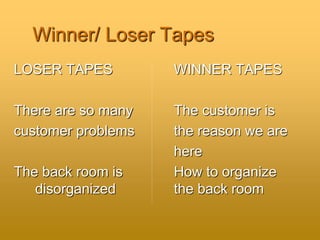
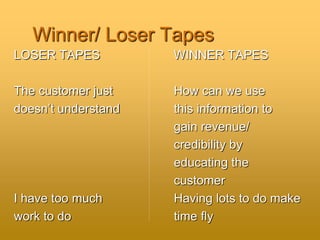
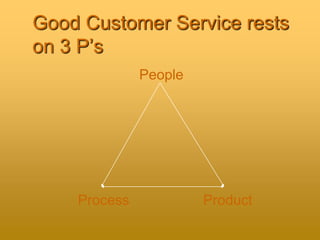
The document outlines foundational concepts in customer service, emphasizing the importance of understanding both internal and external customers, their needs, and the quality characteristics they value. It distinguishes between proactive and reactive customer service, highlighting the benefits of good service for both customers and organizations. Key takeaways include the importance of positive interactions, effective communication, and the emotional impact of customer experiences.