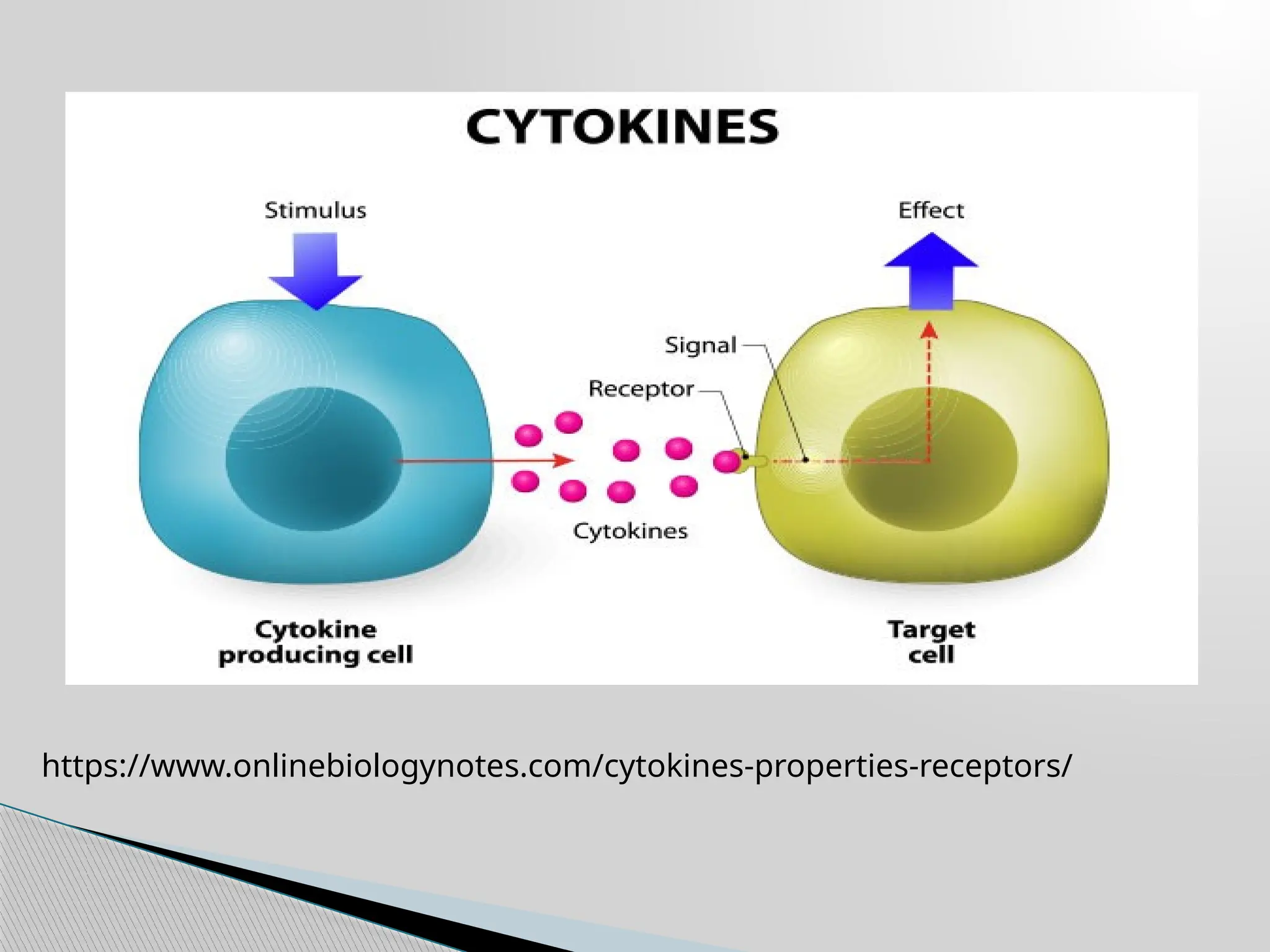
The document presents an assignment focused on cytokines, detailing their types, structures, and biological functions within the immune system. It categorizes cytokines into several types, such as interleukins and interferons, and outlines their roles in regulating immune responses and associated disorders. The conclusion emphasizes the therapeutic potential of cytokines in treating various diseases, particularly cancer and autoimmune disorders.
![VIVEKANANDHA
MM.Sowmiya
II B.SC. Biotechnology
PG & Research Department of Biotechnology
Vivekanandha Arts and Science College For Women
Sankari
Assignment on “ cytokine types and structure and fuction ”
Subject: Immune system and immunotechnology
ARTS & SCIENCE COLLEGE FOR WOMEN
[An ISO 9001:2015 Certified Institution]
(Affiliated to Periyar University, Salem
Recognised Under Section 2(f) &12(B) of the UGC Act, 1956)
Veerachipalayam, Sankari West (Post) – 637 303, Sankari Tk, Salem Dt., Tamil Nadu
PG & RESEARCH DEPARTMENT OF
BIOTECHNOLOGY](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cytokinemm-241019062909-b076fdef/75/CYTOKINE-TYPES-And-FUNCTION-IMMUNE-SYSTEM-And-IMMUNO-TECHNOLOGY-1-2048.jpg)