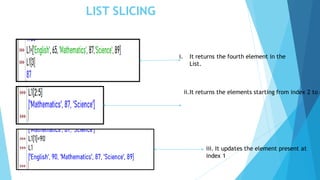
Python categorizes data types into mutable and immutable. Mutable types like lists and dictionaries can have their values changed, while immutable types like numbers, strings, and tuples cannot. Strings are sequences of characters that support operations like concatenation, repetition, and membership testing. They can be indexed and sliced, with positive indices from left to right and negative from right to left. Built-in functions like len() and capitalize() operate on strings. Lists are mutable sequences that can contain different data types and support operations like concatenation, repetition, membership testing, and slicing. Tuples are immutable sequences that behave similarly but cannot be modified once created.


![STRING SLICING
Slicing means to extract a piece/portion of an object from the original
object.
SYNTAX: str[startIndex:endIndex]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datatypesinpython-240206140804-b3ba2de3/85/DATA-TYPES-IN-PYTHON-pdf-4-320.jpg)