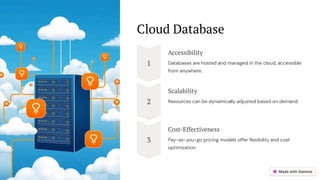
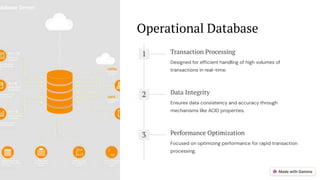
The document provides an overview of databases, detailing their types and structures, including hierarchical, network, object-oriented, relational, cloud, centralized, and operational databases. Each type is characterized by its data organization, relationships, and navigation methods. Additionally, it highlights the importance of SQL in managing relational databases and emphasizes the efficiency and accessibility of cloud databases.