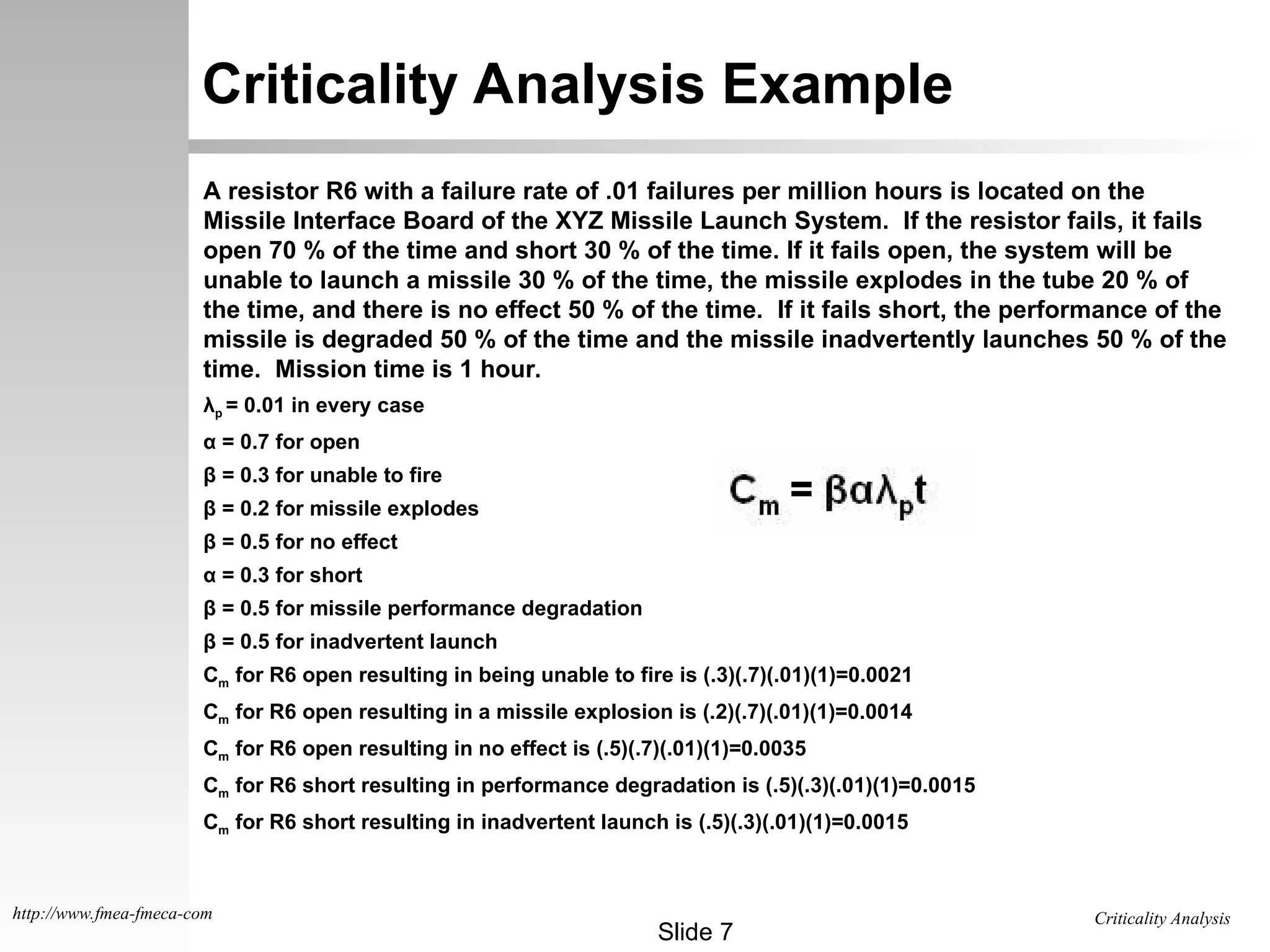
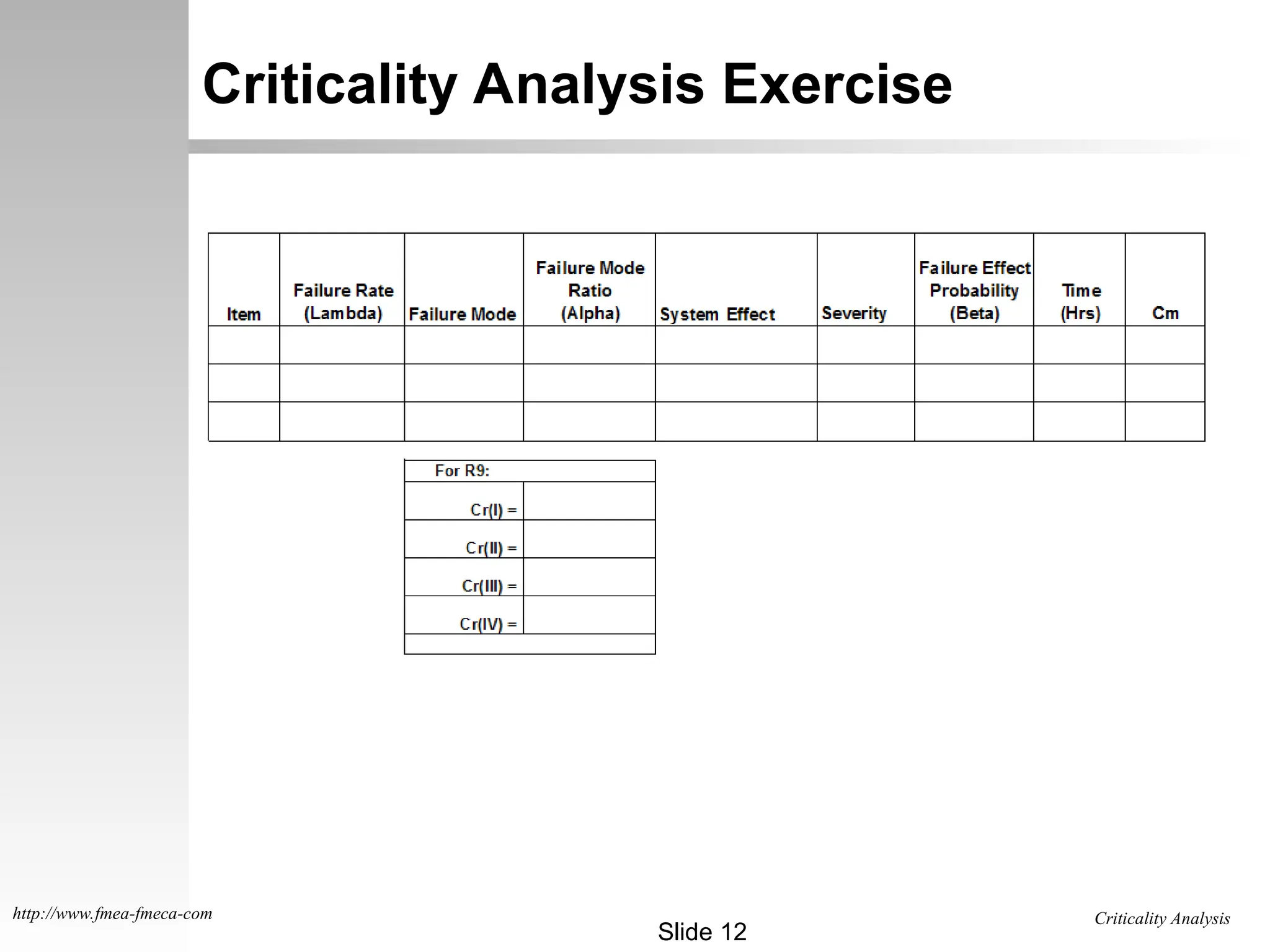
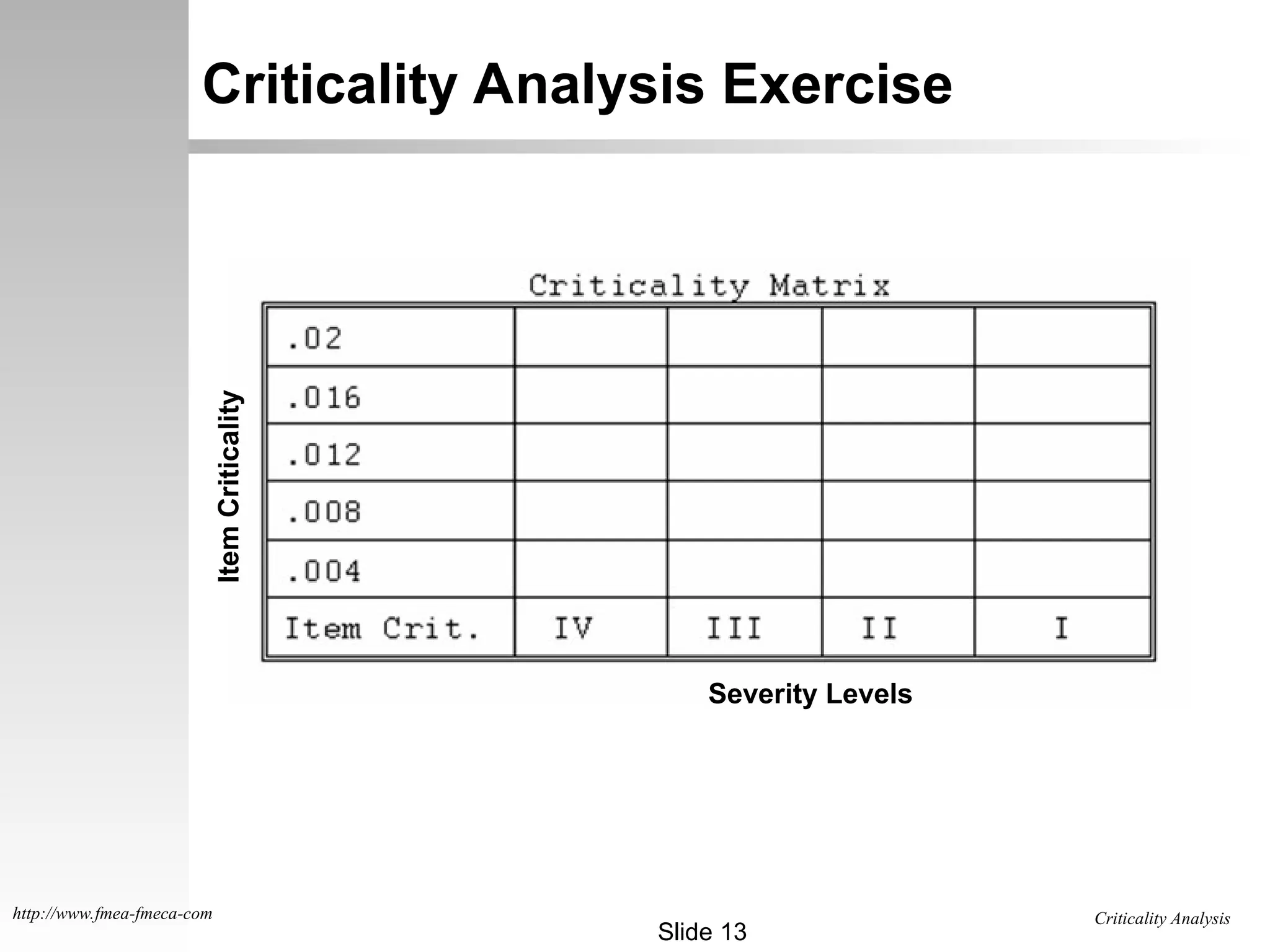
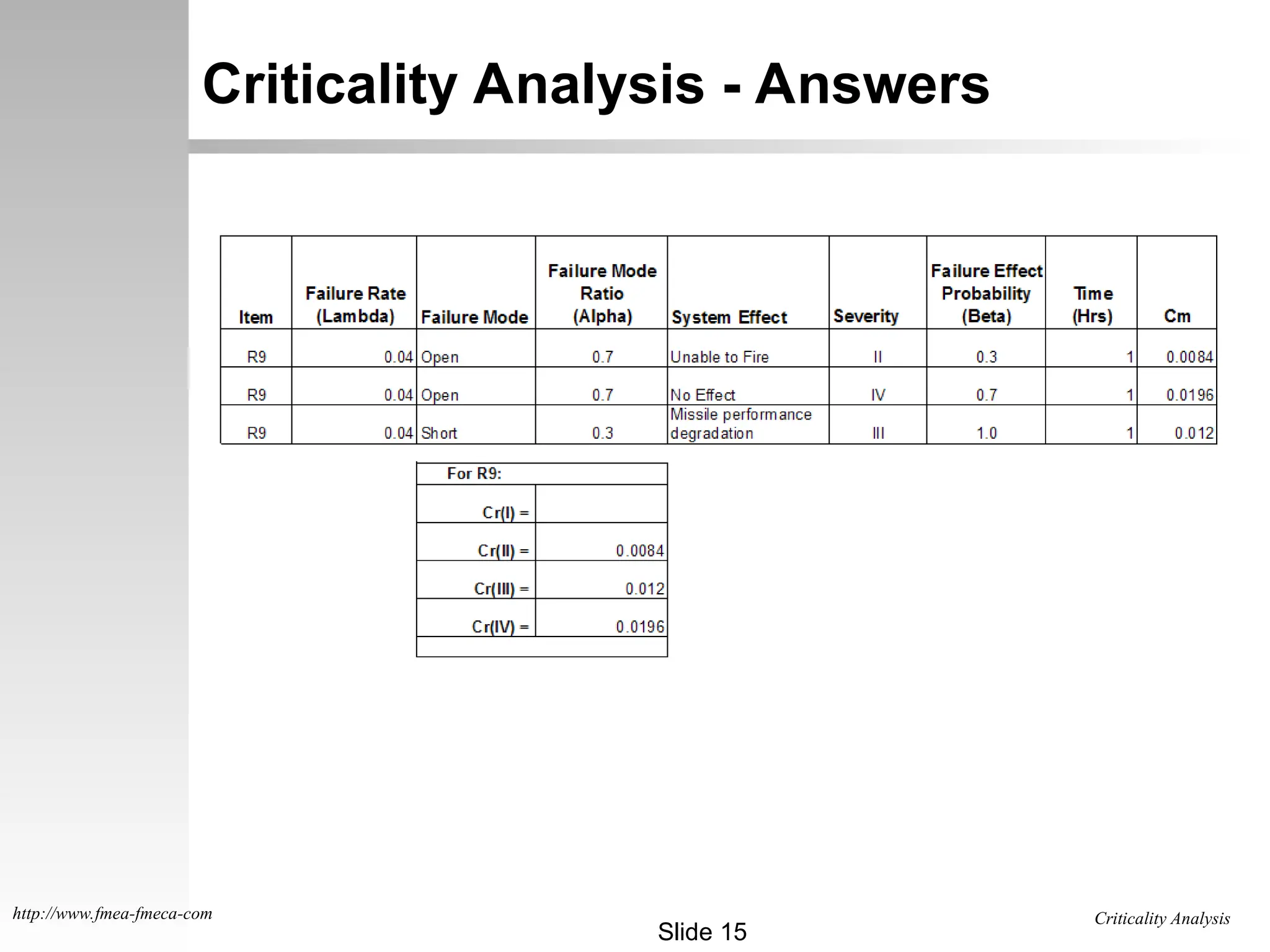
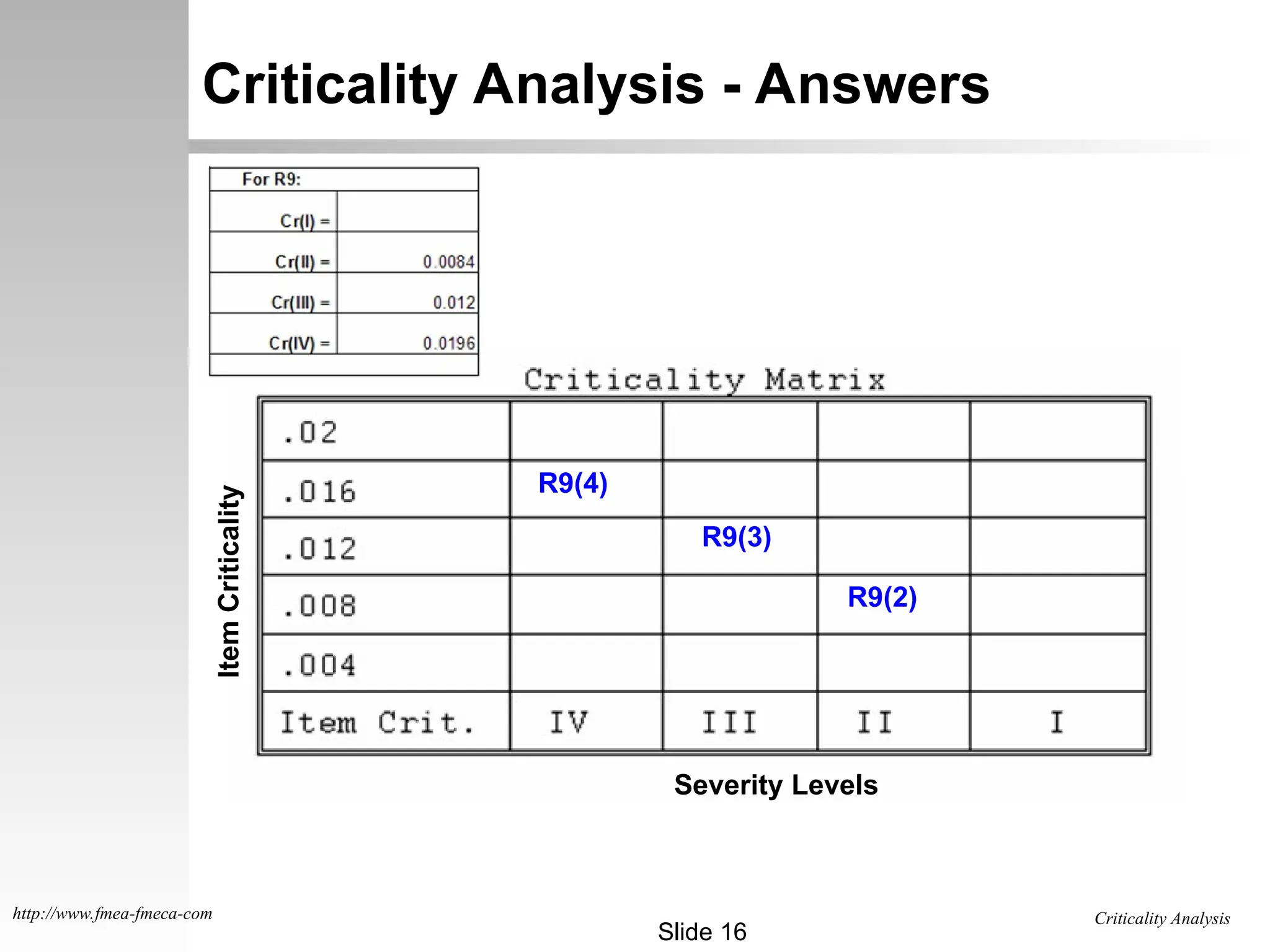
The document outlines the criticality analysis methodologies, distinguishing between qualitative and quantitative approaches to assess failure modes, utilizing MIL-STD-1629 standards. It provides frameworks for evaluating failure probabilities and criticality numbers based on available data, explaining categories of severity levels for potential failures. Additionally, it includes practical examples and exercises for calculating criticality values for specific components in missile systems.