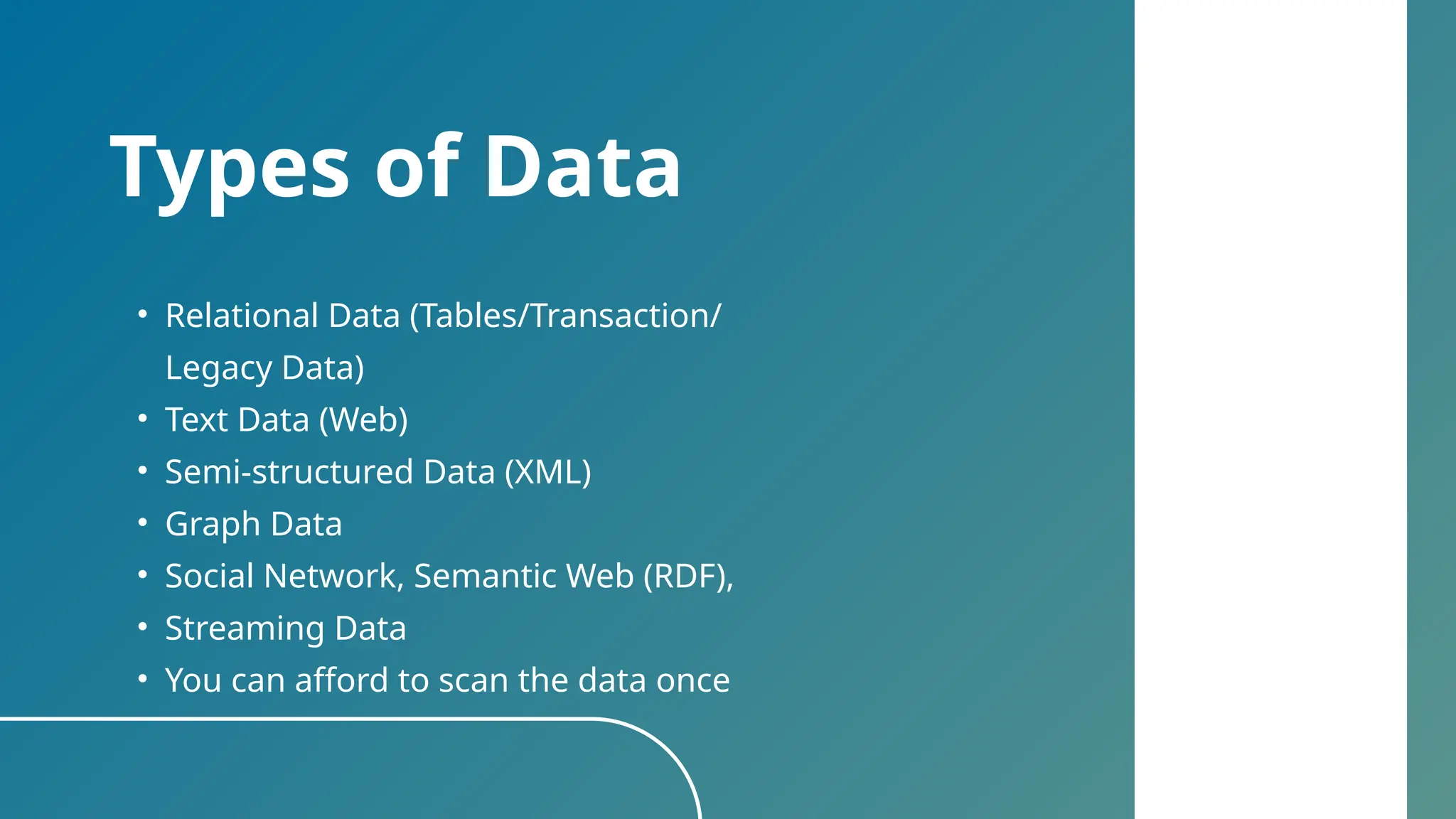
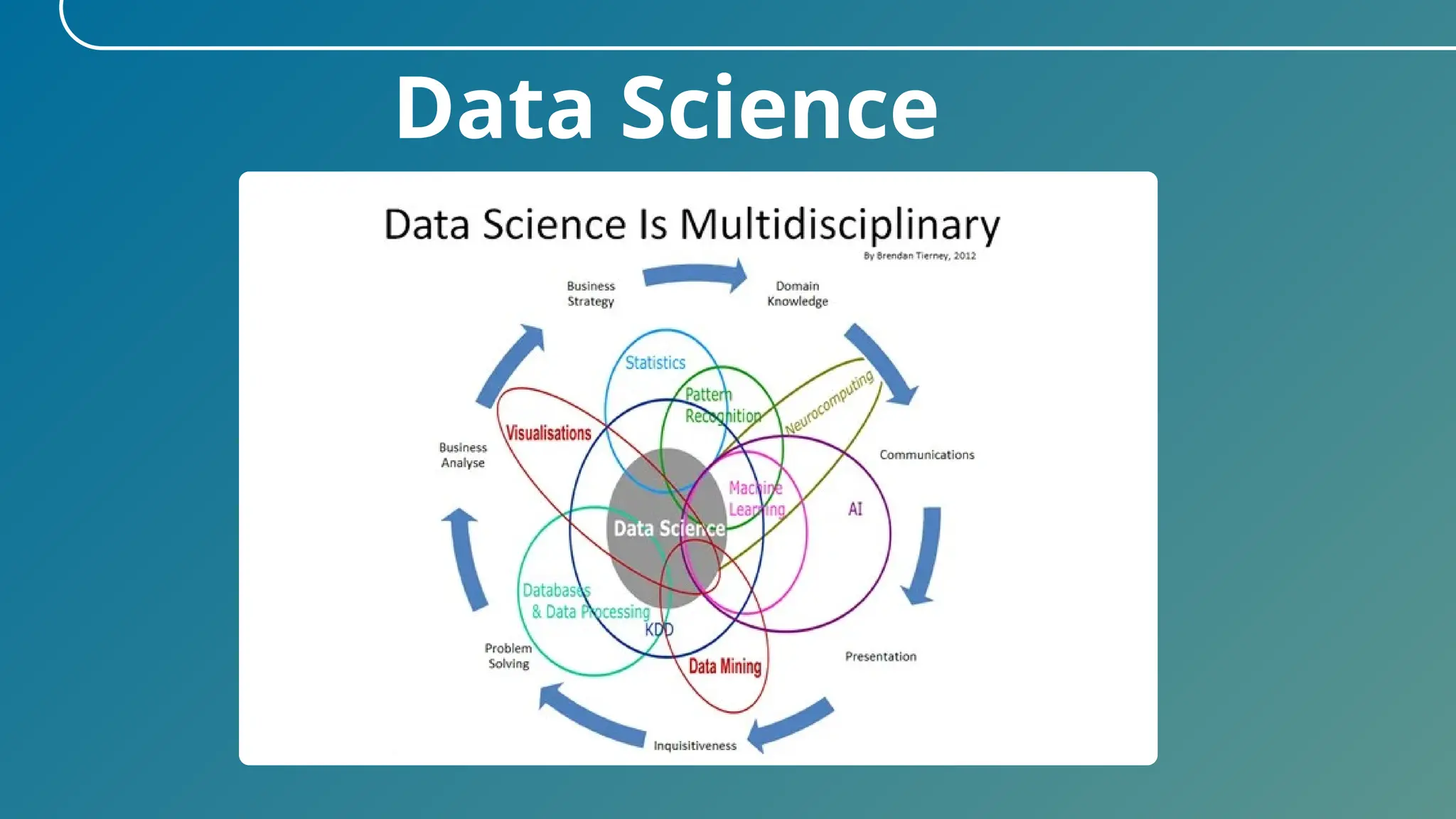
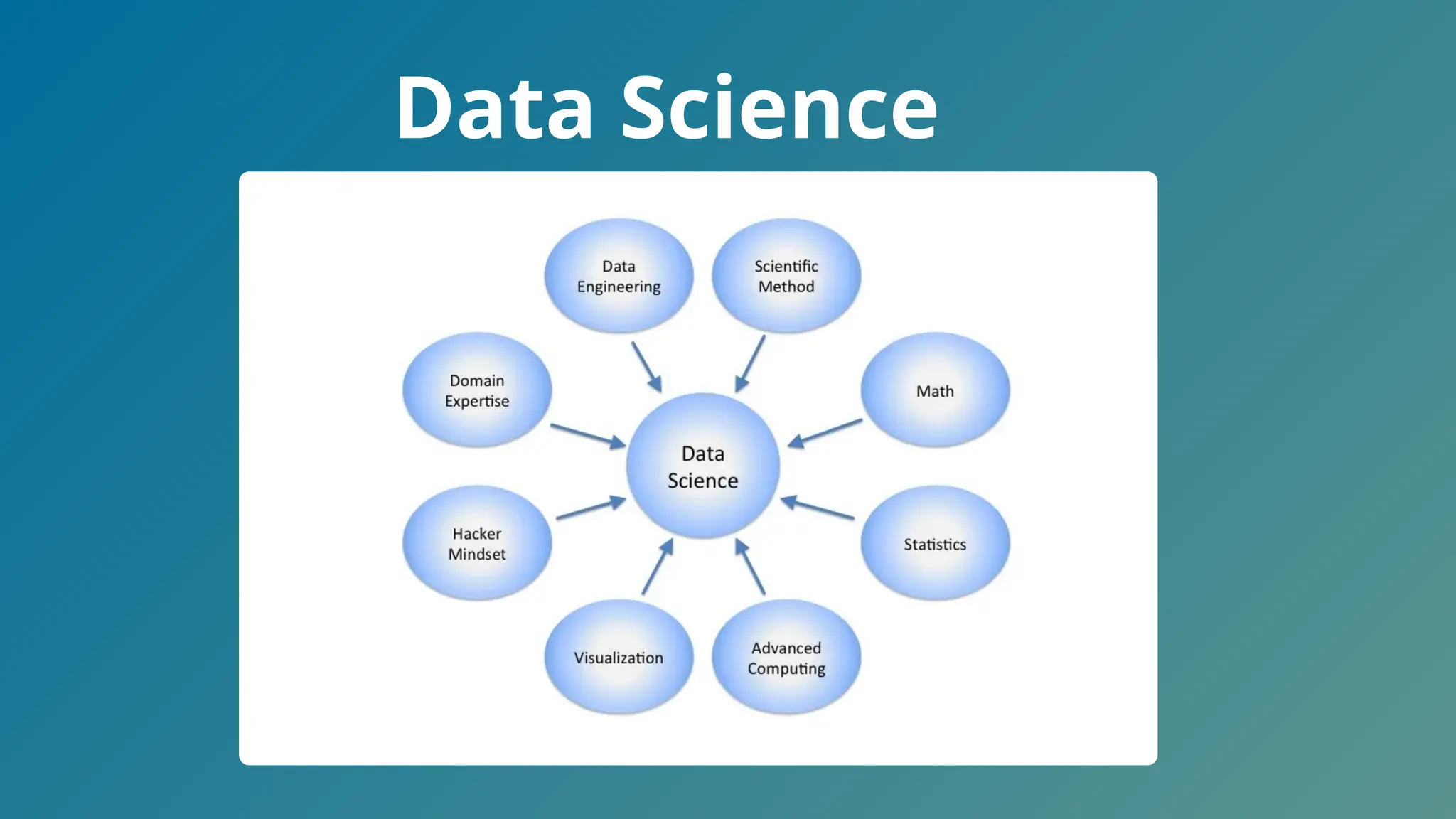
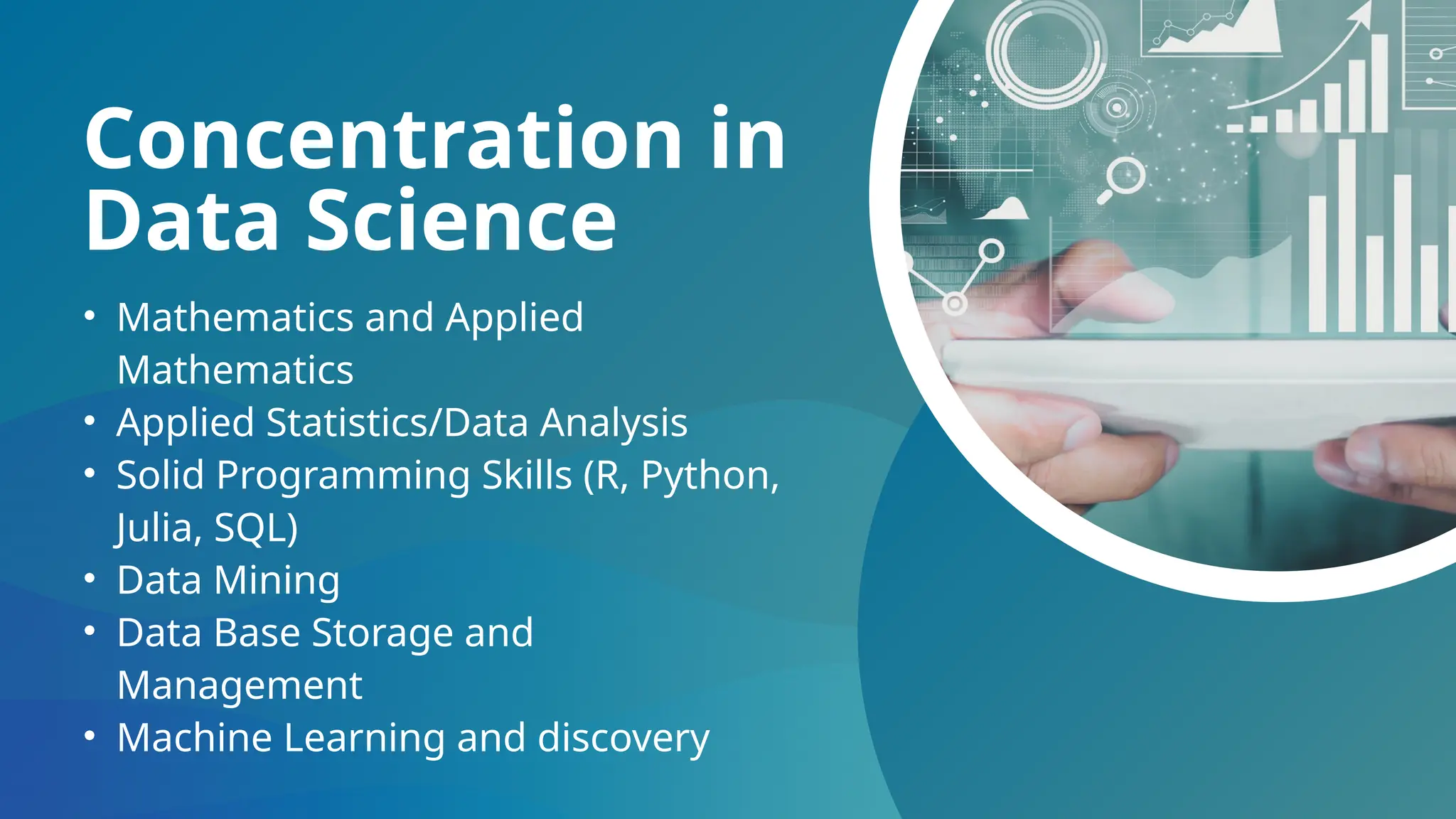
The document provides an overview of data science, describing it as the process of transforming raw data into valuable insights through statistics, coding, and machine learning. It emphasizes the importance of data scientists in uncovering trends and patterns within big data to drive decision-making across various industries. Additionally, the document outlines the necessary skills and courses for pursuing a concentration in data science.