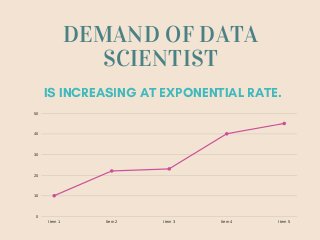
The document discusses data science and the role of a data scientist. It defines data science as the extraction of knowledge from large amounts of structured and unstructured data. A data scientist is described as a hybrid of data hacker, analyst, communicator, and trusted advisor who analyzes and interprets complex digital data to assist businesses. The document outlines the responsibilities of a data scientist in conducting research, extracting and cleaning large volumes of data, developing algorithms and tools, and recommending strategies. It also lists common tools used by data scientists like machine learning, deep learning, and data visualization.