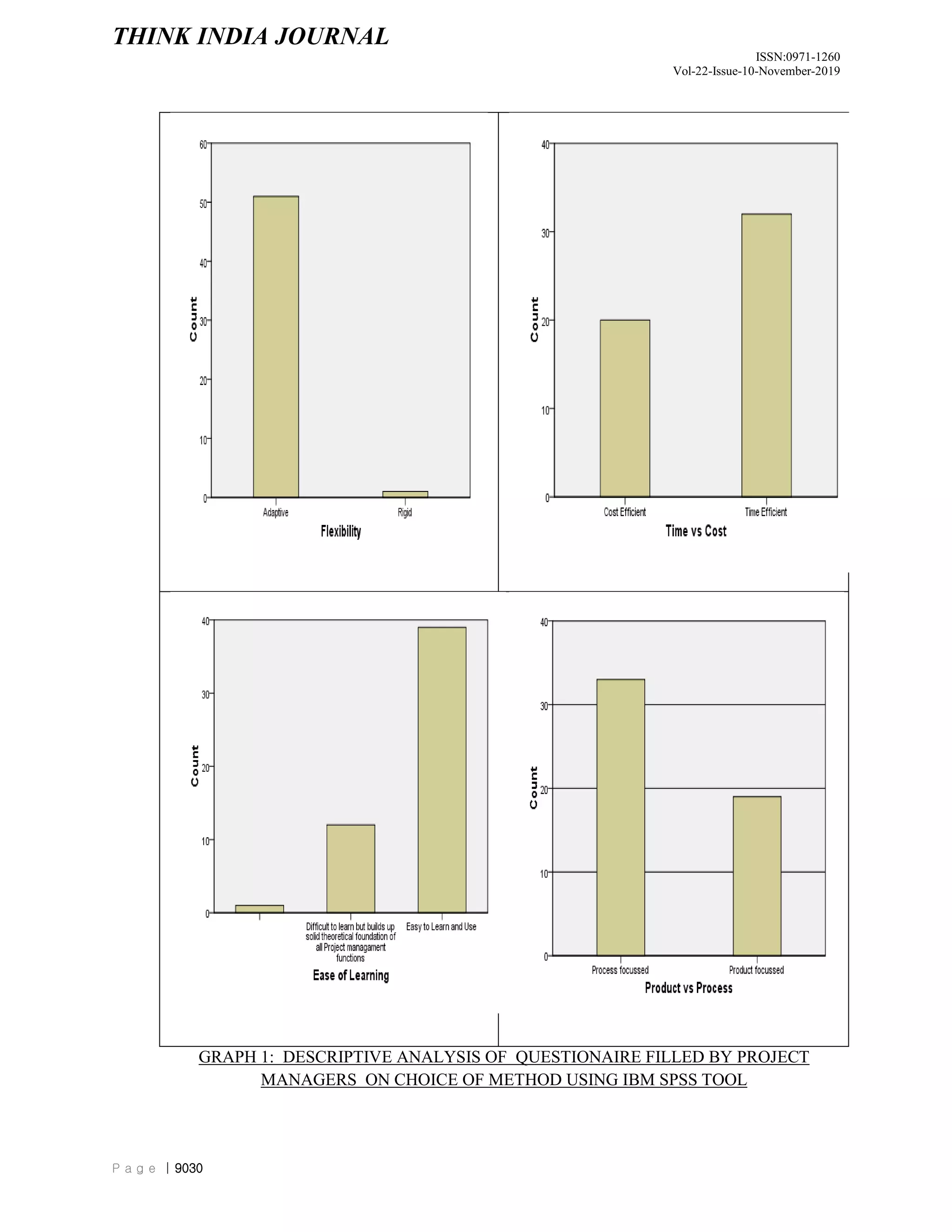
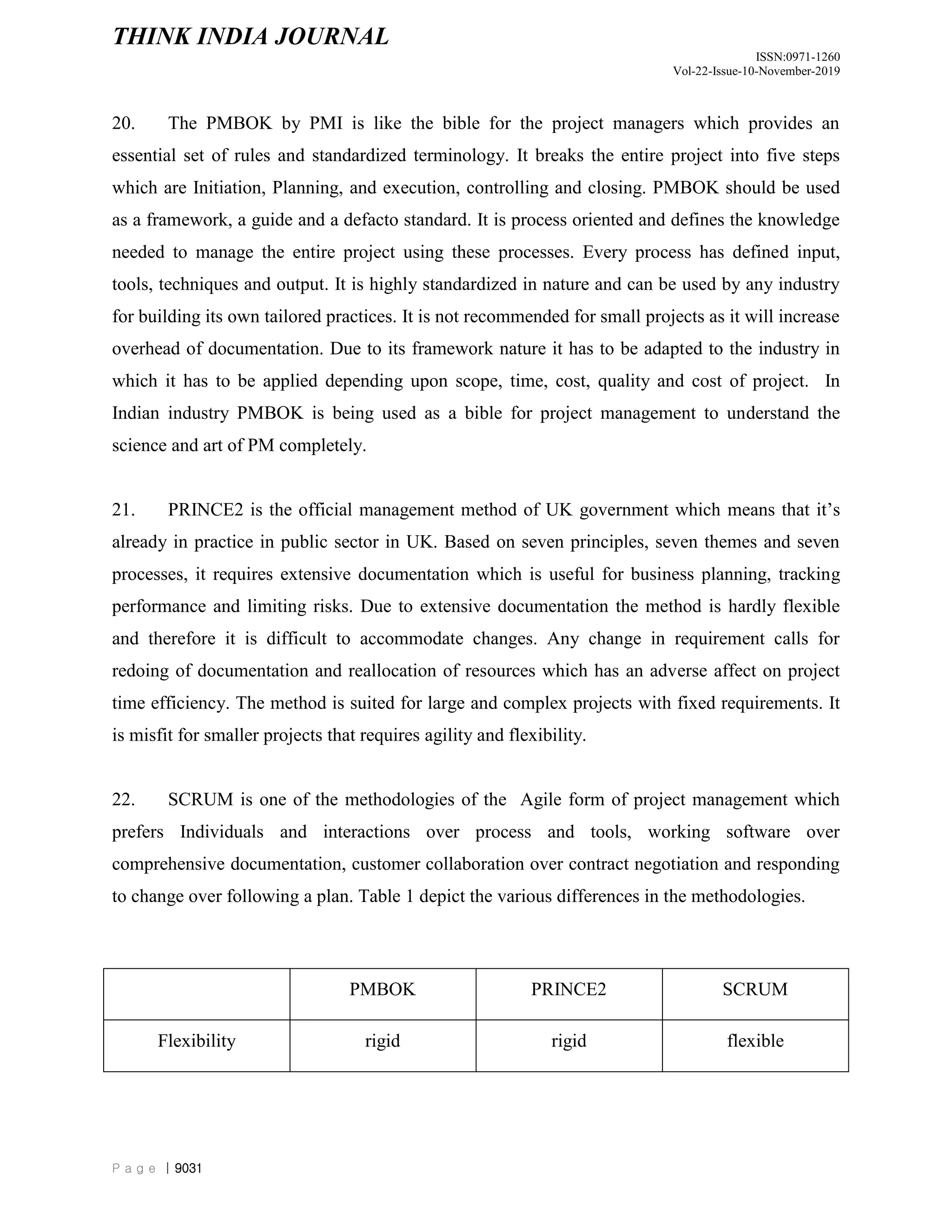
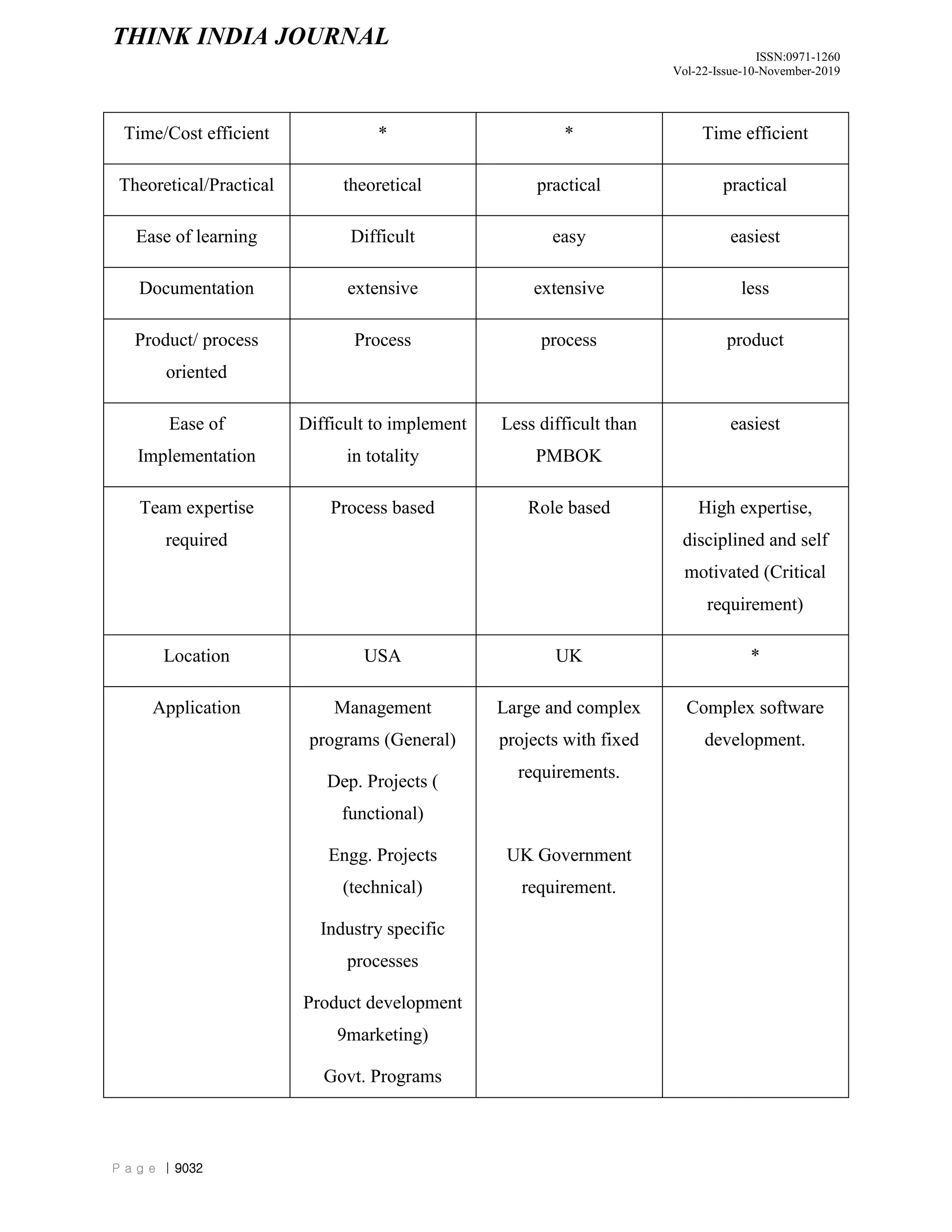
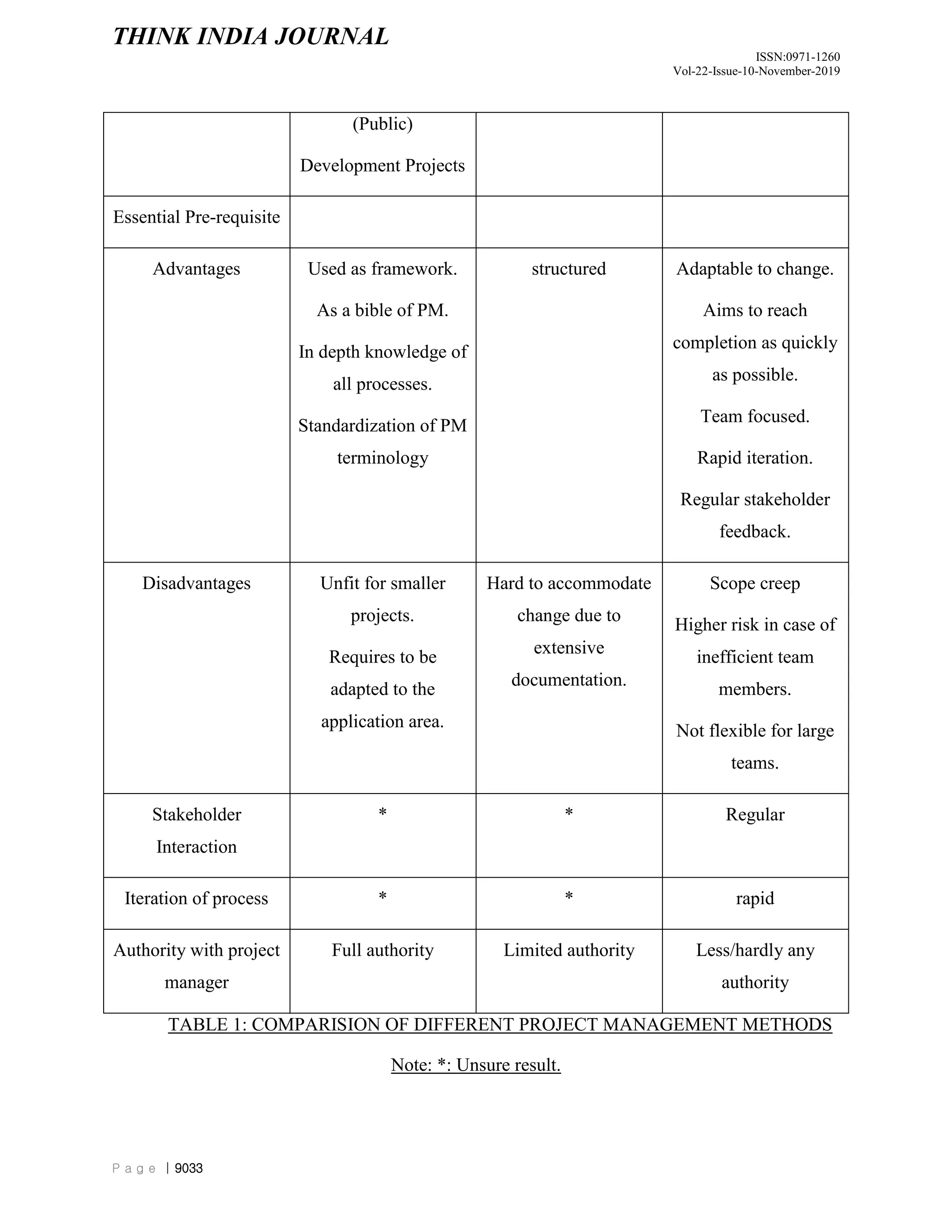
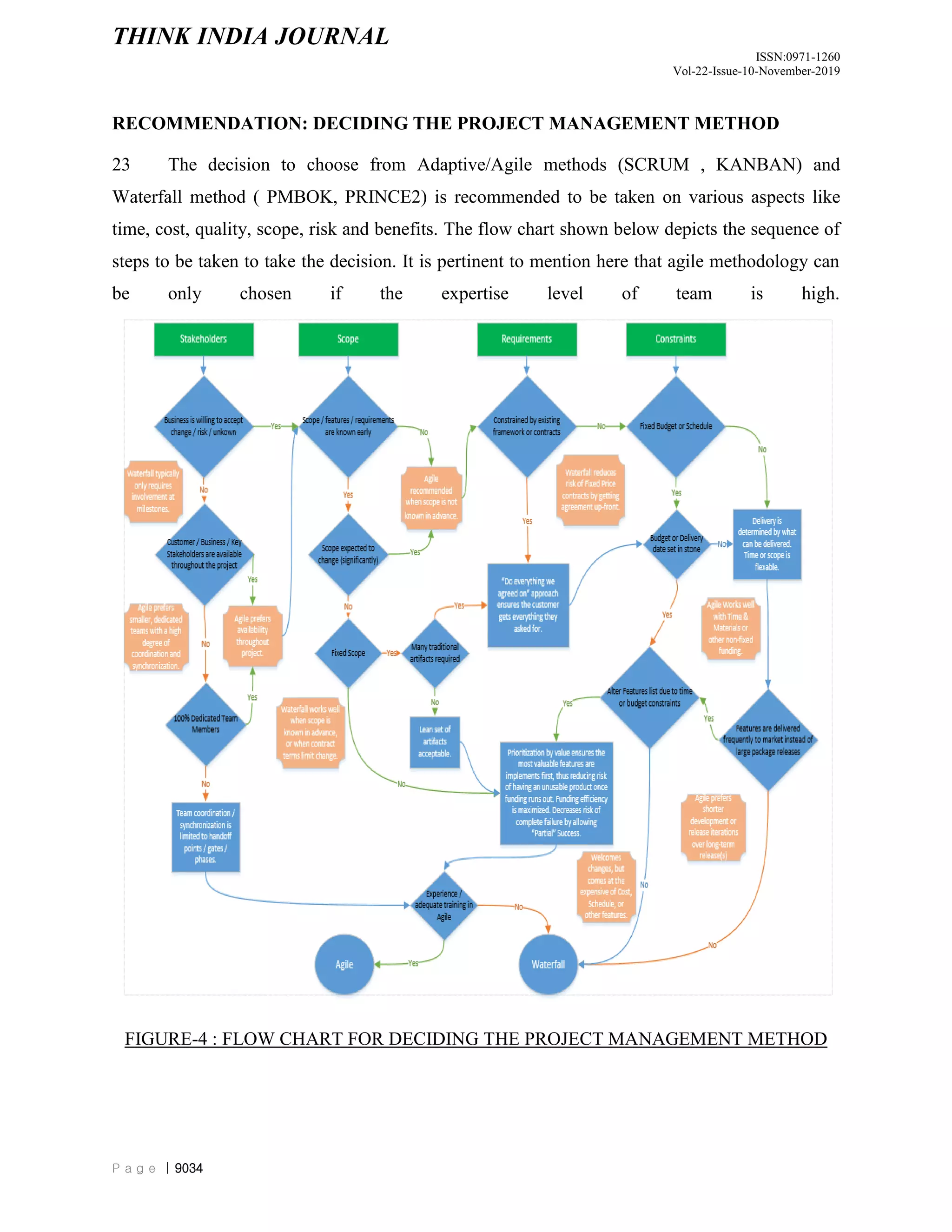
The document discusses and compares different project management methodologies used for e-governance projects in India. It summarizes the PMBOK, PRINCE2, and SCRUM methodologies. It also presents the results of a survey of 52 Indian project managers that indicated a preference for adaptive, time-efficient, and easy to learn methodologies with limited delegation of authority to project managers. Overall, the document analyzes and evaluates different project management methodologies for their suitability for e-governance projects in India.