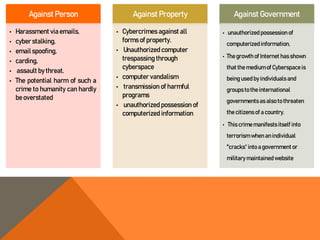
The document provides an overview of cyber crime including its history, evolution, categories, and common types. It discusses how cyber criminals have become more organized over time, moving from basic malware in the 1990s to sophisticated ransomware and banking malware today. The document also outlines three categories of cyber crimes: against persons, property, and government. It gives examples of specific cyber crimes like hacking, denial of service attacks, software piracy, and cyber terrorism. In conclusion, it notes that cyber crime continues to evolve as criminals work to stay ahead of law enforcement.