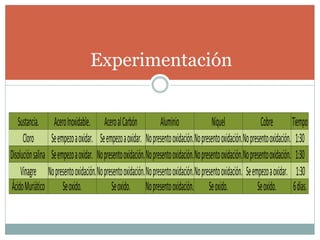
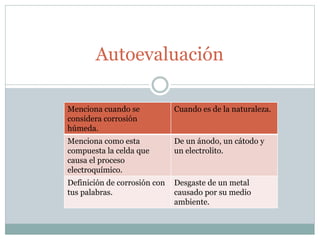
Corrosion is defined as the destructive attack of a metal through a chemical or electrochemical reaction with its environment. There are two main types of corrosion: dry corrosion caused by chemical reactions without electricity, and wet corrosion caused by electrochemical reactions characterized by an electric current within the corrosive medium. Corrosion occurs as metals interact with their surrounding environment, undergoing deterioration of both physical and chemical properties through the formation of anodic and cathodic regions in the presence of an electrolyte.