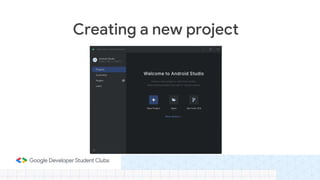
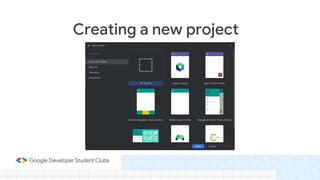
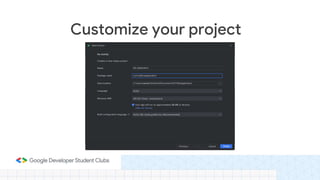
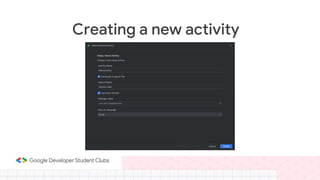
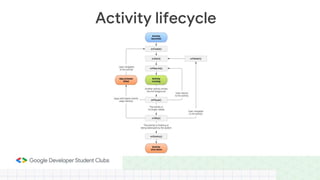
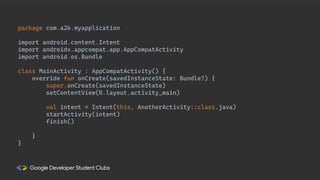
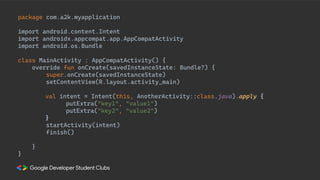
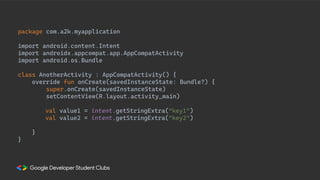
This document provides an overview of setting up an Android development environment and creating a basic "Hello World" Android app. It discusses downloading and installing Android Studio, creating a new project, customizing the project, and adding a new activity. It also covers basic Kotlin concepts like variables, loops, and switch statements. Additionally, it explains activities, intents, and how to share data between activities using intents and extras.