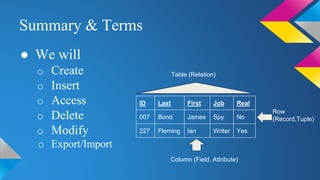
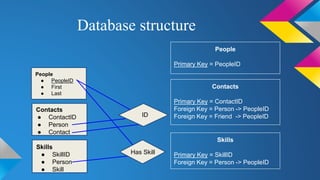
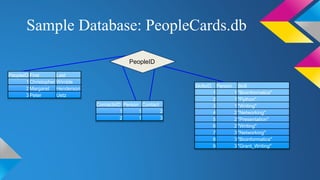
SQLite is a lightweight database that is useful for personal applications, websites under 500,000 hits per day, and data analysis. It allows users to create, insert, access, delete, and modify data in tables using SQL commands. Sample tables in a SQLite database might include a People table with fields for ID, first name, and last name, and a Skills table with fields to link people to their skills. The database can then be queried to view, add, or modify the data.