Embed presentation
Download to read offline

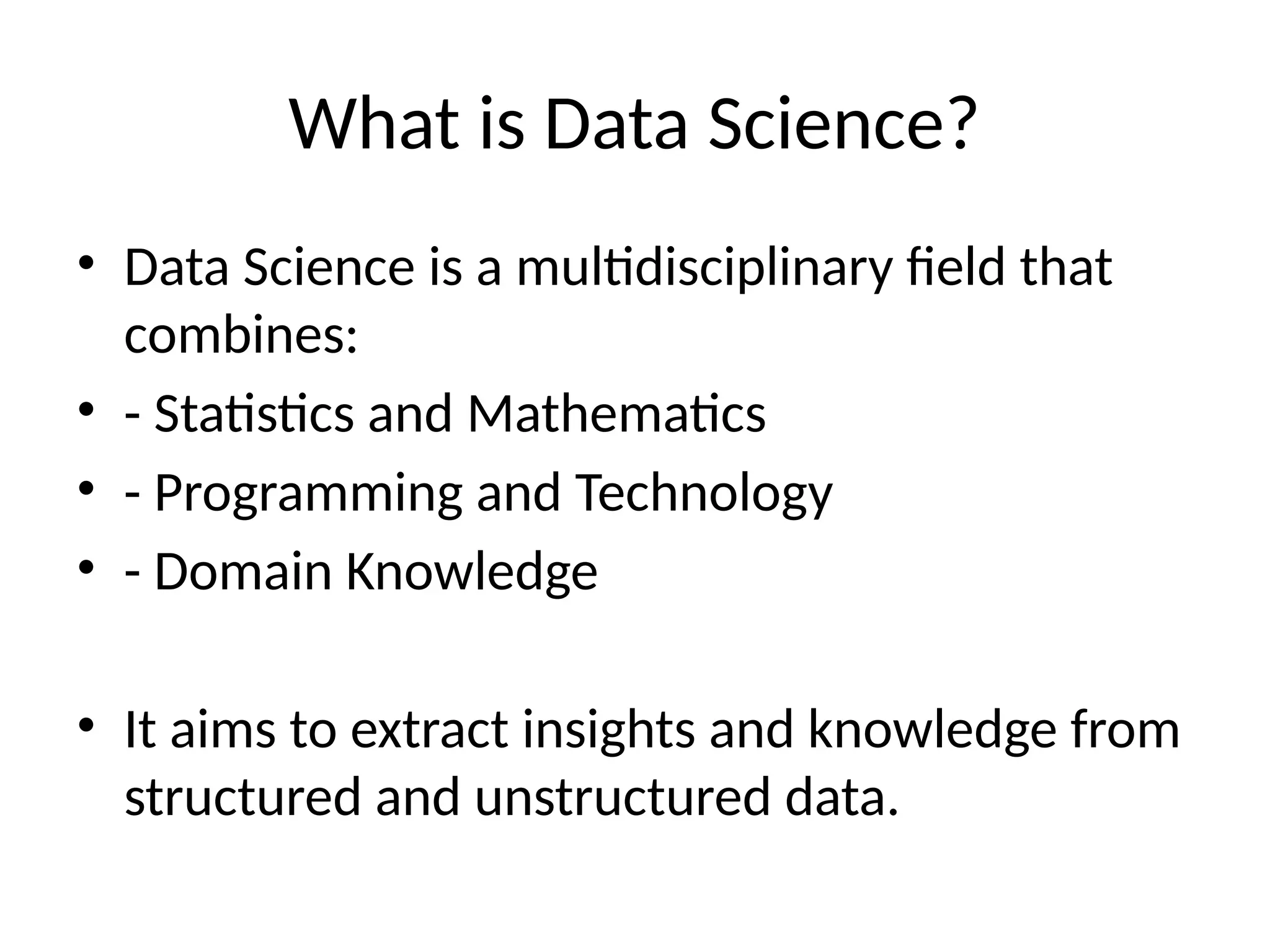


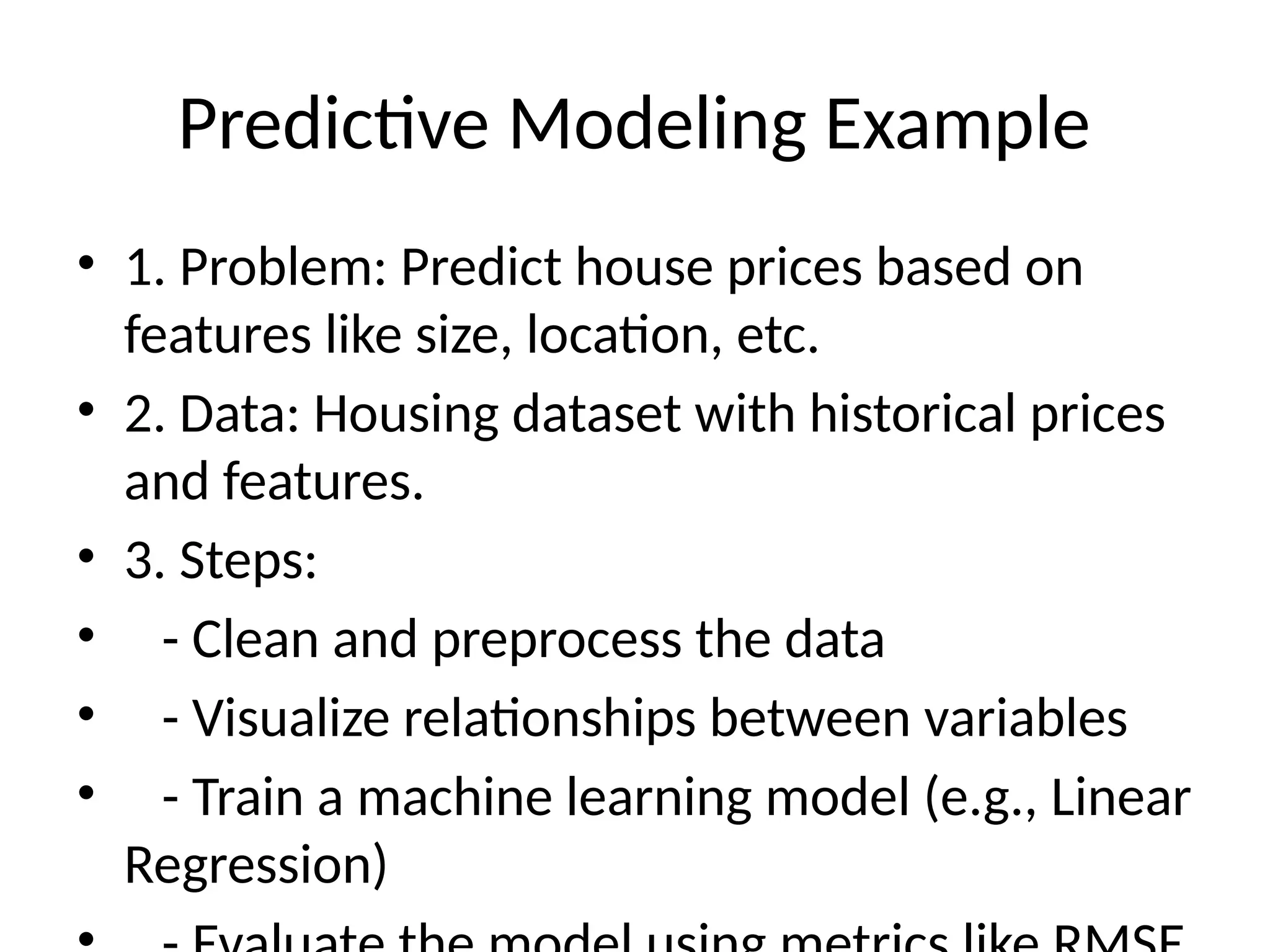
Data science is a multidisciplinary field that integrates statistics, programming, and domain knowledge to derive insights from various data types. The data science workflow includes problem definition, data collection, exploration, modeling, evaluation, and deployment, utilizing tools such as Python, R, and machine learning libraries. An example includes predicting house prices by analyzing historical datasets and applying machine learning techniques.




