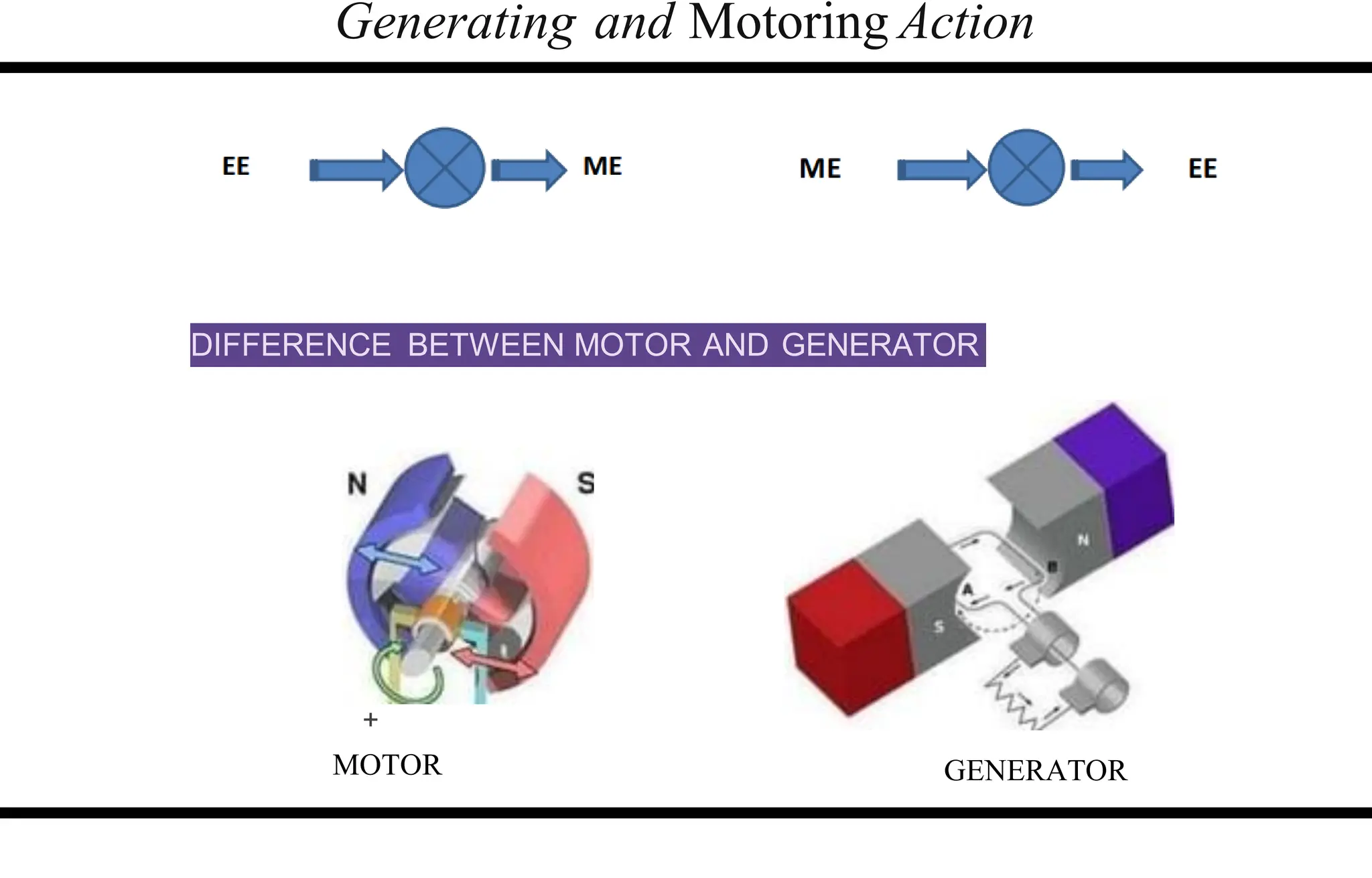
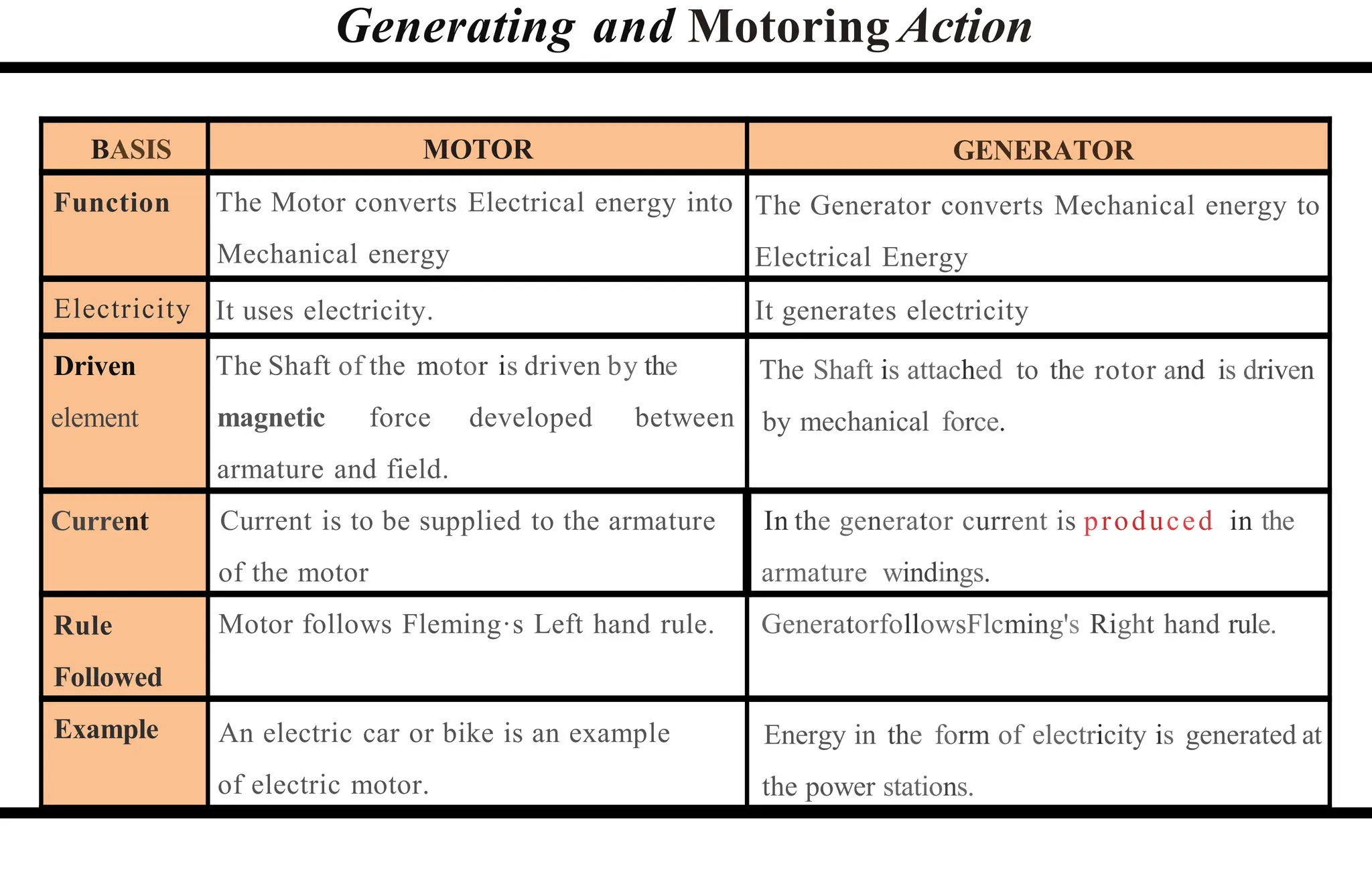
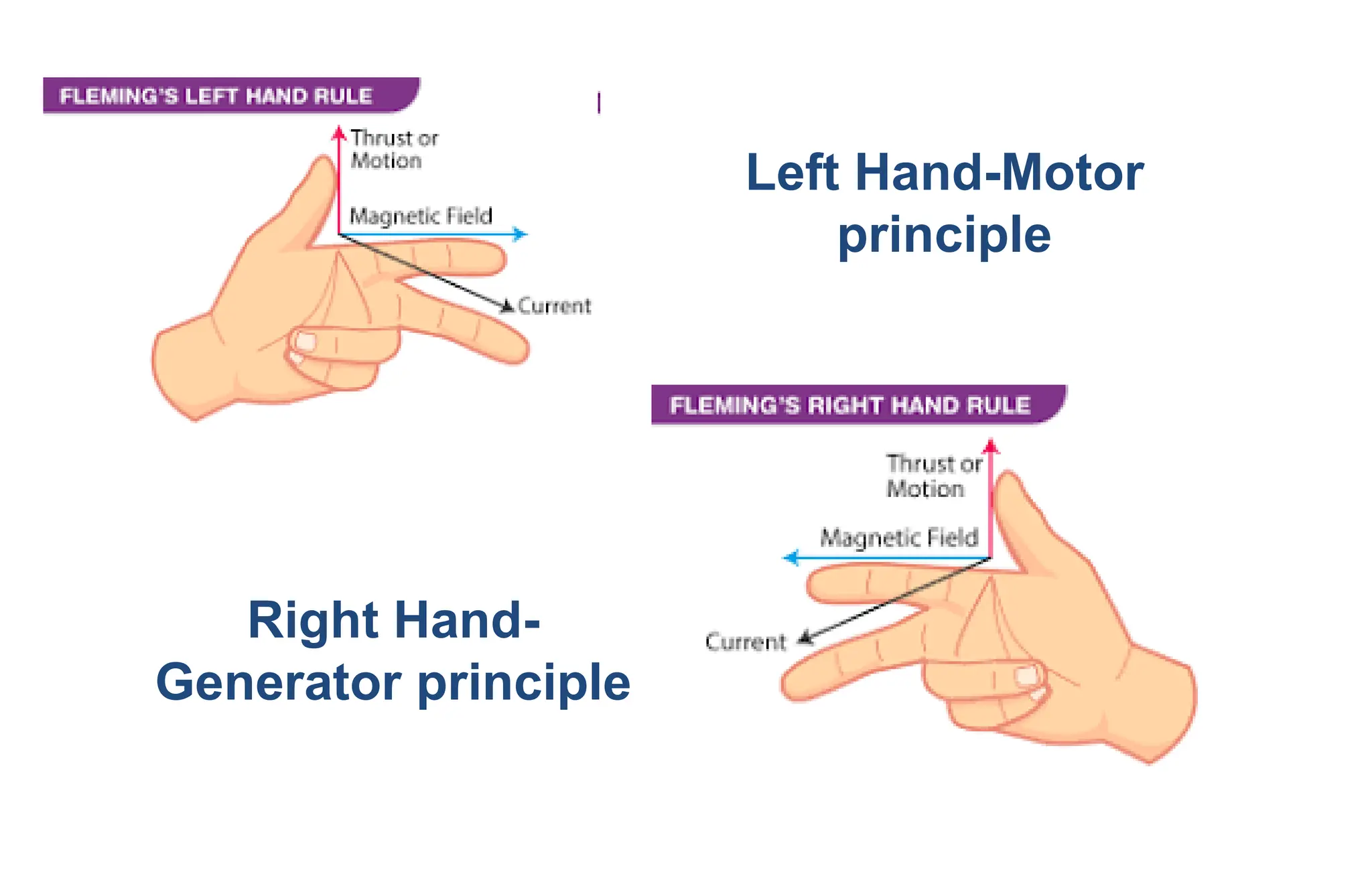
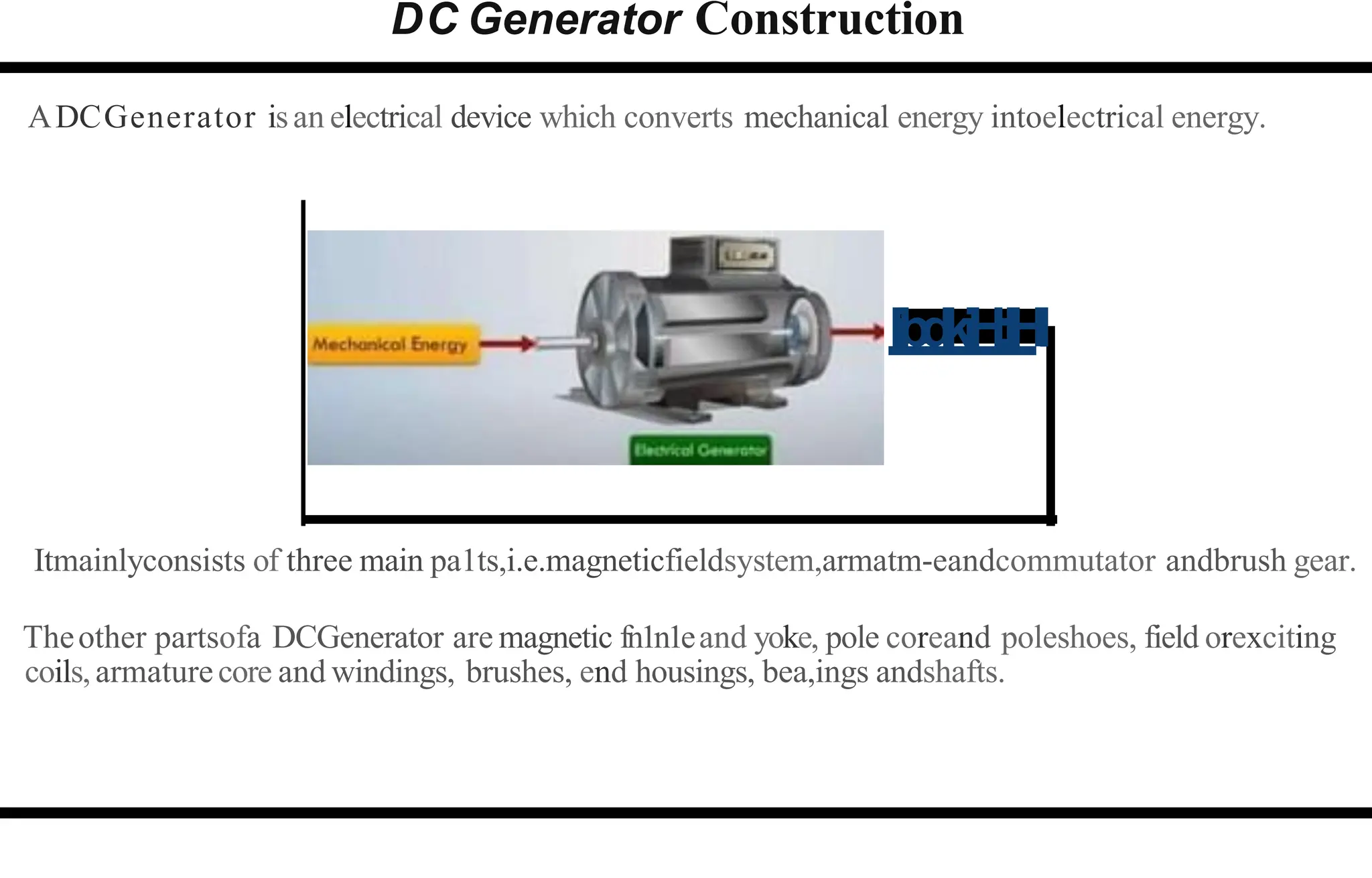
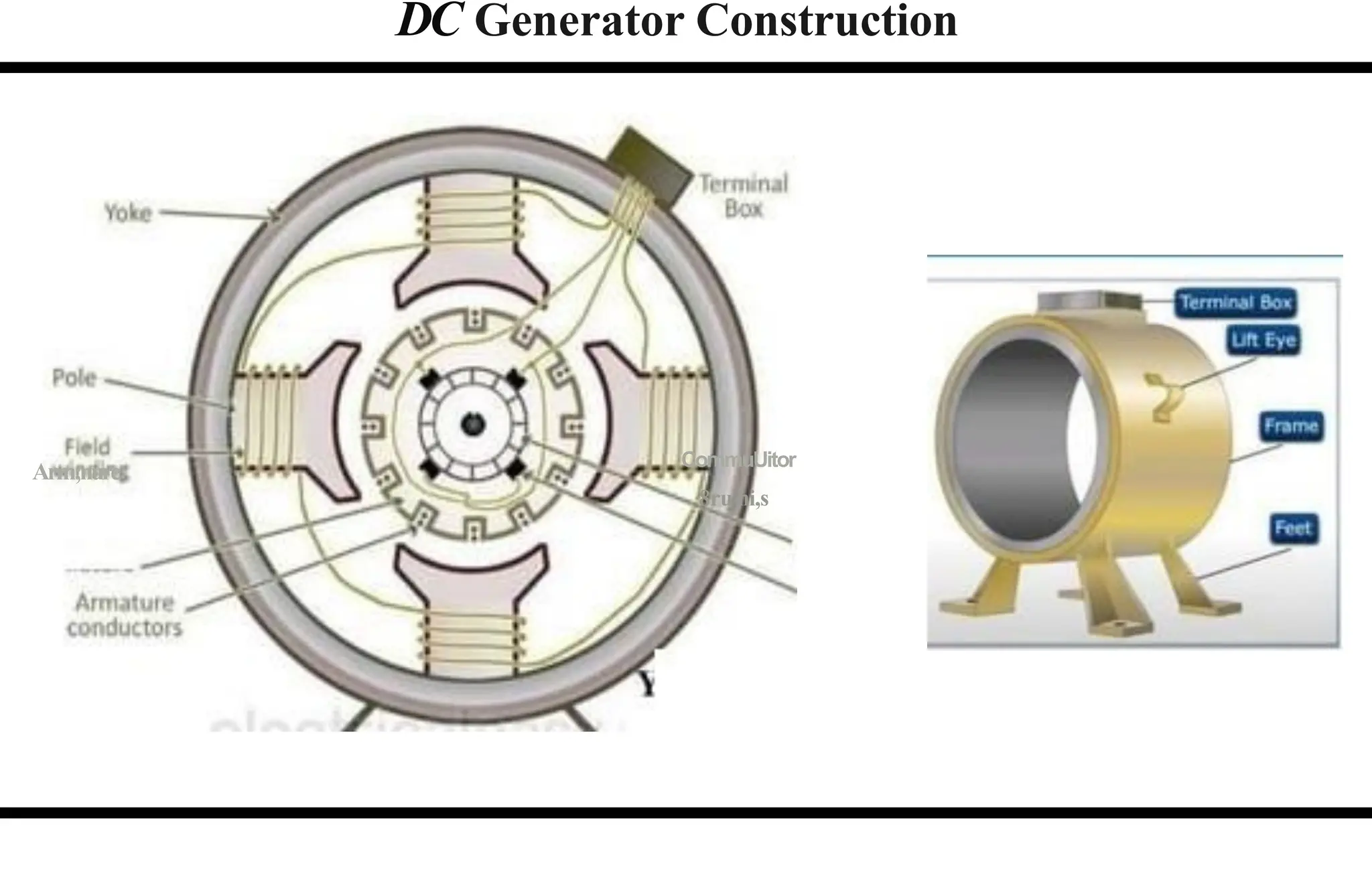
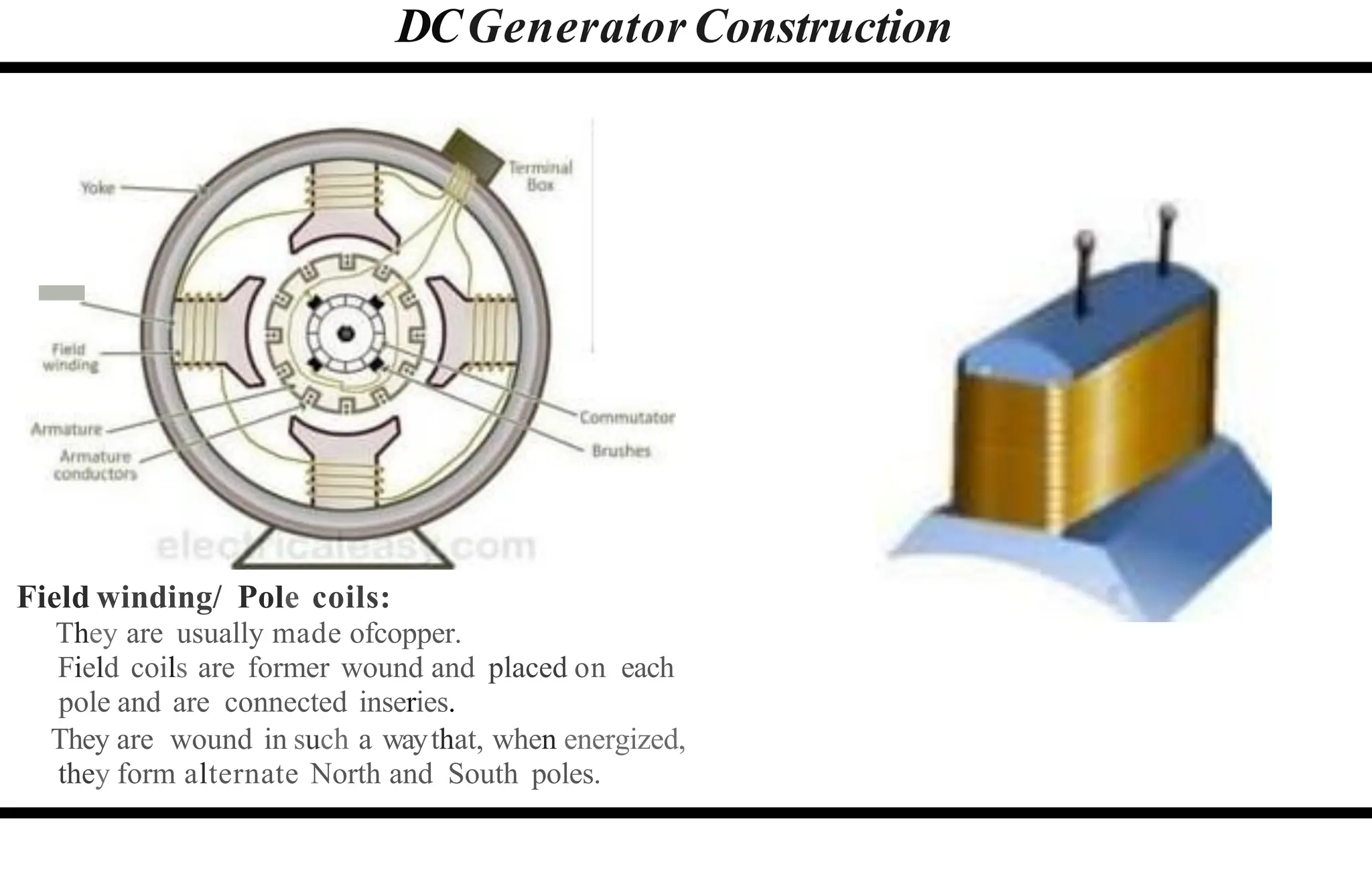
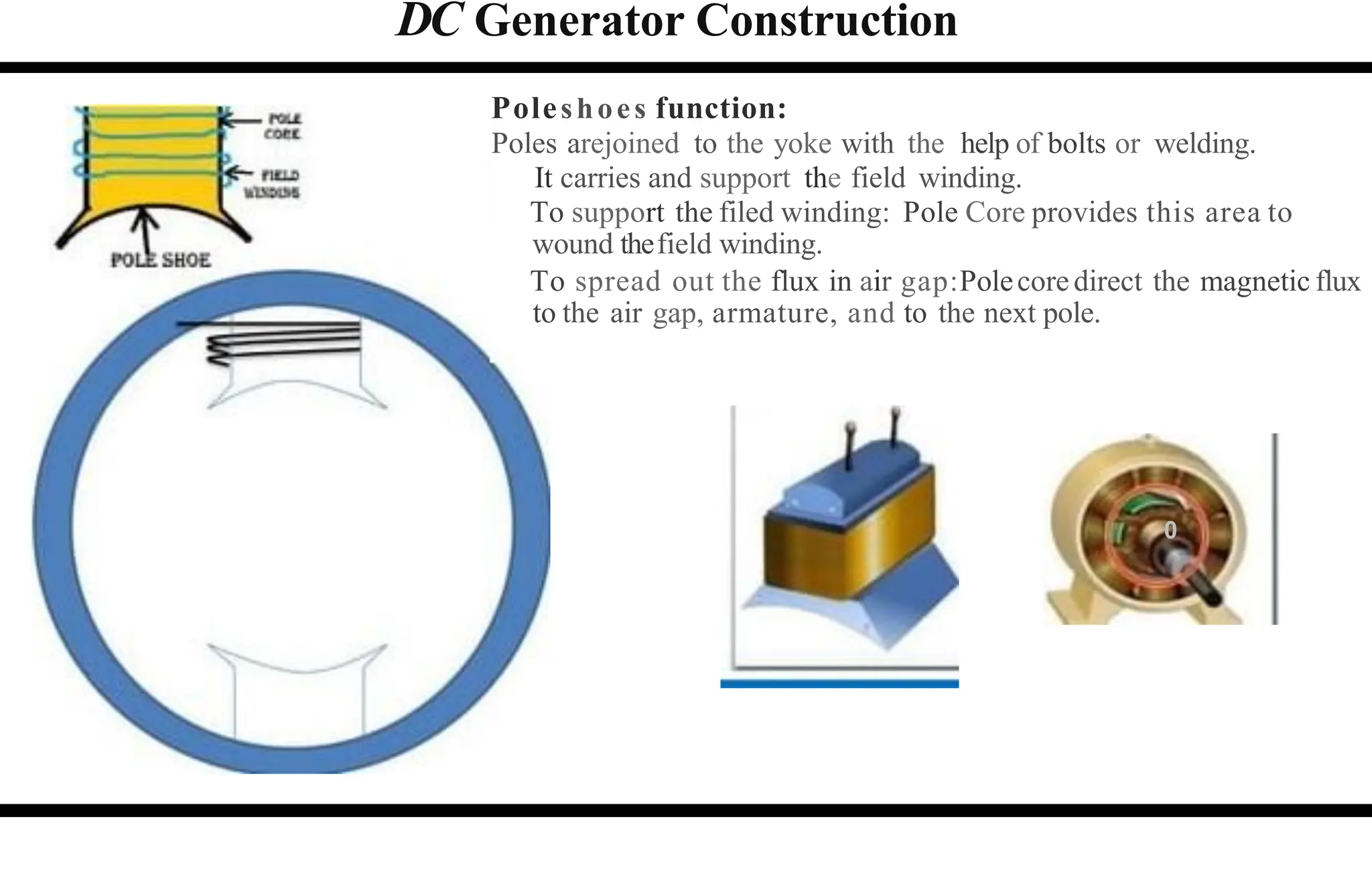
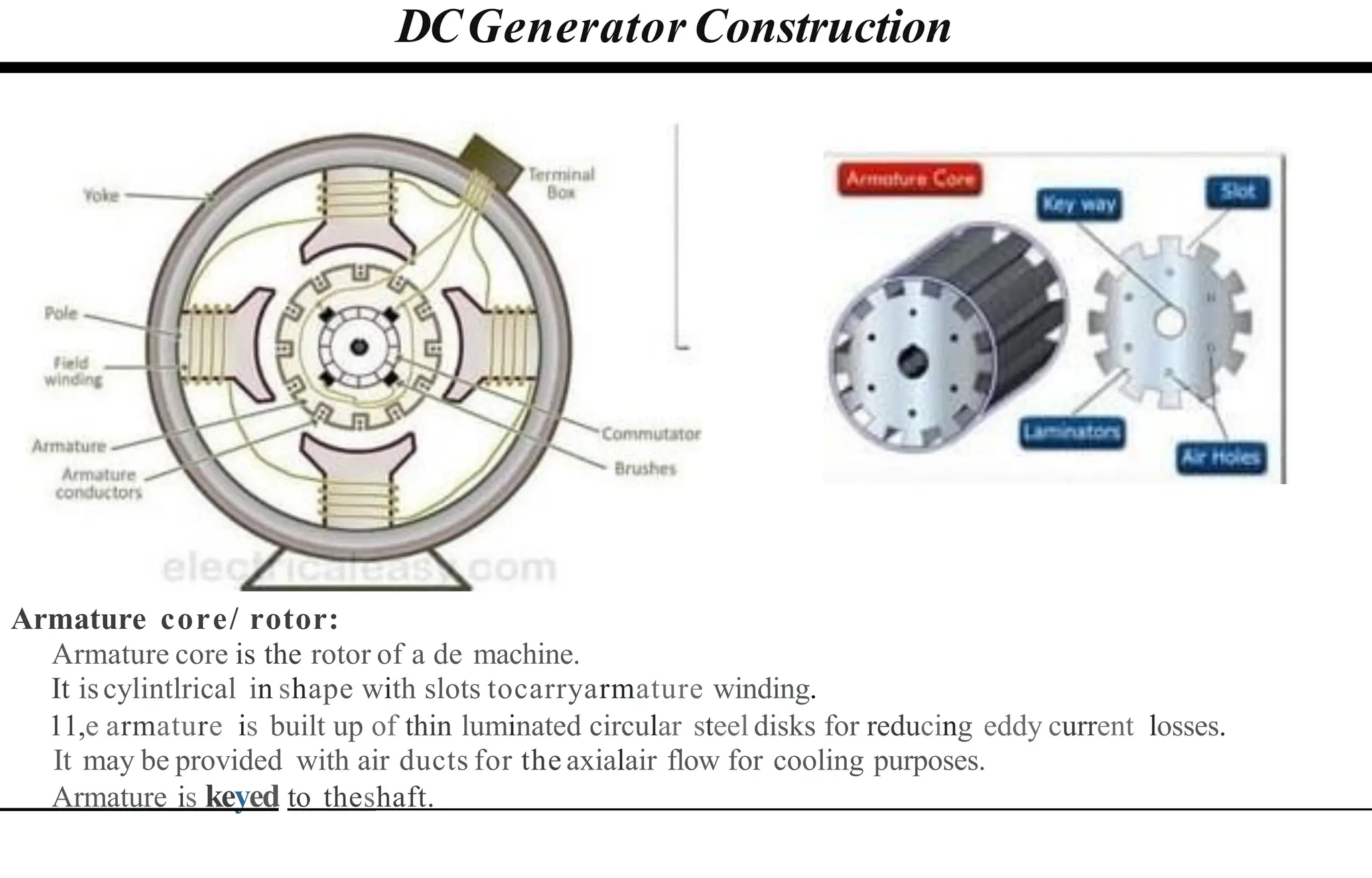
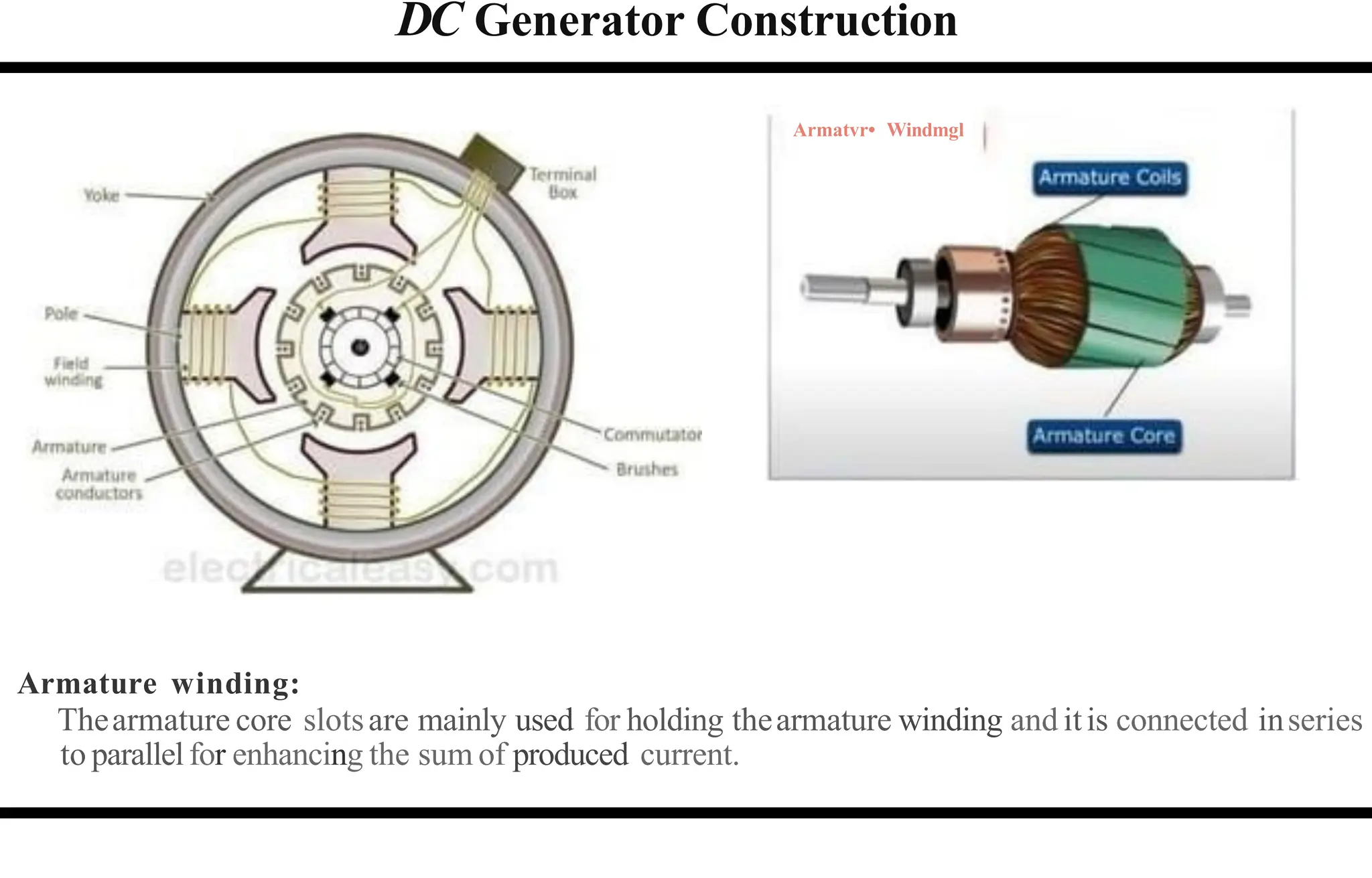
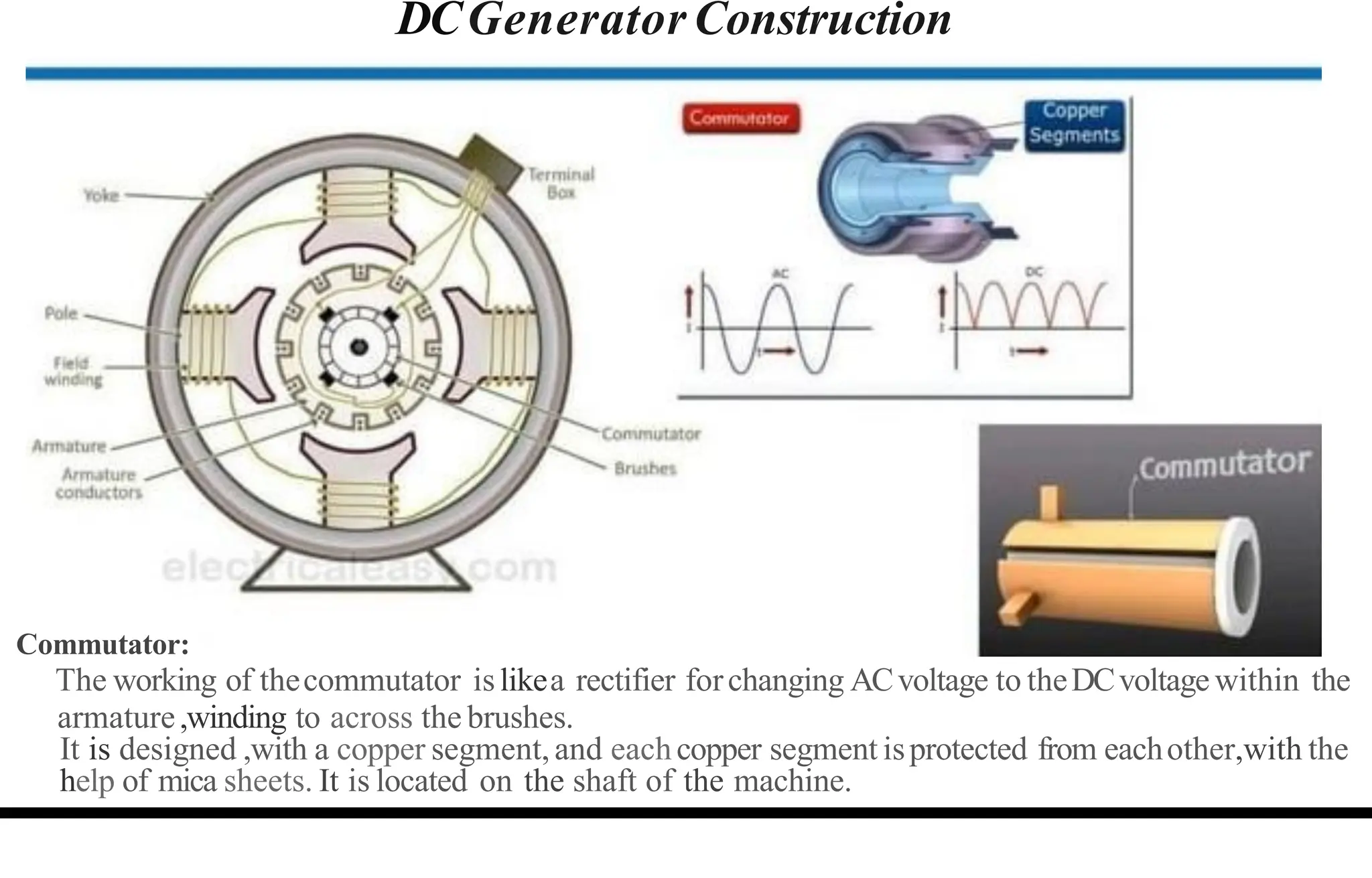
The document provides an overview of DC machines, focusing on the principles and components of motors and generators. It explains the conversion of electrical energy to mechanical energy in motors and mechanical energy to electrical energy in generators, alongside details about their construction and functionality. Key elements discussed include the armature, magnetic field system, and the working rules for motors and generators.