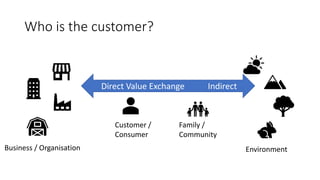
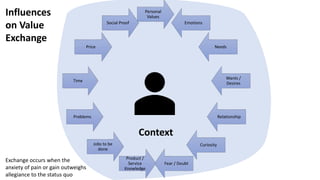
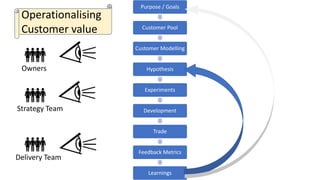
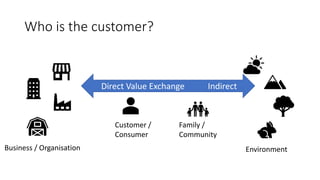
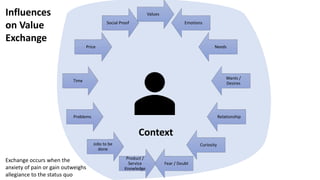
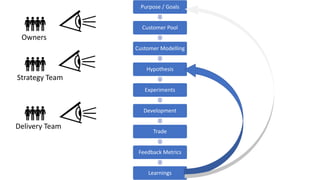
This document outlines a session led by David Williams focusing on customer value, aiming to identify gaps in understanding and to derive actionable insights. It defines customer value as the difference between what a customer receives and what they must give, highlighting its importance for business success. The session includes group discussions, interviews, and interactive activities to explore the concepts of value exchange and customer-centric business strategies.