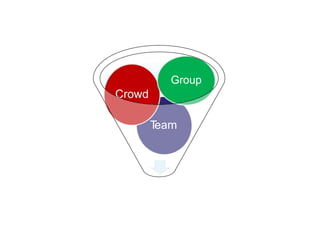
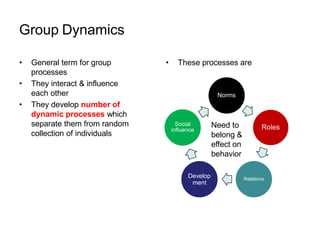
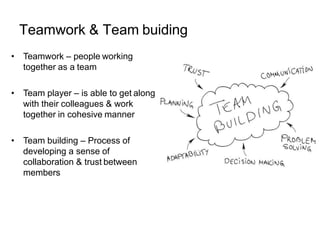
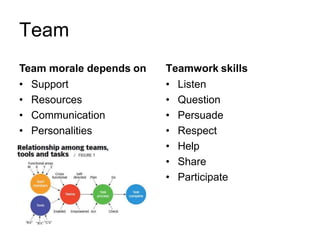
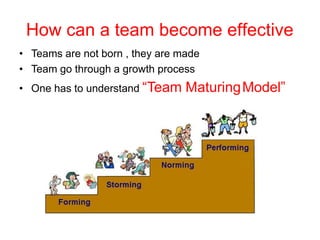
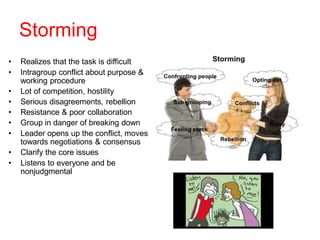
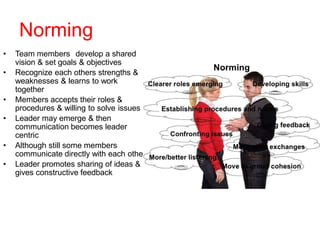
This document discusses group dynamics and team building. It defines the differences between a crowd, group, and team. A team is a collection of people with complementary abilities working together toward common goals. Effective teamwork requires skills like listening, questioning, persuading, and respecting others. Teams go through stages of forming, storming, norming, and performing as they mature. Key aspects of effective teams include appropriate leadership, clear goals, defined roles, and periodic evaluation. The role of the leader is to help all members feel included and bring out the strengths of each individual. Managing group dynamics through techniques like active listening and consensus building helps discussions flow smoothly. Working as a team leads to greater productivity, creativity, and higher quality outcomes