The document summarizes key events leading up to and during World War II:
1) Germany signed the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact with the Soviet Union in 1939 to divide Eastern Europe between them, allowing Germany to invade Poland and starting World War II.
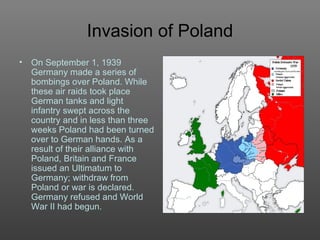
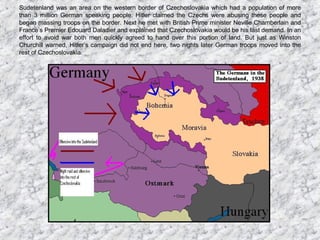
2) Germany continued expanding by taking the Sudetenland from Czechoslovakia against British and French appeasement efforts. Germany then occupied the rest of Czechoslovakia.
3) Germany then invaded France through the Ardennes region, trapping Allied soldiers in Dunkirk and leading to the Fall of France in 1940. Germany began bombing Britain that summer.