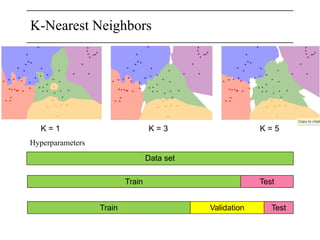
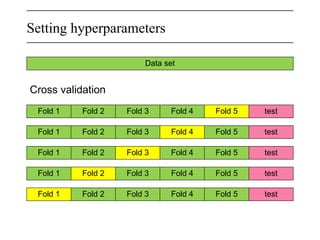
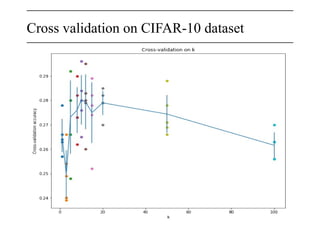
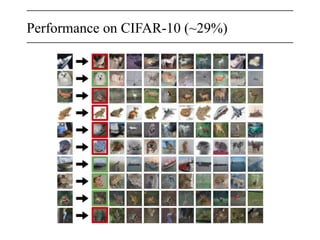
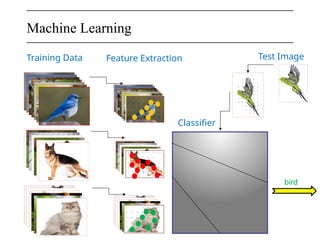
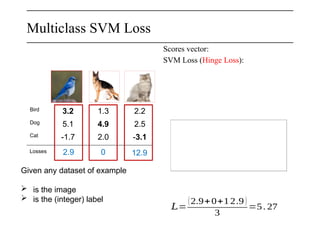
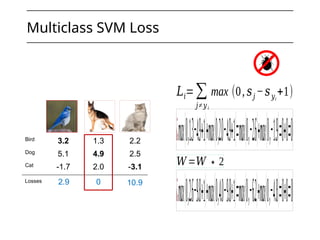
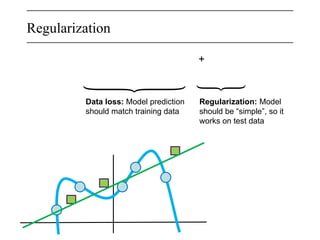
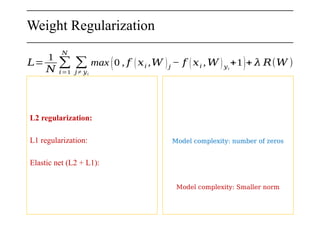
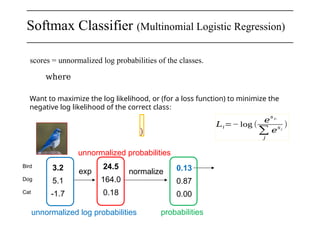
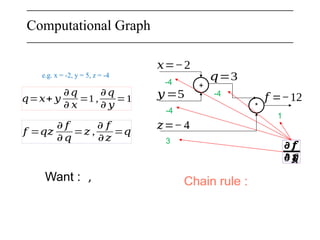
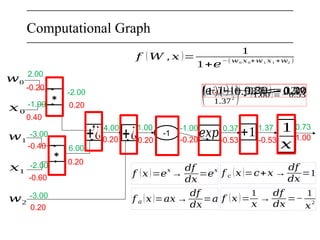
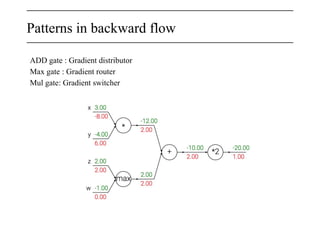
The document discusses neural networks, deep learning, and challenges related to them, with a focus on the CIFAR-10 dataset, which includes 50,000 training images. It details various classification techniques such as linear classifiers and softmax classifiers, and it emphasizes the importance of regularization and loss functions in machine learning. Additionally, it mentions the use of computational graphs and optimization methods for training neural networks.







![Linear Classification
[ 32 x 32 x 3 ] (3072 numbers in total)
10 numbers
Indicating class scores
¿𝑾 𝒙
Parametric approach
10
x
3072
3072
x
1
10
x
1
0.2 -0.5 0.1 2.0
1.5 1.3 2.1 0.0
0.0 0.25 0.2 -0.3
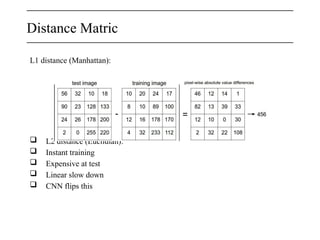
56
231
24
2
+
1.1
3.2
-1.2
-96.8
437.9
60.75
Bird score
Dog score
Cat score
𝑊
𝑥𝑖
𝑏 𝑓 (𝑥𝑖 ;𝑊 ,𝑏)
Stress pixels into single column
𝒇 (𝒙,𝑾 ) + b
56 231
24 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cvpr01-250121171727-8cab7022/85/CVPR_01-On-Image-Processing-and-application-of-various-alogorithms-17-320.jpg)


![Numeric Gradient
Follow the slope
[
0.34
-1.11
0.78
0.12
0.55
2.81
-3.1
-1.5
0.33
… ]
[
0.34
-1.11
0.78
0.12
0.55
2.81
-3.1
-1.5
0.33
… ]
[
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
… ]
Current W W + h Gradient dW
+ 0.0001
+ 0.0001
loss 1.25347 loss 1.25322
?
?
-2.5
loss 1.25353
0.6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cvpr01-250121171727-8cab7022/85/CVPR_01-On-Image-Processing-and-application-of-various-alogorithms-25-320.jpg)

![Vectorized example
∈ℝ𝑛
∈ℝ𝑛×𝑛
*
𝑊 =
[ 0 .1 0.5
− 0.3 0.8 ]
𝑥=[0 .2
0.4 ]
𝑞=𝑊.𝑥=
[𝑊1,1𝑥1+¿⋯ +𝑊1,𝑛𝑥𝑛
⋮ ¿
⋮¿𝑊𝑛,1𝑥1+¿⋯¿+𝑊𝑛,𝑛𝑥𝑛¿]
L2
[0 .2 2
0. 26 ] 0.116
1.00
[0 . 4 4
0. 52 ]
𝜕 𝑓
𝜕𝑞𝑖
=2𝑞𝑖
𝑓 (𝑞)
𝑞
𝜕𝑞𝑘
𝜕𝑊𝑖, 𝑗
=1𝑘=𝑖 𝑥 𝑗
𝑓 (𝑞)=‖𝑞‖
2
=𝑞1
2
+…+𝑞𝑛
2
[0 . 088 0. 104
0. 176 0. 208]
𝜕𝑞𝑘
𝜕 𝑥𝑖
=𝑊 𝑘,𝑖
[−0. 1 12
0.636 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cvpr01-250121171727-8cab7022/85/CVPR_01-On-Image-Processing-and-application-of-various-alogorithms-30-320.jpg)