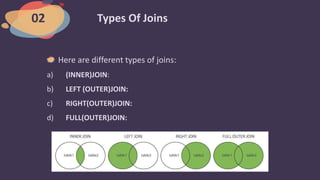
This document discusses different types of joins in SQL, including inner, left outer, right outer, and full outer joins. It explains that a join clause combines rows from two or more tables based on related columns. The main types of joins covered are inner joins, which select records that match in both tables; left outer joins, which return all rows from the left table with matching or null rows from the right; right outer joins, which return all rows from the right table with matching or null rows from the left; and full outer joins, which return all rows from both tables including unmatched rows filled with nulls. Syntax examples are provided for each join type.