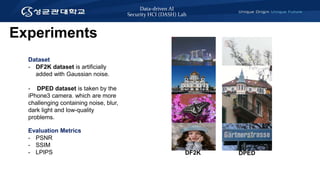
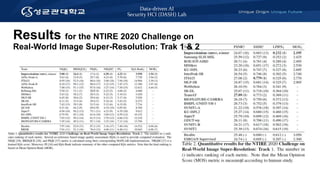
The document discusses a realistic degradation framework for super-resolution (ReaLSR) developed to improve image quality by addressing issues related to traditional bicubic down-sampling methods, which often result in blurry images and lost frequency details. ReaLSR utilizes kernel estimation and noise injection to generate more accurate low-resolution images that preserve domain attributes, ultimately enhancing performance in super-resolution tasks. The framework has shown success in evaluations, winning the NTIRE 2020 challenge for real-world image super-resolution.