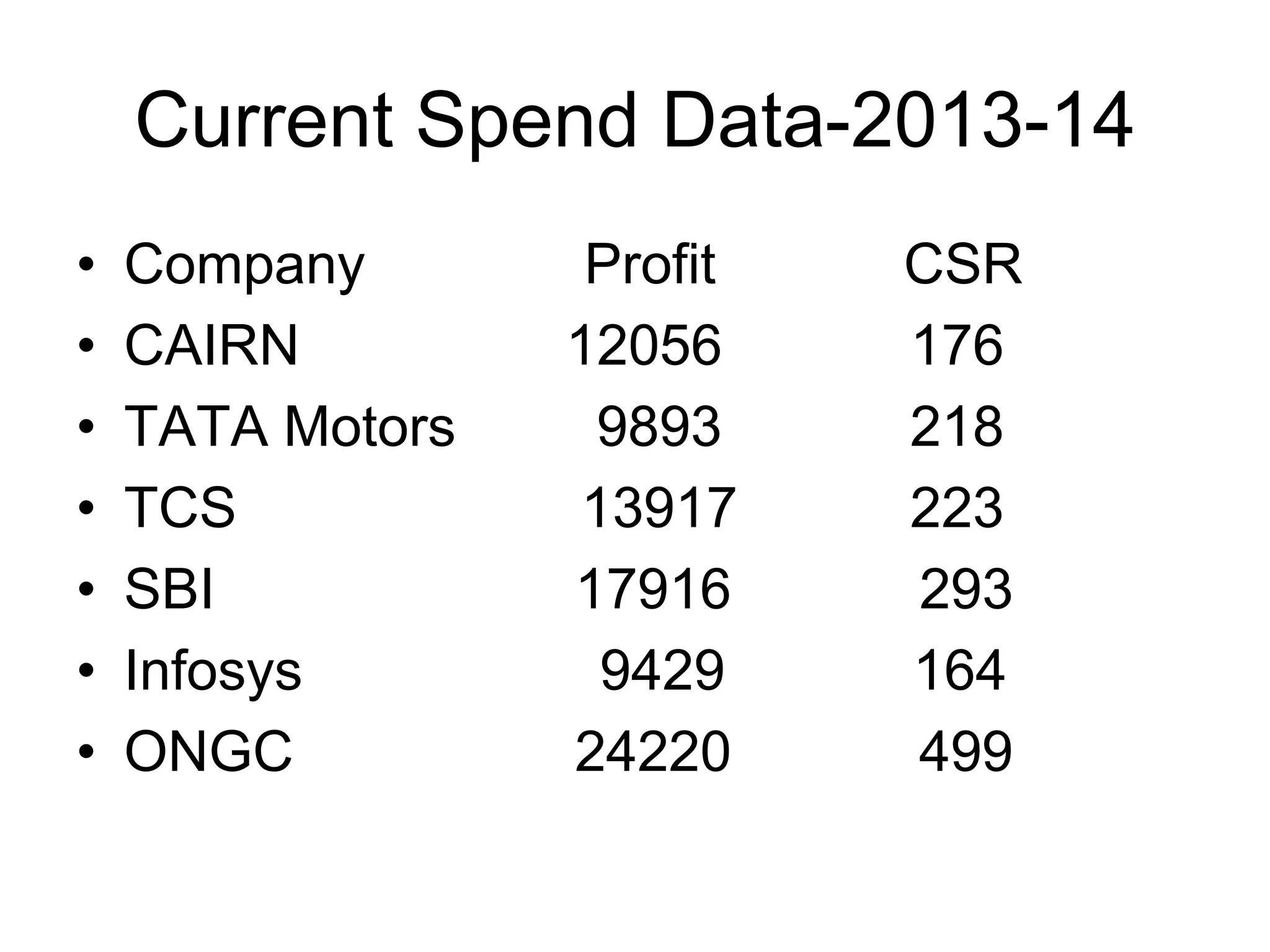
This document discusses corporate social responsibility (CSR) as presented in a seminar. It defines CSR as a continuing commitment by businesses to behave ethically and contribute to sustainable development. It outlines criticisms of corporations, how CSR benefits various stakeholders, and new trends in CSR like partnerships with NGOs and focus on society. It also discusses the establishment of the National Foundation for Corporate Social Responsibility to facilitate CSR programs and the benefits of good CSR practices.