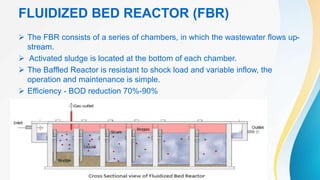
The document discusses decentralized treatment systems (DTS) for wastewater. A DTS treats wastewater using natural processes and cascades treatment through several modules, including anaerobic modules like a biogas settler, fluidized bed reactor, and fixed film reactor. It can reuse treated water and sludge. Case studies show DTS can achieve high removal rates of contaminants like BOD and meet discharge standards. Key advantages of DTS include being 100% sustainable with near zero energy and maintenance costs.