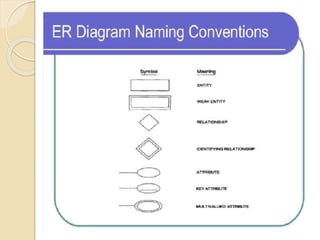
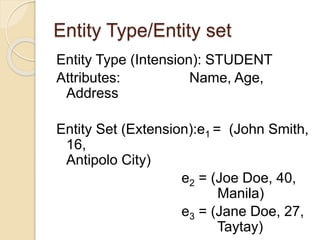
Data independence refers to the ability to modify either the conceptual or internal schema without requiring changes to the other. There are two types of data independence: physical data independence, which allows changes to the physical storage structure without affecting the conceptual schema, and logical data independence, which allows changes to the conceptual schema without affecting external schemas. An entity-relationship model uses entities, attributes, and relationships to graphically represent how data is organized within a database. Entities can have simple, composite, derived, single-value, or multi-value attributes, and keys uniquely identify entities within an entity set.