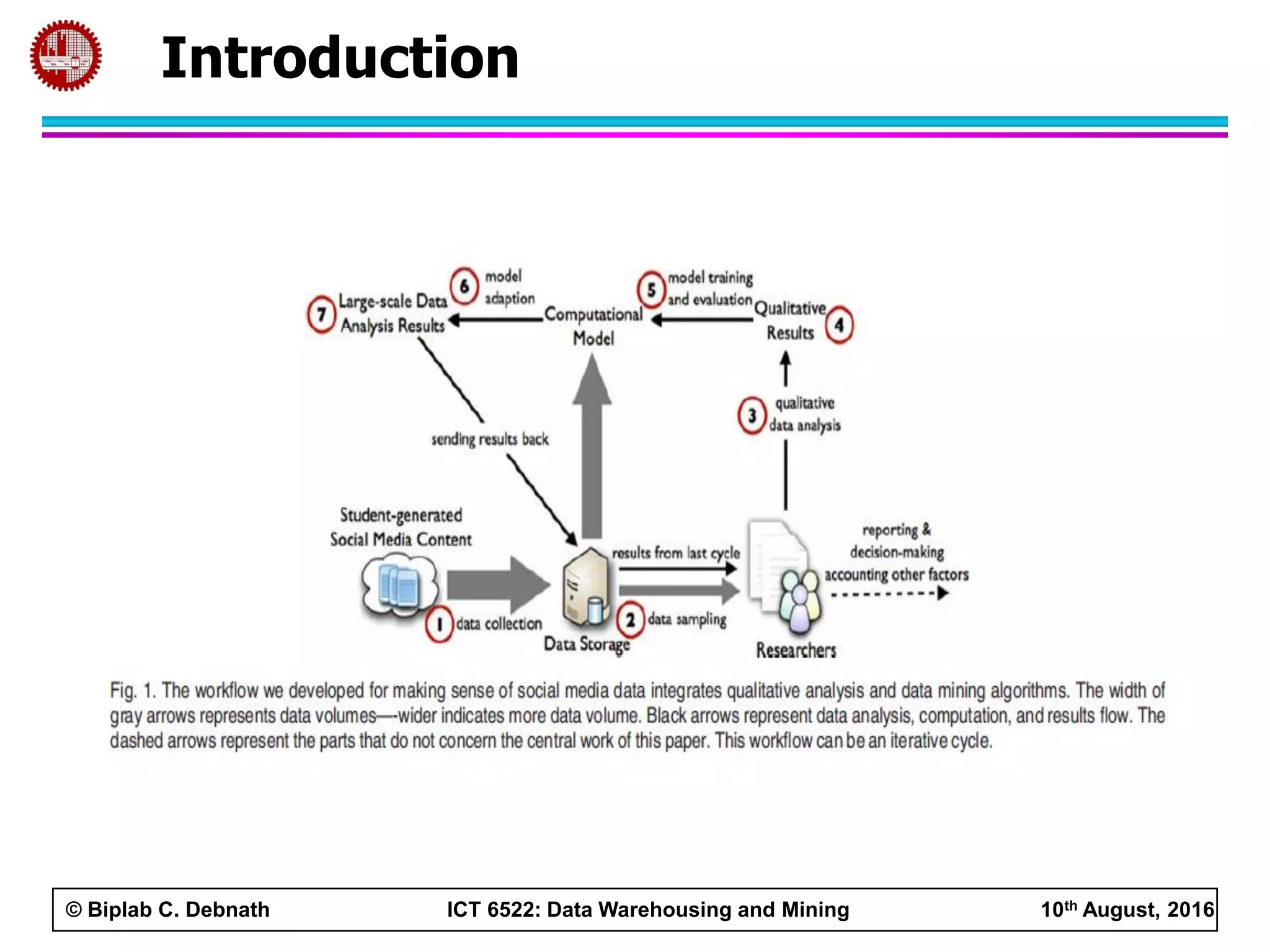
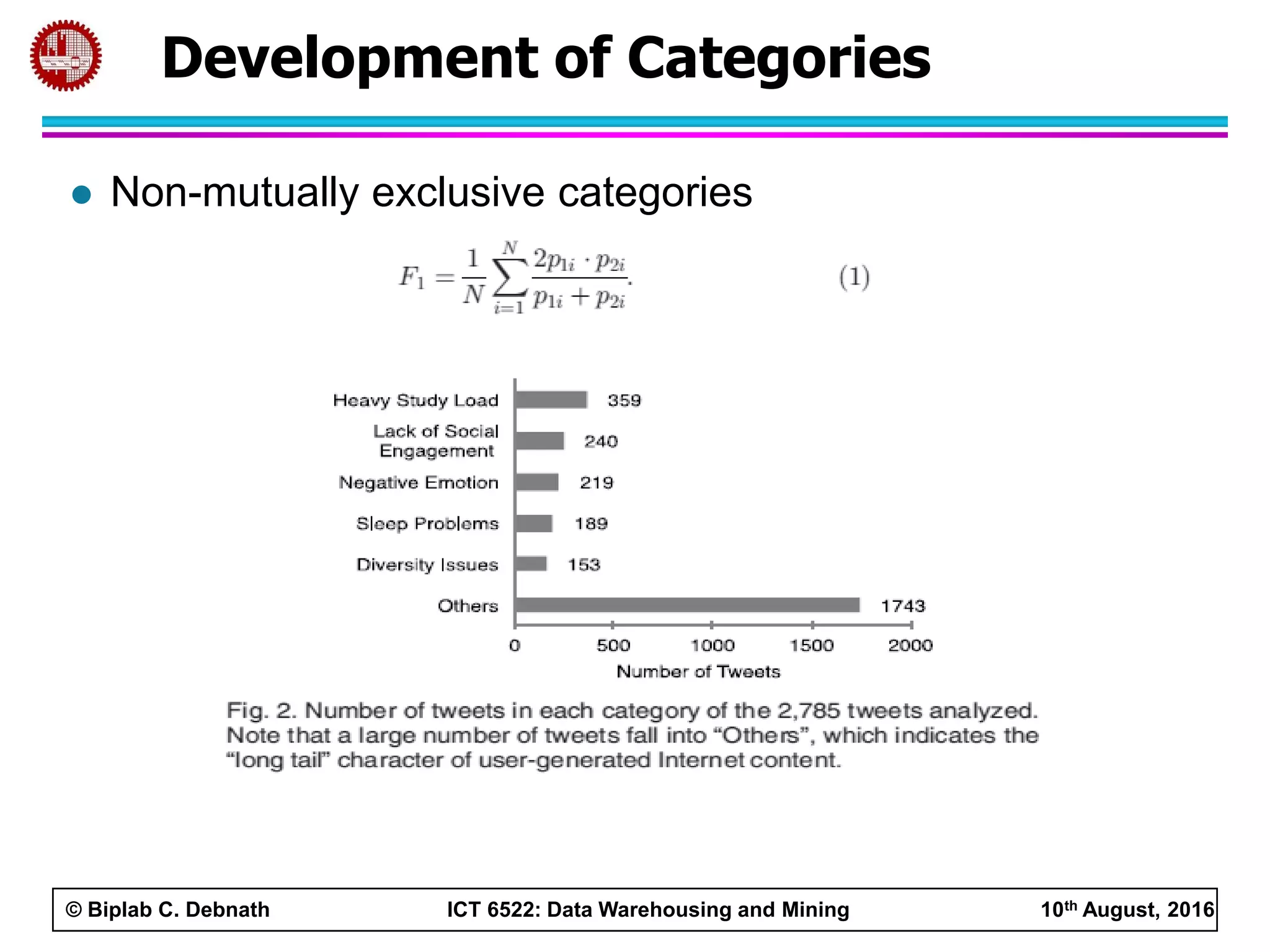
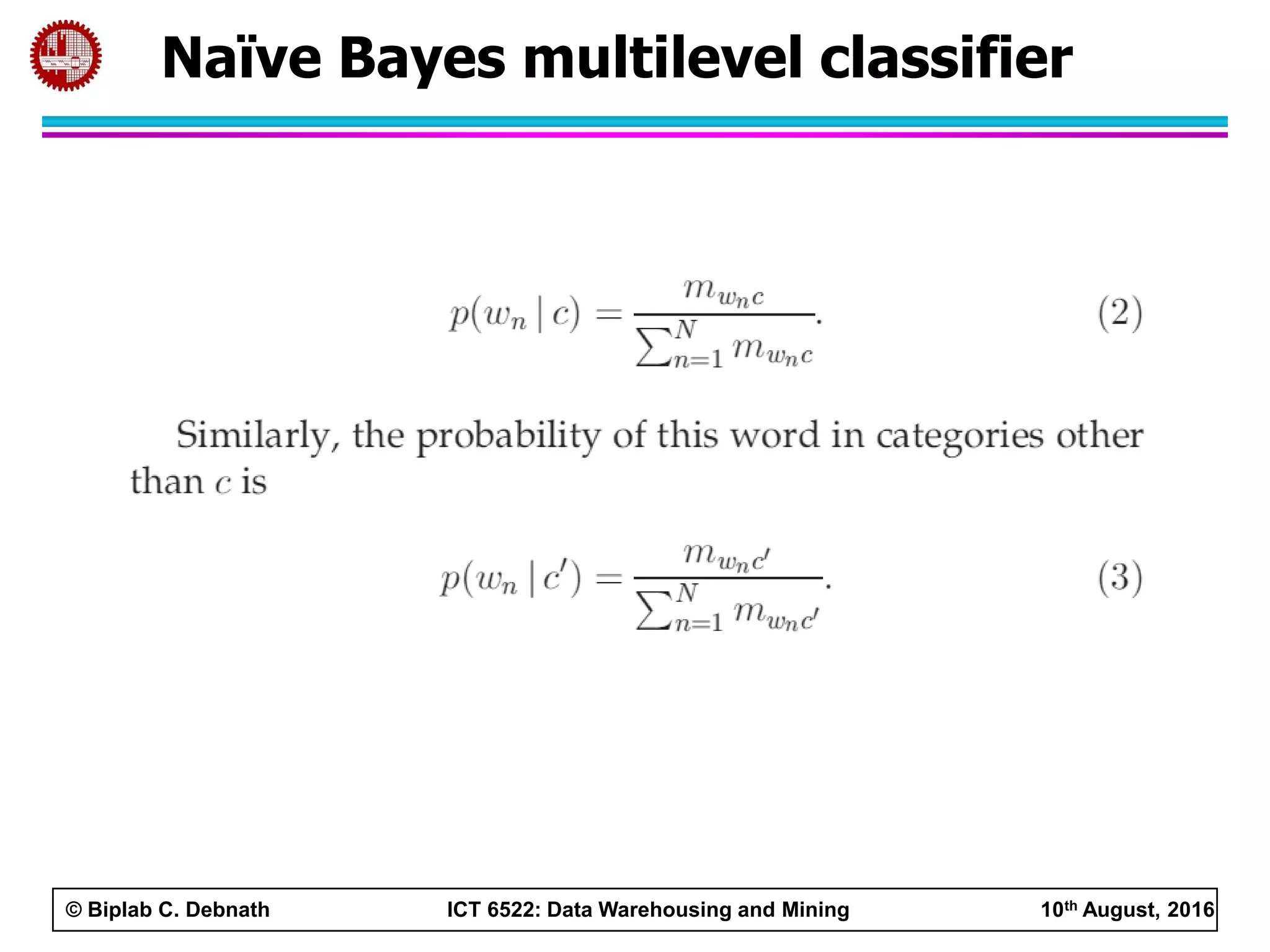
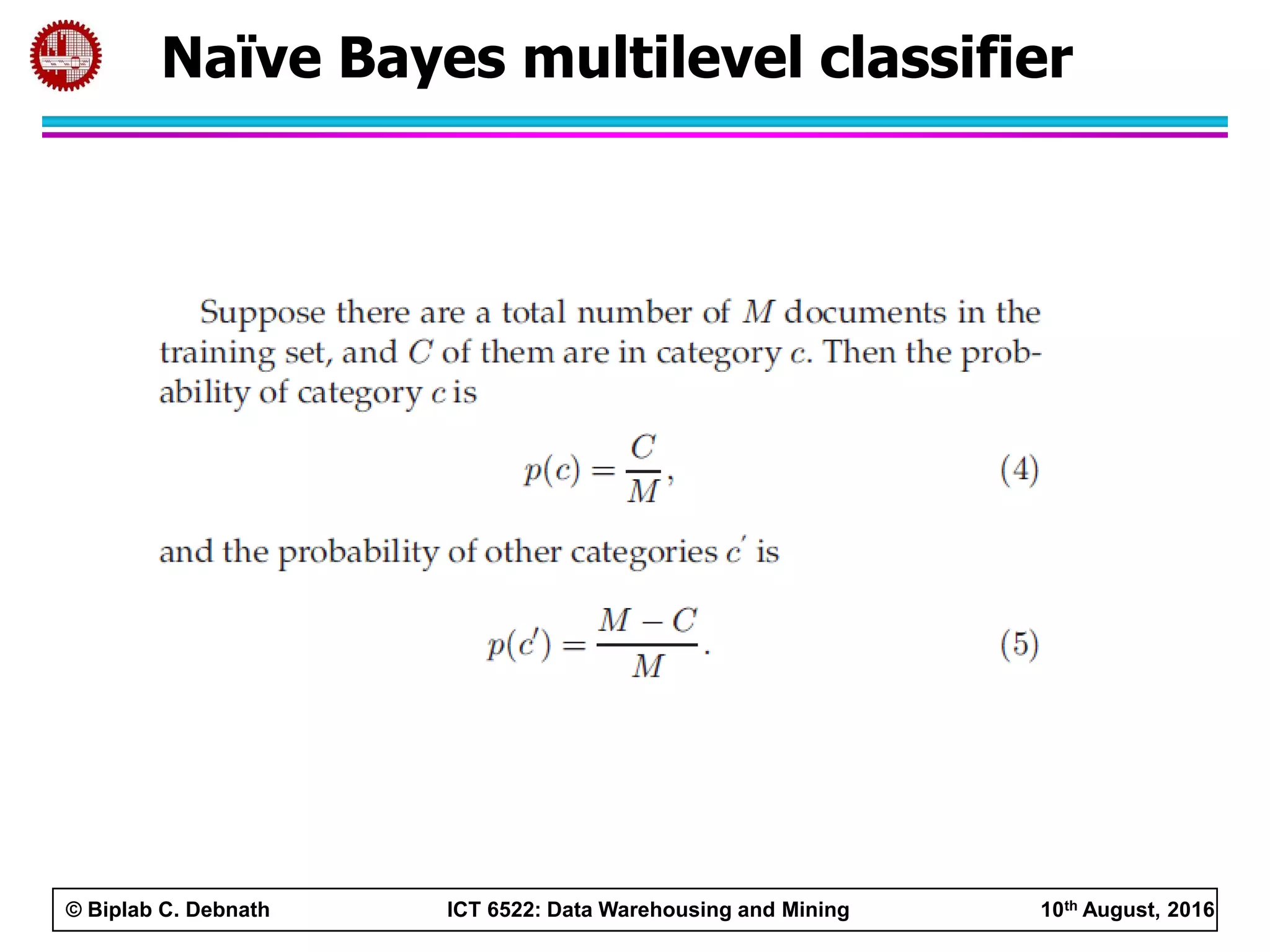
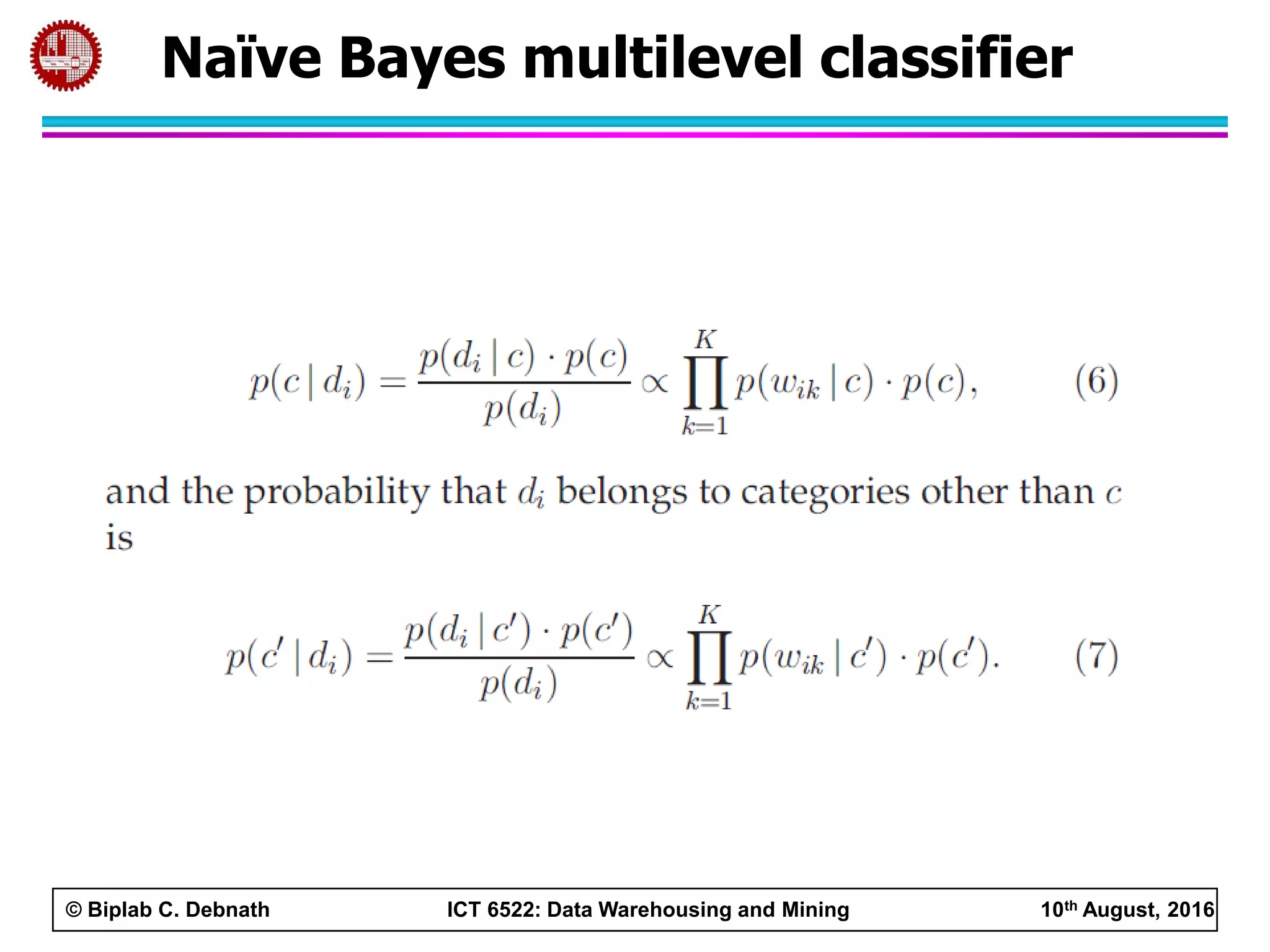
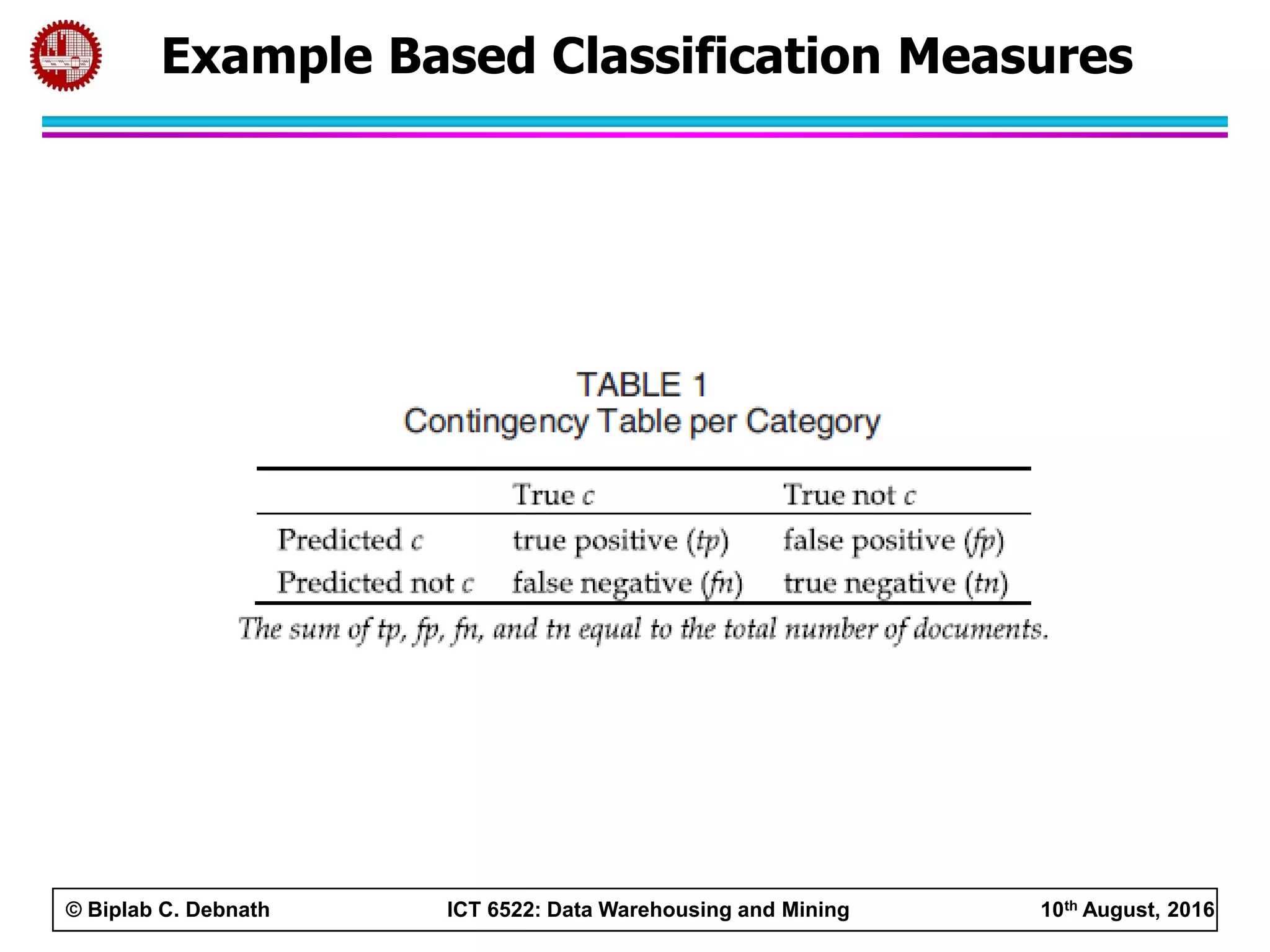
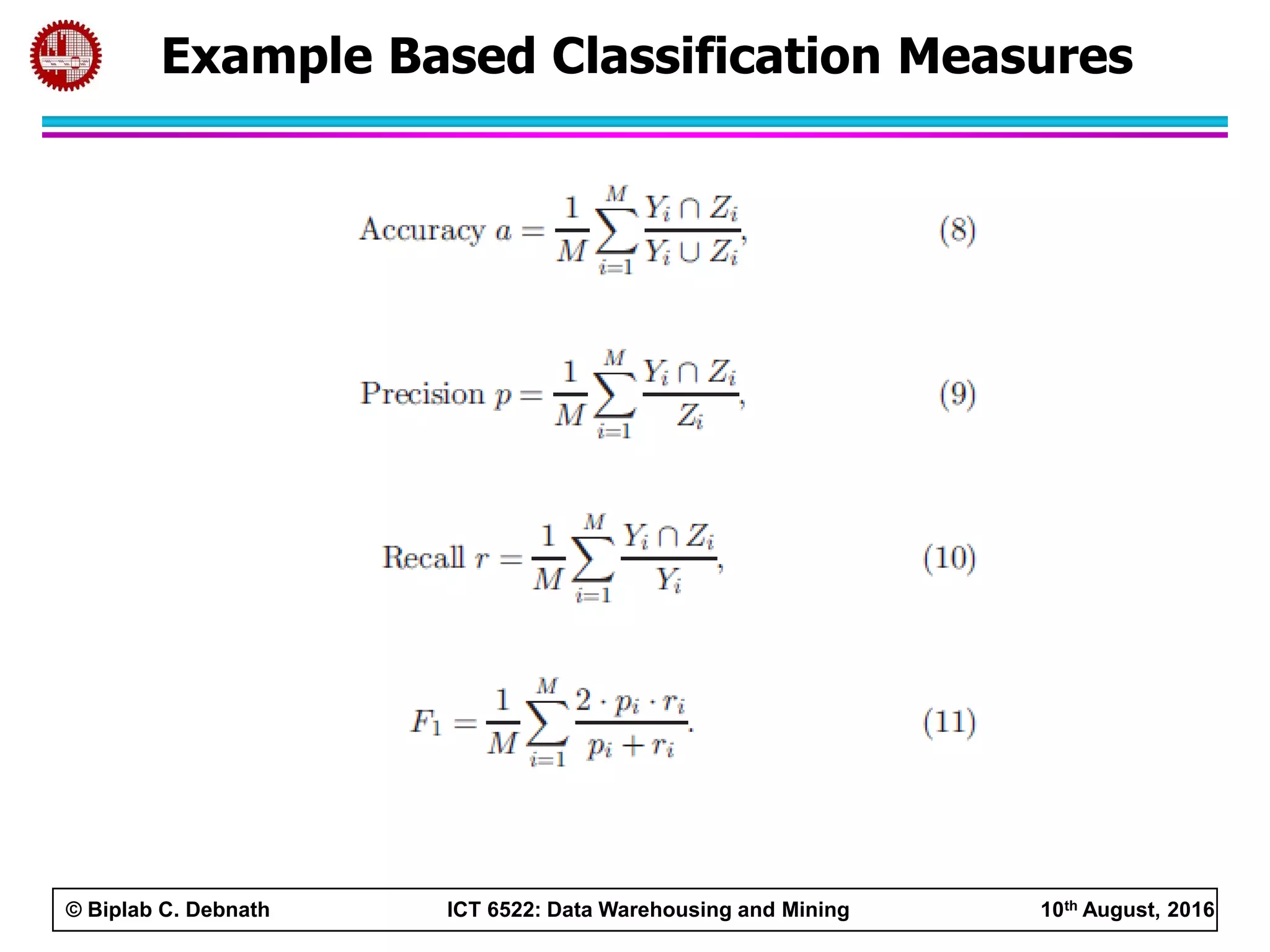
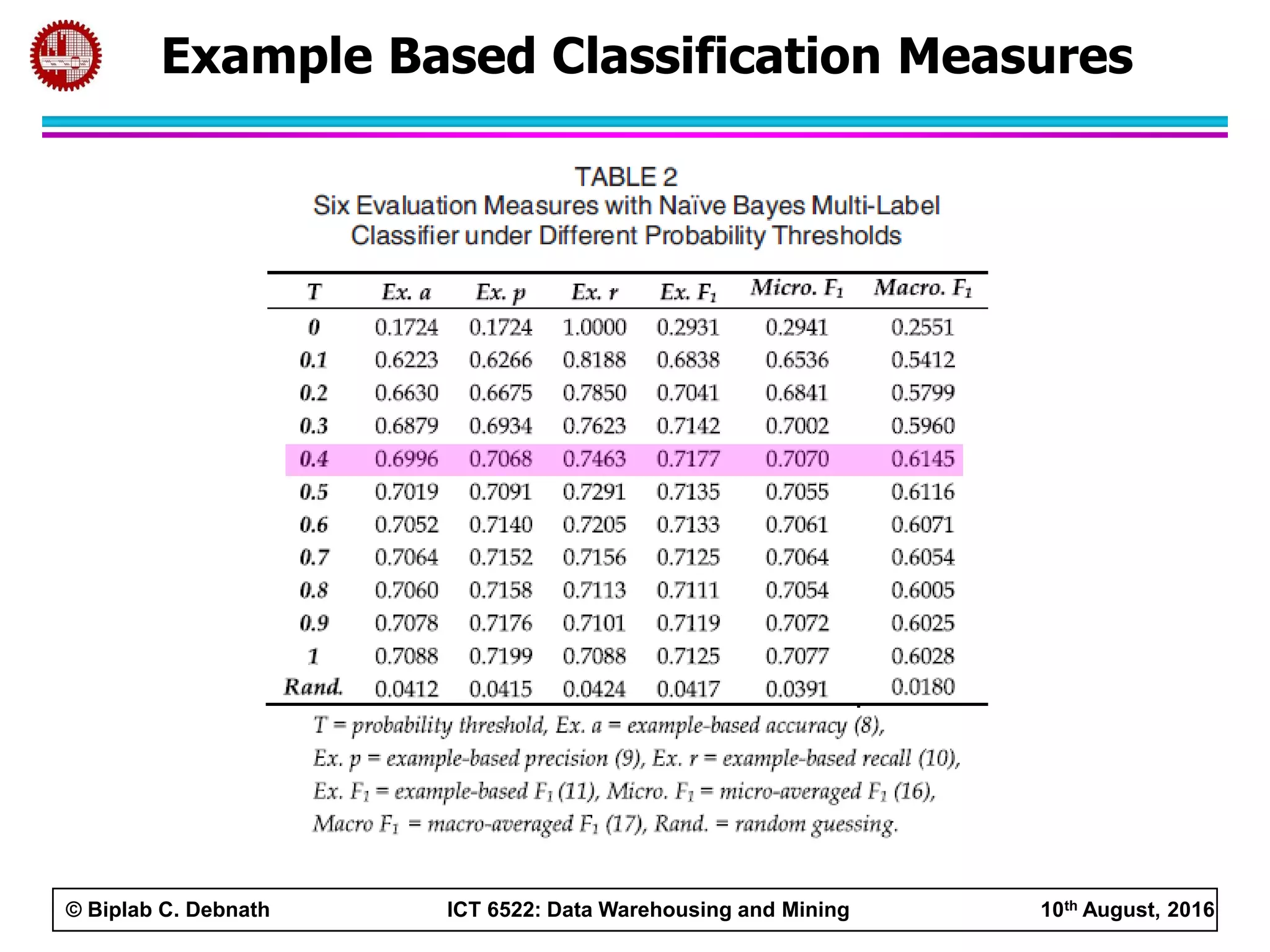
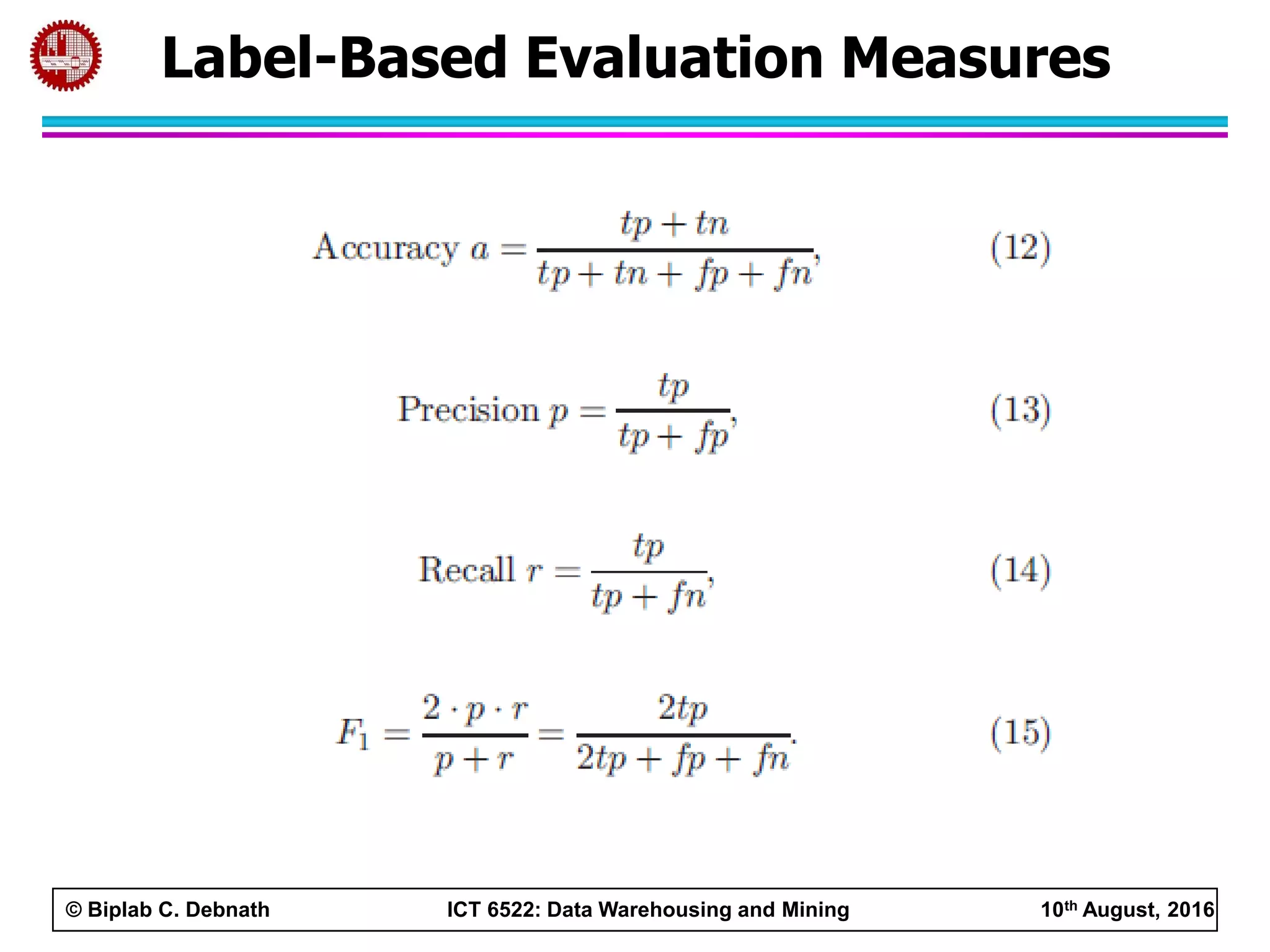
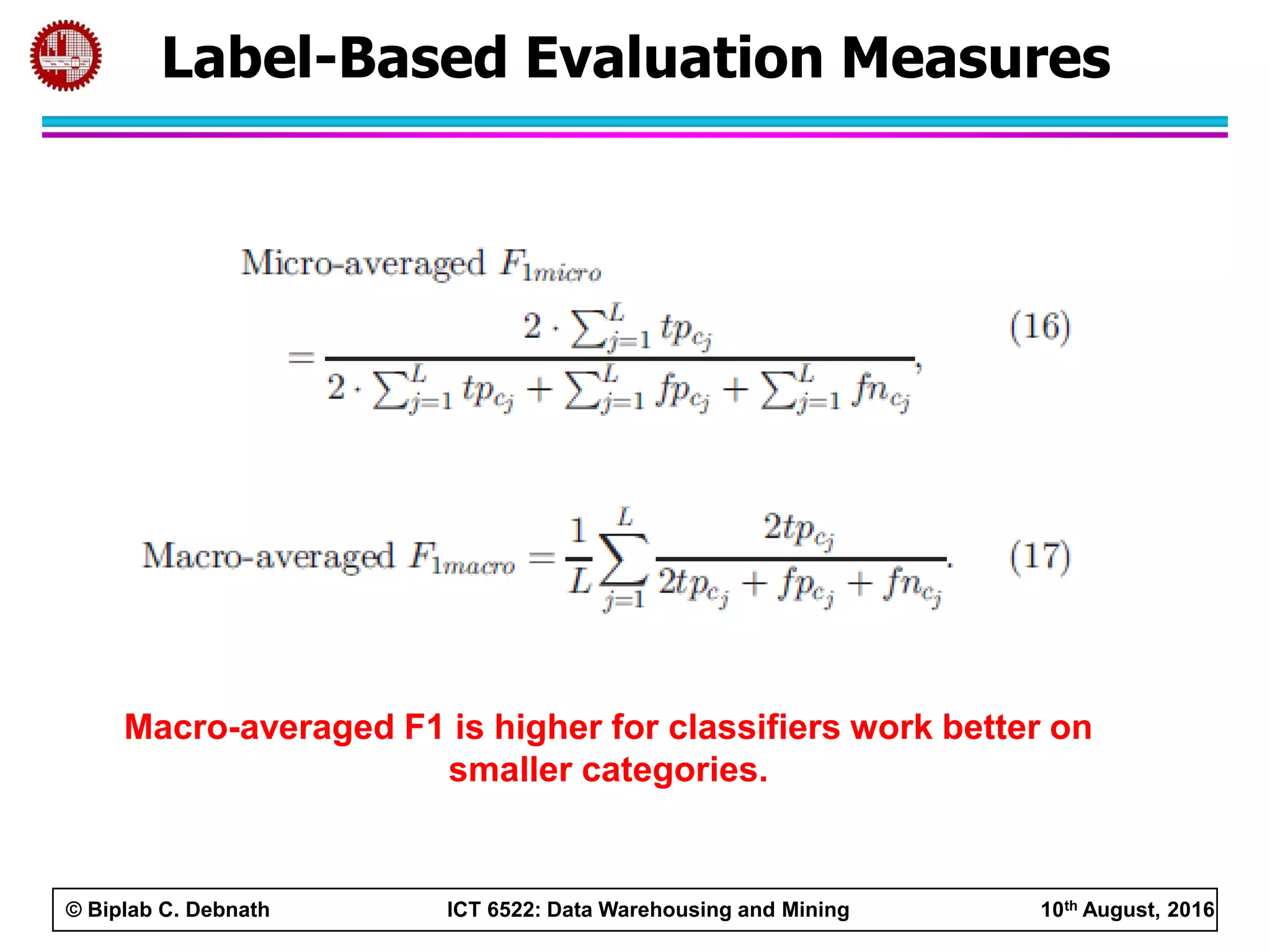
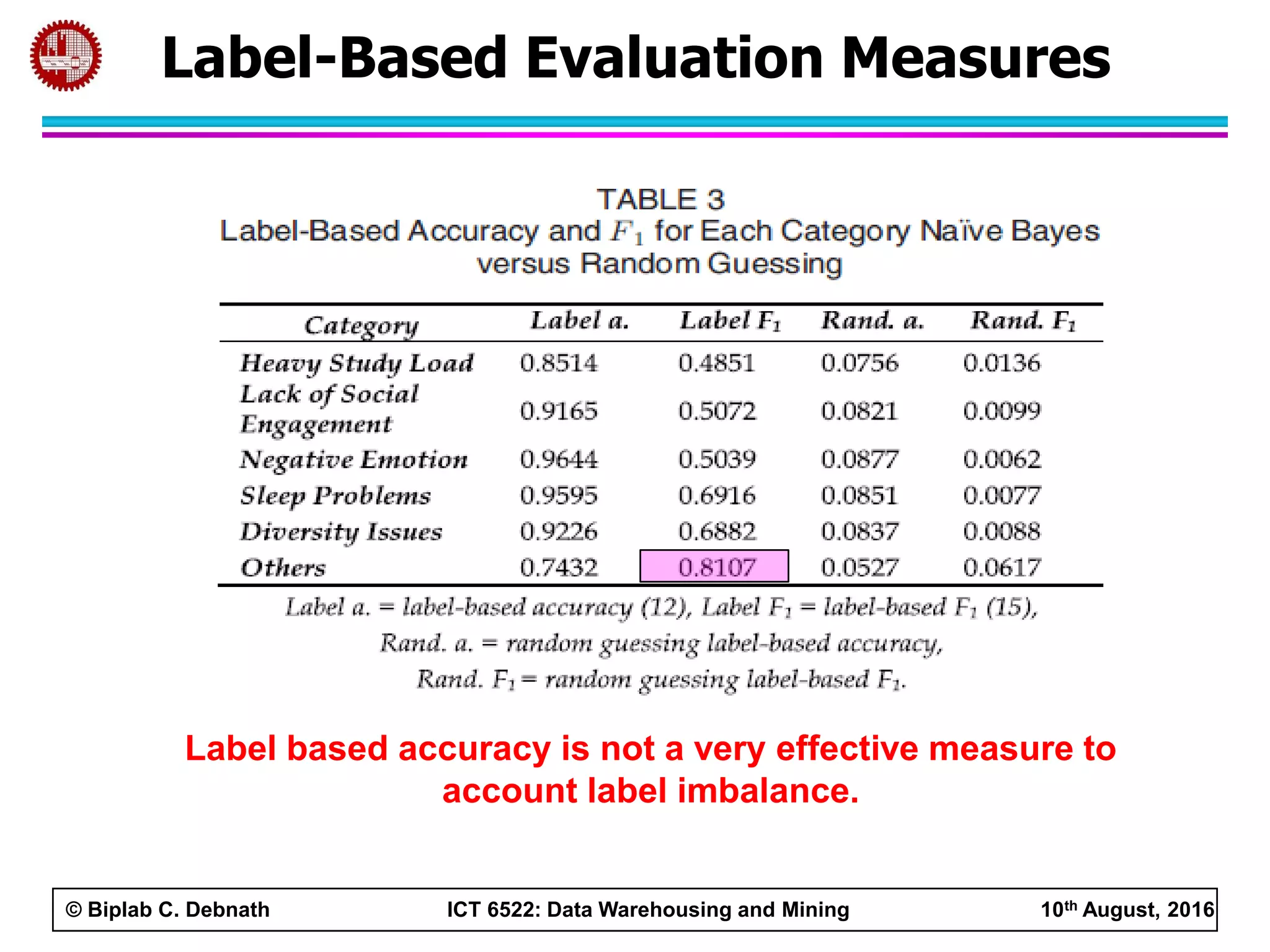
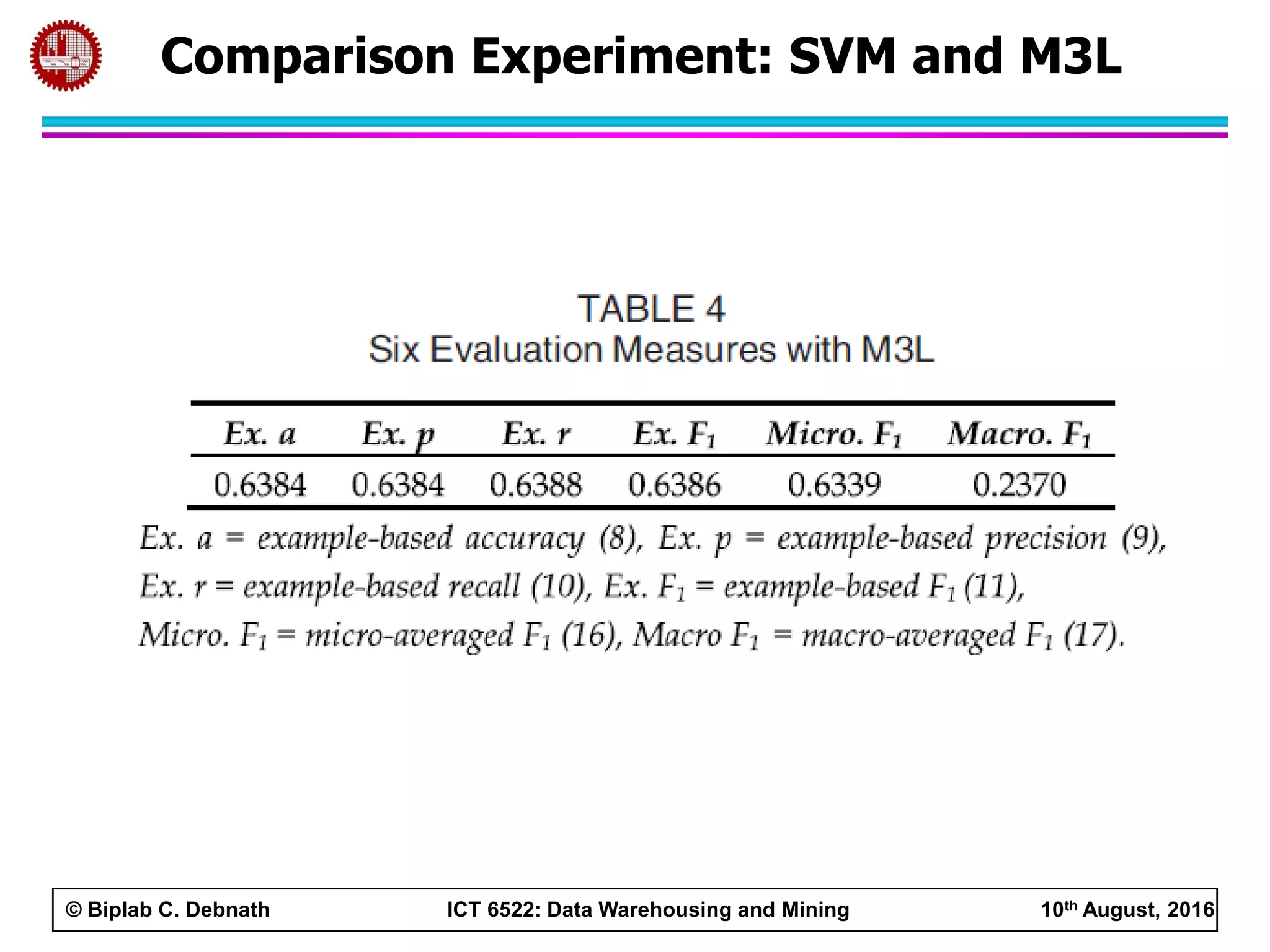
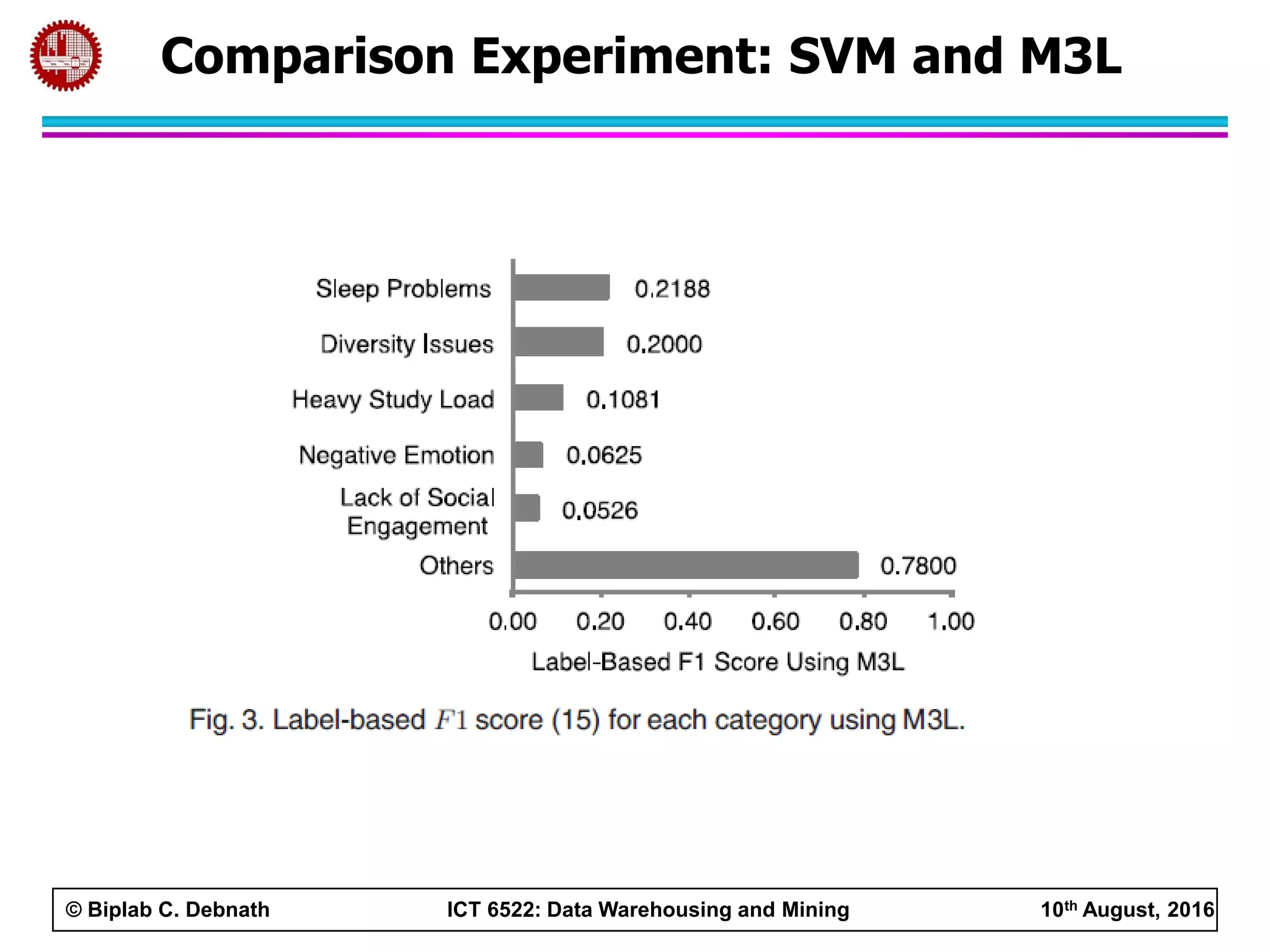
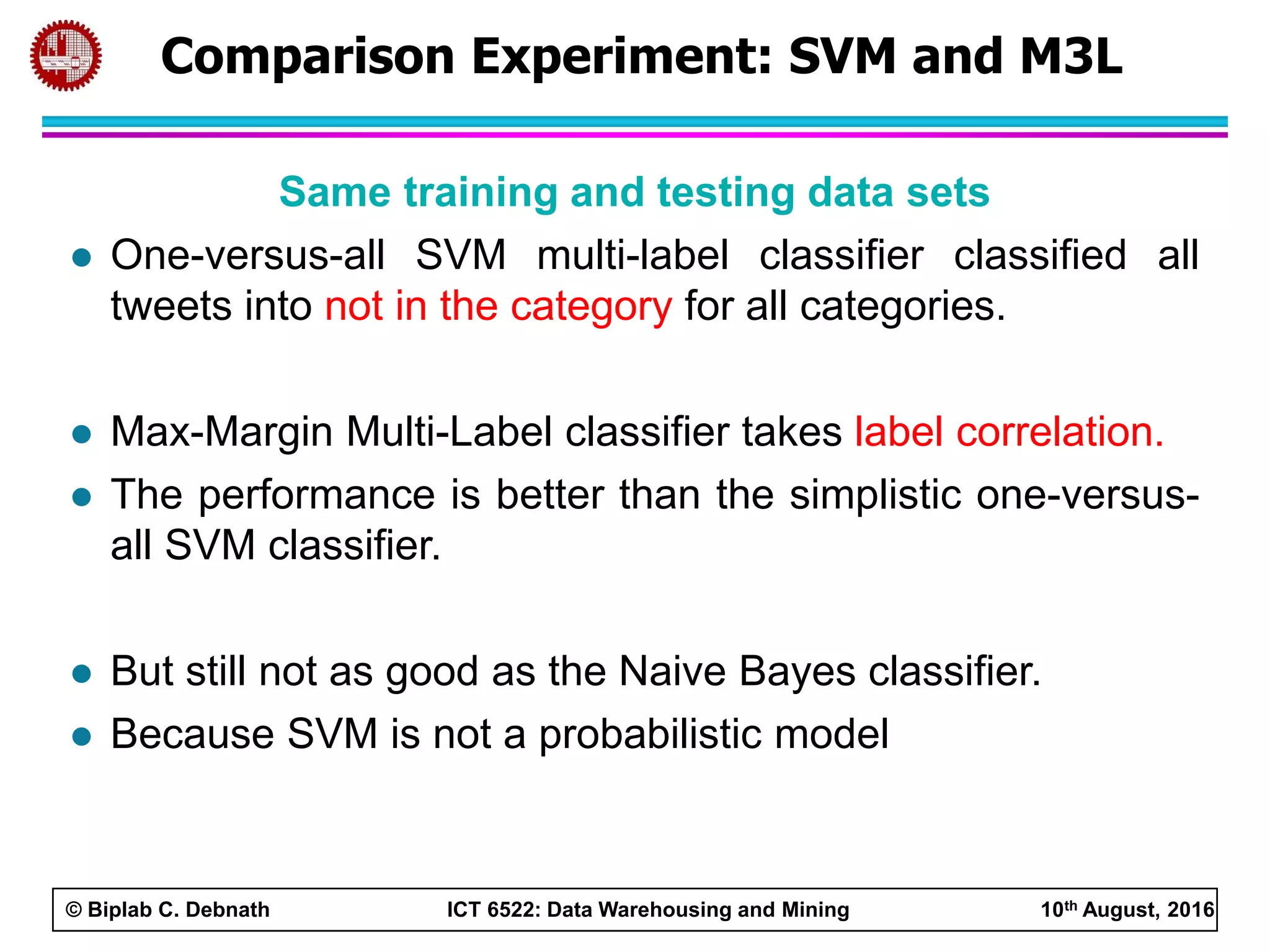
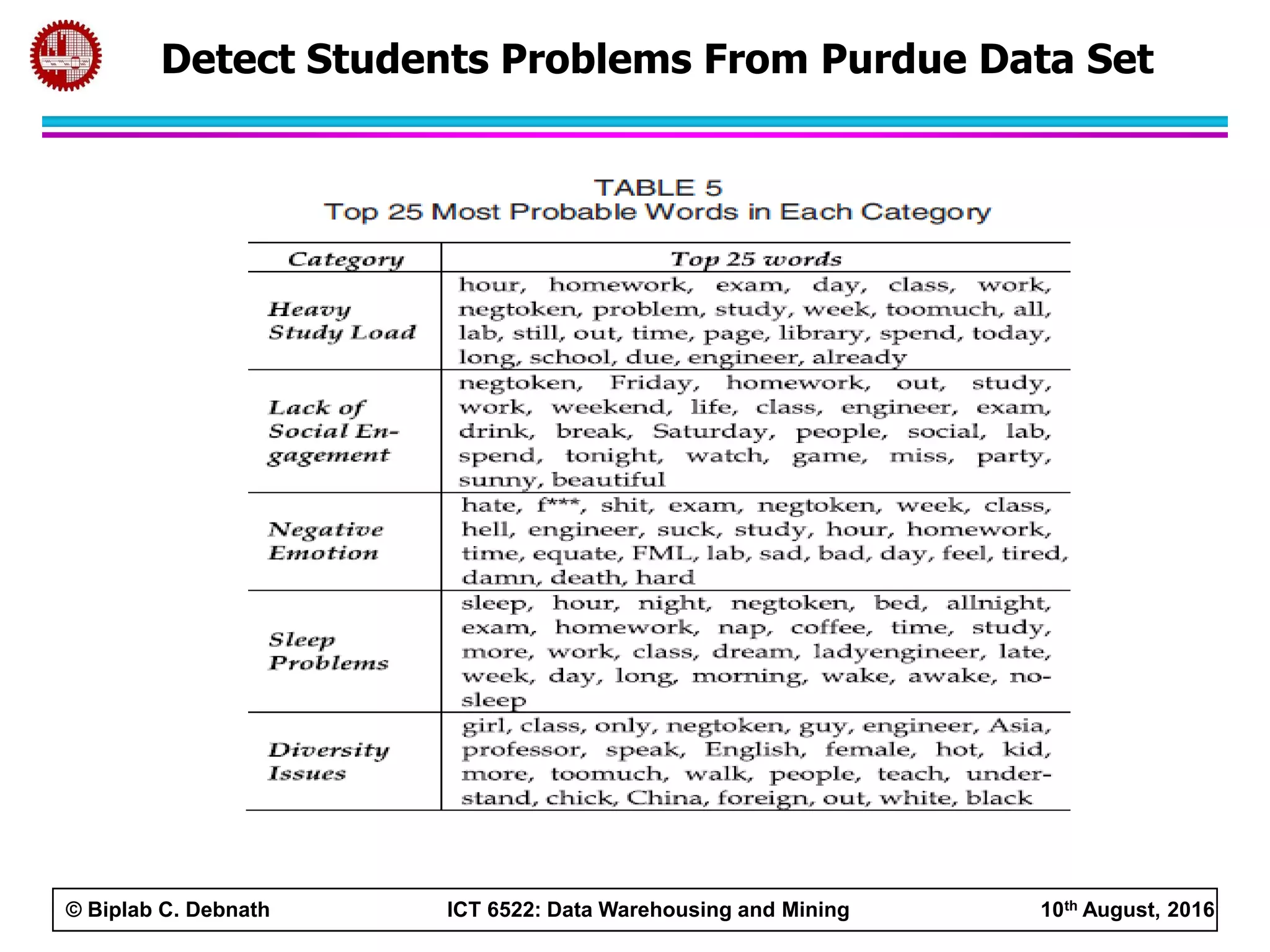
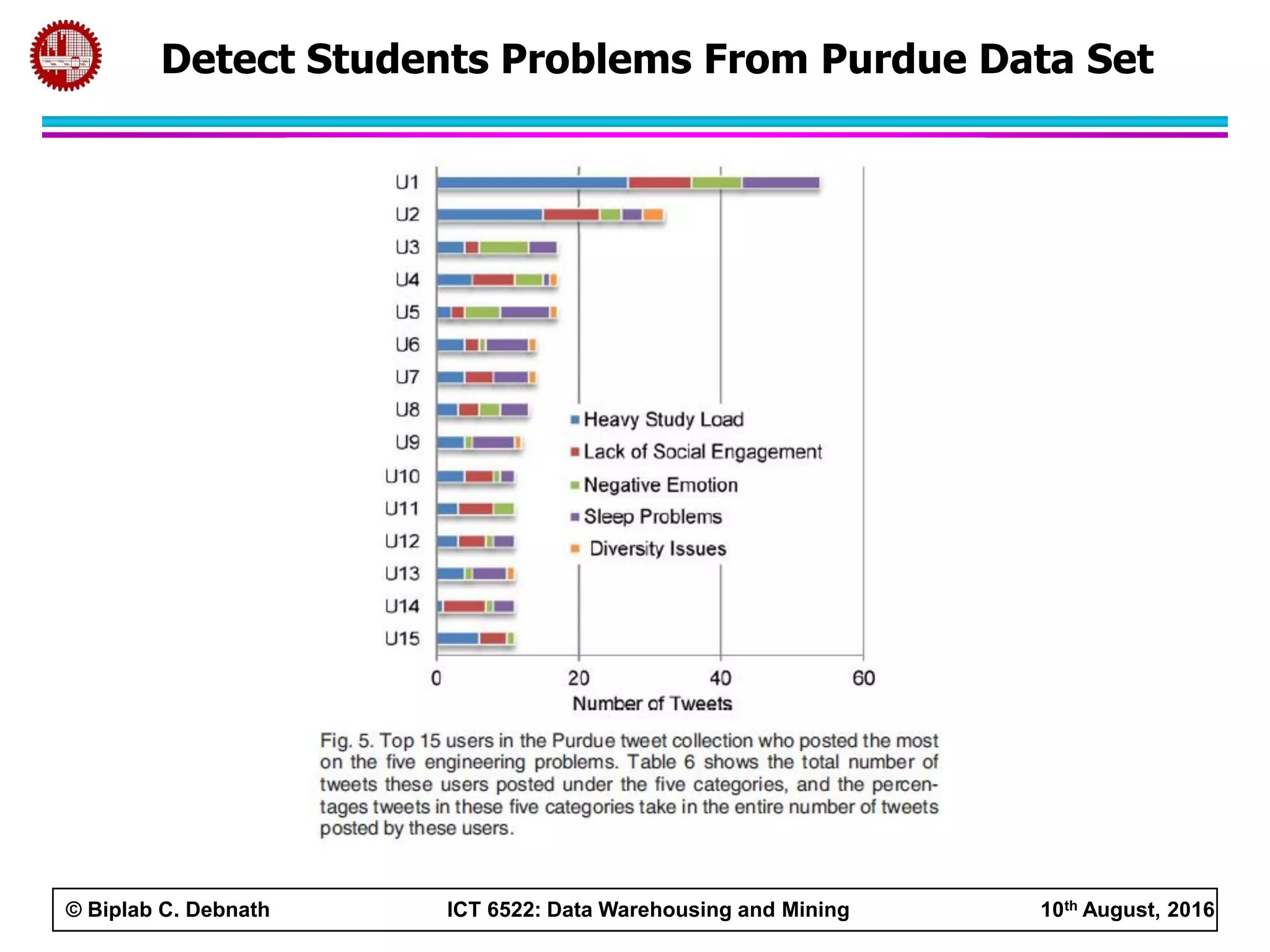
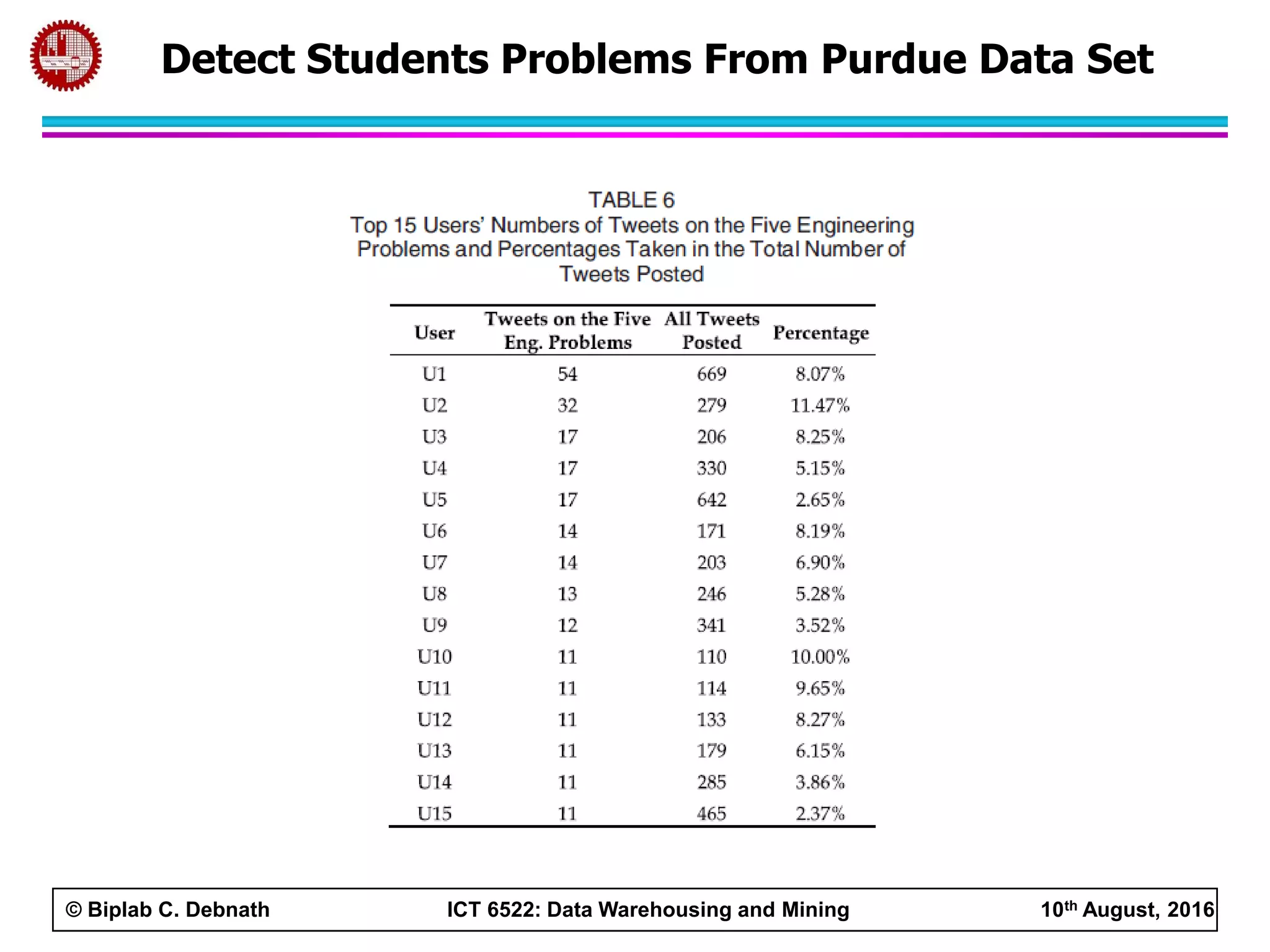
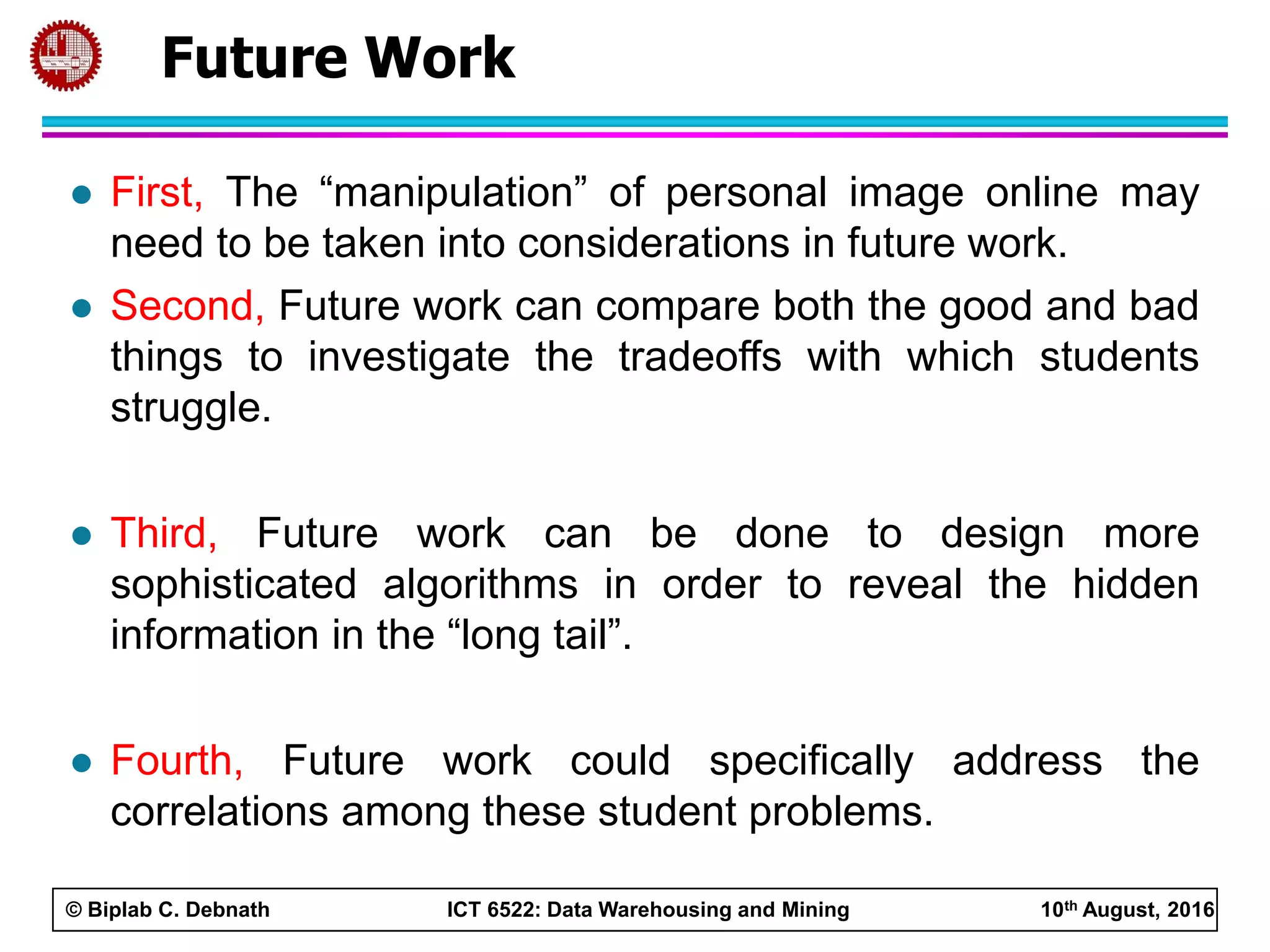
This document summarizes research on mining social media data to understand engineering students' learning experiences. The researchers collected tweets with hashtags about engineering problems to qualitatively analyze common challenges and quantitatively classify them using a Naive Bayes model. Key findings include engineering students struggling with heavy study loads, which can negatively impact social, sleep, and mental health. The classifier developed could help detect at-risk students by monitoring social media posts.