Recommended
PDF
PPTX
An-Introduction-to-the-Data-Science.pptx
PPTX
Data Science Training in Chandigarh h
PDF
Introduction to Data Science: Concepts, Tools, and Career Overview
PDF
Join data mining with brief introduction to data science
DOCX
Data Science: Powering the Future of Innovation(2).docx
PDF
Data science mastery course in pitampura
PPTX
The Power of Data Science by DICS INNOVATIVE.pptx
PDF
Data Science Overview and a brief introduction to data science.pdf
PDF
Decoding Data: Turning Numbers into Actionable Insights
PDF
The Power of Data Science Building a Smarter Future
PPTX
The Power of Data Science Building a Smarter Future
PDF
A Beginner’s Guide to An Incredible Technology Data Science.pdf
PDF
a-beginner-guide-to-an-incredible-technology-data-science.pdf
PDF
Data Science Demystified_ Journeying Through Insights and Innovations
PDF
What is Data Science and How to Start a Career in It | IABAC
PDF
Defining Data Science: A Comprehensive Overview
PPTX
DILEEP DATA SCIERNCES PROJECT POWERPOINT PPT
PPTX
Data Science Course in Koramangala, Bangalore | Data Science Course in Indira...
PPTX
Data Science for Innovation: From Raw Data to Real-World Insights & Solutions
PDF
Data Science: Concepts, Workflow & Applications PPT
PPTX
Data Science Mastery Course in Pitampura
PPTX
alok ppt.pptxasdfghjklsdfghjsdfghjxcvbndfghj
PDF
Where to study Data Science Course in Kerala
PPTX
_Data Science_ Unlocking Insights and Driving Innovation”.pptx
PPTX
Data_Science_Basics in the begining.pptx
PDF
Data Science: Unlocking Insights and Transforming Industries
PPTX
data_intelligence_presentation beginner friendly to use the instances
PPTX
Complete solution for Recurrent neural network.pptx
PPTX
Electronic devices and circuits.pptx
More Related Content
PDF
PPTX
An-Introduction-to-the-Data-Science.pptx
PPTX
Data Science Training in Chandigarh h
PDF
Introduction to Data Science: Concepts, Tools, and Career Overview
PDF
Join data mining with brief introduction to data science
DOCX
Data Science: Powering the Future of Innovation(2).docx
PDF
Data science mastery course in pitampura
PPTX
The Power of Data Science by DICS INNOVATIVE.pptx
Similar to Data_Science_visual for engineers and.pptx
PDF
Data Science Overview and a brief introduction to data science.pdf
PDF
Decoding Data: Turning Numbers into Actionable Insights
PDF
The Power of Data Science Building a Smarter Future
PPTX
The Power of Data Science Building a Smarter Future
PDF
A Beginner’s Guide to An Incredible Technology Data Science.pdf
PDF
a-beginner-guide-to-an-incredible-technology-data-science.pdf
PDF
Data Science Demystified_ Journeying Through Insights and Innovations
PDF
What is Data Science and How to Start a Career in It | IABAC
PDF
Defining Data Science: A Comprehensive Overview
PPTX
DILEEP DATA SCIERNCES PROJECT POWERPOINT PPT
PPTX
Data Science Course in Koramangala, Bangalore | Data Science Course in Indira...
PPTX
Data Science for Innovation: From Raw Data to Real-World Insights & Solutions
PDF
Data Science: Concepts, Workflow & Applications PPT
PPTX
Data Science Mastery Course in Pitampura
PPTX
alok ppt.pptxasdfghjklsdfghjsdfghjxcvbndfghj
PDF
Where to study Data Science Course in Kerala
PPTX
_Data Science_ Unlocking Insights and Driving Innovation”.pptx
PPTX
Data_Science_Basics in the begining.pptx
PDF
Data Science: Unlocking Insights and Transforming Industries
PPTX
data_intelligence_presentation beginner friendly to use the instances
More from ArunKumar674066
PPTX
Complete solution for Recurrent neural network.pptx
PPTX
Electronic devices and circuits.pptx
PDF
unit-5 digital electronics.pdf
PPTX
PPTX
Digital design_unit I.pptx
PDF
PDF
Gerd Keiser - Optical Fiber Communications-McGraw-Hill Education (2010).pdf
Recently uploaded
PDF
Infinite Sequence and Series: It Includes basic Sequence and Series
PPTX
Value engineering and cost analysis with case study
PPTX
ME3592 - Metrology and Measurements - Unit - 1 - Lecture Notes
PPTX
A professional presentation on Cosmos Bank Heist
PPTX
uADPF Topology_SFP requirements_locked slides.pptx
PDF
Model QP 2025 scheme Q &A- Module 1 and 2.pdf
PPTX
Fitting Infiltration Models to Infiltration using Excel (1).pptx
PDF
Shear Strength of Soil/Mohr Coulomb Failure Criteria-1.pdf
PDF
Chad Ayach - An Accomplished Mechanical Engineer
PPTX
operating_systems.pptx m,nm,nm,n,nm,n,nm,nikl
PDF
Plasticity and Structure of Soil/Atterberg Limits.pdf
PPTX
traffic safety section seven (Traffic Control and Management) of Act
PPT
Oracle Advanced subquery and types of subquery
PPT
Ceramic Matrix Composites Slide from Composite Materials
PDF
engineering management chapter 5 ppt presentation
PPTX
GET 211- Computing and Software Engineering (1).pptx
PDF
Industrial Tools Manufacturers In India : Torso Tools
PPTX
Designing Work for Humans, Not Machines: Human-Centered Maintenance Excellence
PPTX
ISO 13485.2016 Awareness's Training material
PDF
Decision-Support-Systems-and-Decision-Making-Processes.pdf
Data_Science_visual for engineers and.pptx 1. 2. Introduction to Data Science
• Data Science is an interdisciplinary field that
combines statistics, computer science, and
domain expertise to extract insights and
knowledge from data. It plays a critical role in
decision-making across industries.
Data-Driven
Insights
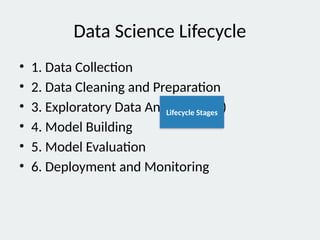
3. Data Science Lifecycle
• 1. Data Collection
• 2. Data Cleaning and Preparation
• 3. Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
• 4. Model Building
• 5. Model Evaluation
• 6. Deployment and Monitoring
Lifecycle Stages
4. Key Tools and Technologies
• - Programming Languages: Python, R
• - Data Visualization: Tableau, Power BI,
Matplotlib
• - Machine Learning: Scikit-learn, TensorFlow,
PyTorch
• - Big Data: Hadoop, Spark
• - Databases: SQL, NoSQL
Popular Tools
5. Applications of Data Science
• - Healthcare: Predictive analytics, medical
imaging
• - Finance: Fraud detection, risk management
• - Retail: Customer analytics, recommendation
systems
• - Marketing: Targeted advertising, sentiment
analysis
• - Transportation: Route optimization, self-
driving cars
Real-World Use
Cases
6. Challenges in Data Science
• - Handling large volumes of data
• - Ensuring data privacy and security
• - Managing data quality and consistency
• - Interpreting complex models
• - Bridging the gap between technical and
business teams
Overcoming
Challenges
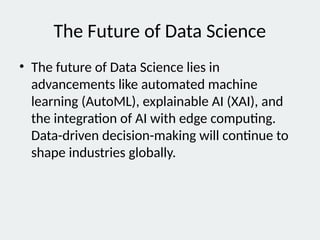
7. 8. The Future of Data Science
• The future of Data Science lies in
advancements like automated machine
learning (AutoML), explainable AI (XAI), and
the integration of AI with edge computing.
Data-driven decision-making will continue to
shape industries globally.
9.





![Video Demonstration: Data Science
in Action
• 🎥 [Insert a video here showcasing a Data
Science project or case study]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datasciencevisual-250225091038-fc6302a2/85/Data_Science_visual-for-engineers-and-pptx-7-320.jpg)