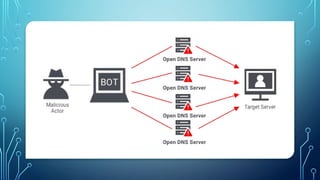
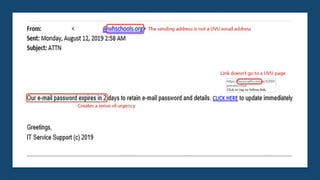
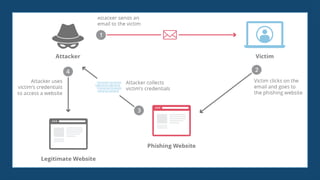
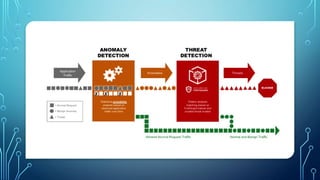
Cybersecurity fundamentals and ethical hacking are intertwined disciplines focused on protecting digital assets. Here's a breakdown:
Cybersecurity Fundamentals:
Cybersecurity is the practice of protecting systems, networks, and programs from digital attacks. These attacks are often aimed at accessing, changing, or destroying sensitive information; extorting money from users; or interrupting normal business processes. Key fundamental concepts include:
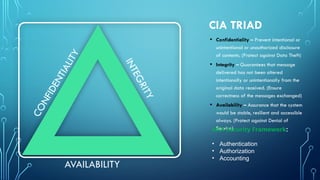
* Confidentiality: Ensuring that information is accessible only to authorized individuals. This is achieved through encryption, access controls, and data masking.
* Integrity: Maintaining the accuracy and completeness of data. This involves preventing unauthorized modifications through hashing, digital signatures, and version control.
* Availability: Guaranteeing that authorized users have reliable access to information and systems when needed. This is supported by redundancy, failover systems, and disaster recovery plans.
* Risk Management: Identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential threats and vulnerabilities. This involves risk assessments, vulnerability scanning, and security audits.
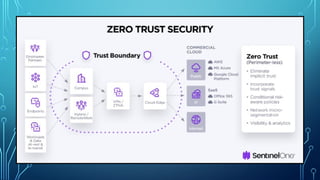
* Network Security: Protecting computer networks from unauthorized access and attacks. This includes firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and virtual private networks (VPNs).
* Endpoint Security: Securing individual devices, such as laptops, smartphones, and servers, from malware and other threats. This involves antivirus software, endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools, and device encryption.
* Security Awareness: Educating users about cybersecurity best practices and potential threats. This is crucial for preventing social engineering attacks and other human errors.
* Cryptography: The practice and study of techniques for secure communication in the presence of third parties called adversaries. This includes encryption, decryption, hashing, and digital signatures.
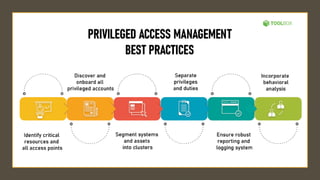
* Access Control: Mechanisms that determine who is allowed to access what resources. This includes authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA).
Ethical Hacking:
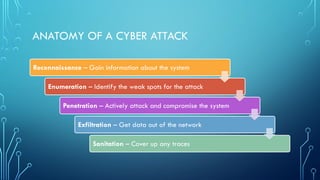
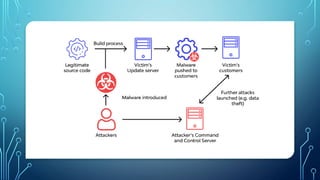
Ethical hacking, also known as penetration testing, is the practice of using hacking techniques to identify vulnerabilities in systems and networks with the permission of the owner. Ethical hackers simulate real-world attacks to uncover weaknesses before malicious actors can exploit them. Key aspects include:
* Permission: Ethical hacking is conducted with the explicit consent of the system owner. This distinguishes it from illegal hacking.
* Scope: The scope of the ethical hacking engagement is clearly defined, outlining the systems and networks to be tested.
* Reporting: Ethical hackers provide detailed reports of their findings, including vulnerabilities, potential impact, and remediation recommendations.
* Methodologies: Ethical hackers use a variety of tools and techniques, including:
* Vulnerability scanning: Automated tools to identify known vulnerabili