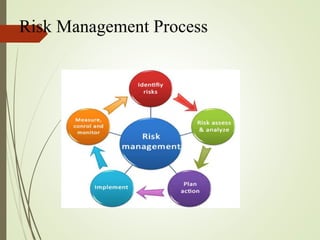
Risk management is a logical and systematic method to identify, analyze, treat and monitor risks involved in any customs activity or process. It helps managers make best use of limited resources by focusing on higher risk areas. The main components of risk are probability, consequence, and perception. The risk management process involves identifying, analyzing, evaluating and prioritizing risks, then treating risks through measures like risk profiling and targeting systems to develop selection criteria for inspecting shipments. Regular monitoring and review helps ensure risk profiles and criteria remain effective.