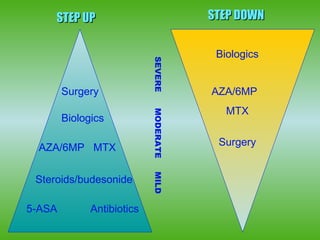
1) Step-down therapy using immunosuppressants or biologics early in treatment may alter the course of Crohn's disease by reducing steroid use, hospitalizations, and need for surgery over the long term.
2) Clinical trials show step-down therapy results in higher rates of clinical remission and mucosal healing compared to conventional step-up therapy.
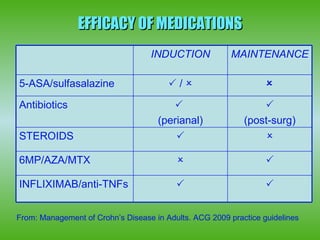
3) Biologics are effective for moderate-severe or fistulizing Crohn's disease that is refractory to conventional treatments but their long-term safety requires ongoing monitoring due to risks of infection and malignancy.