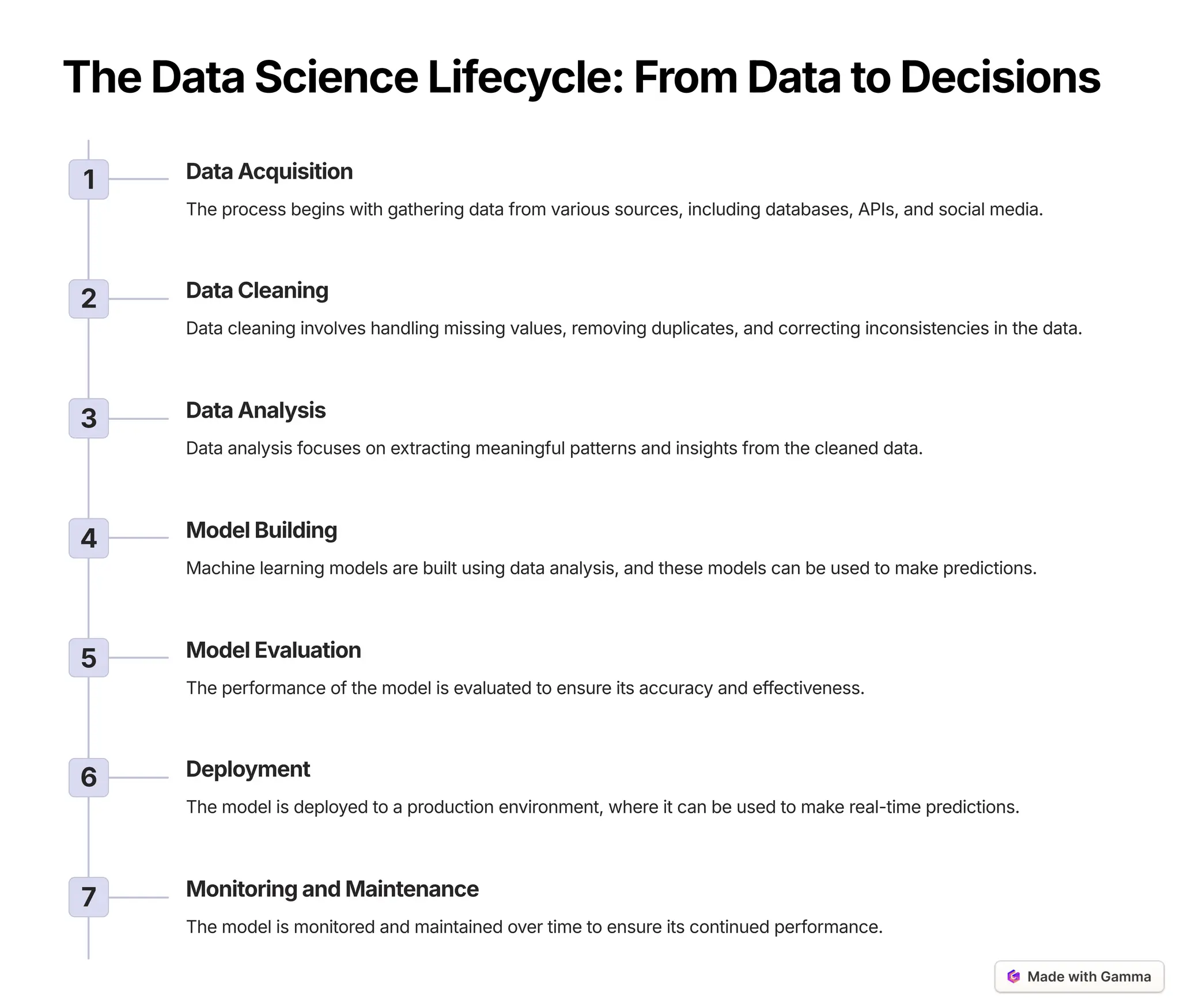
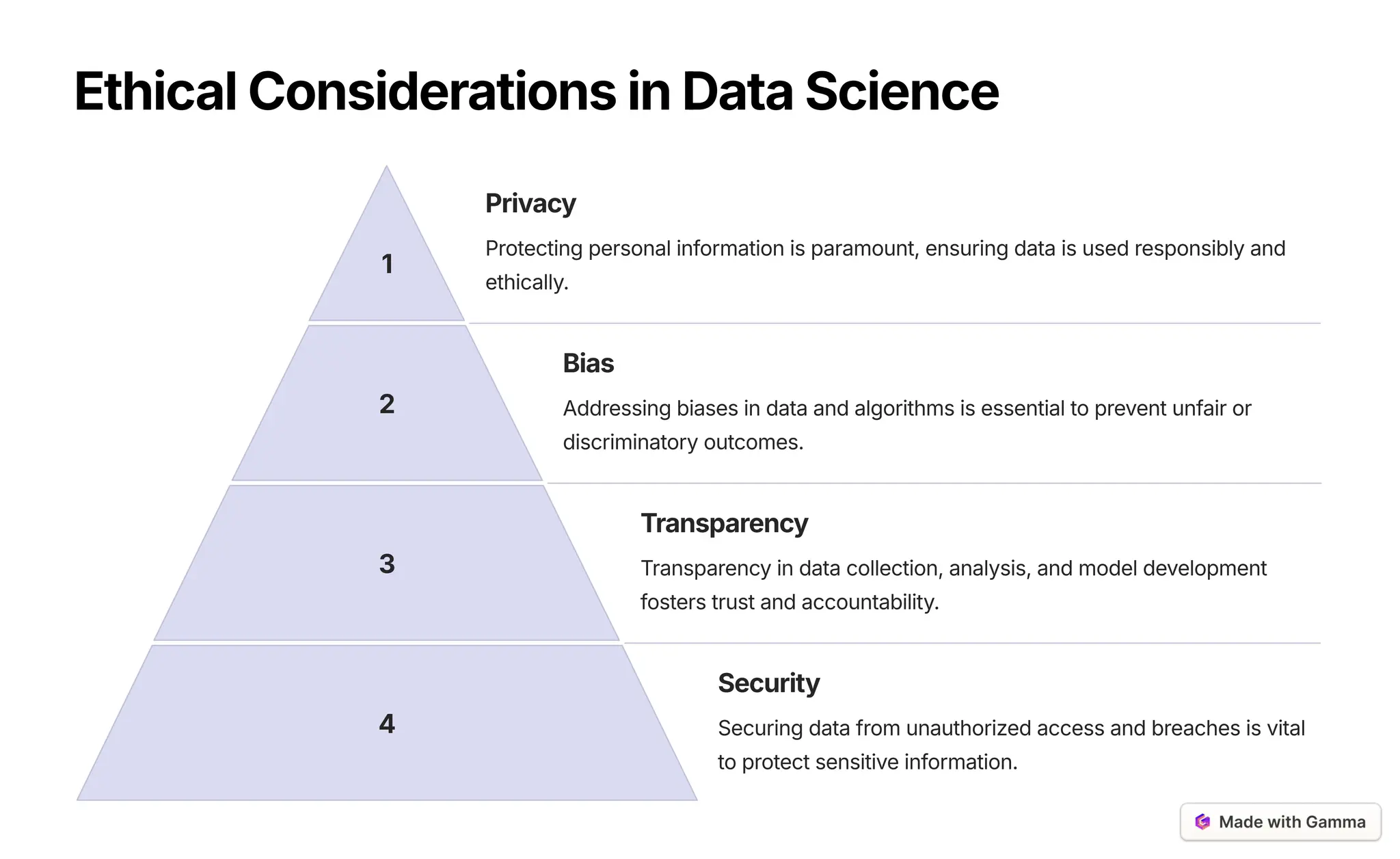
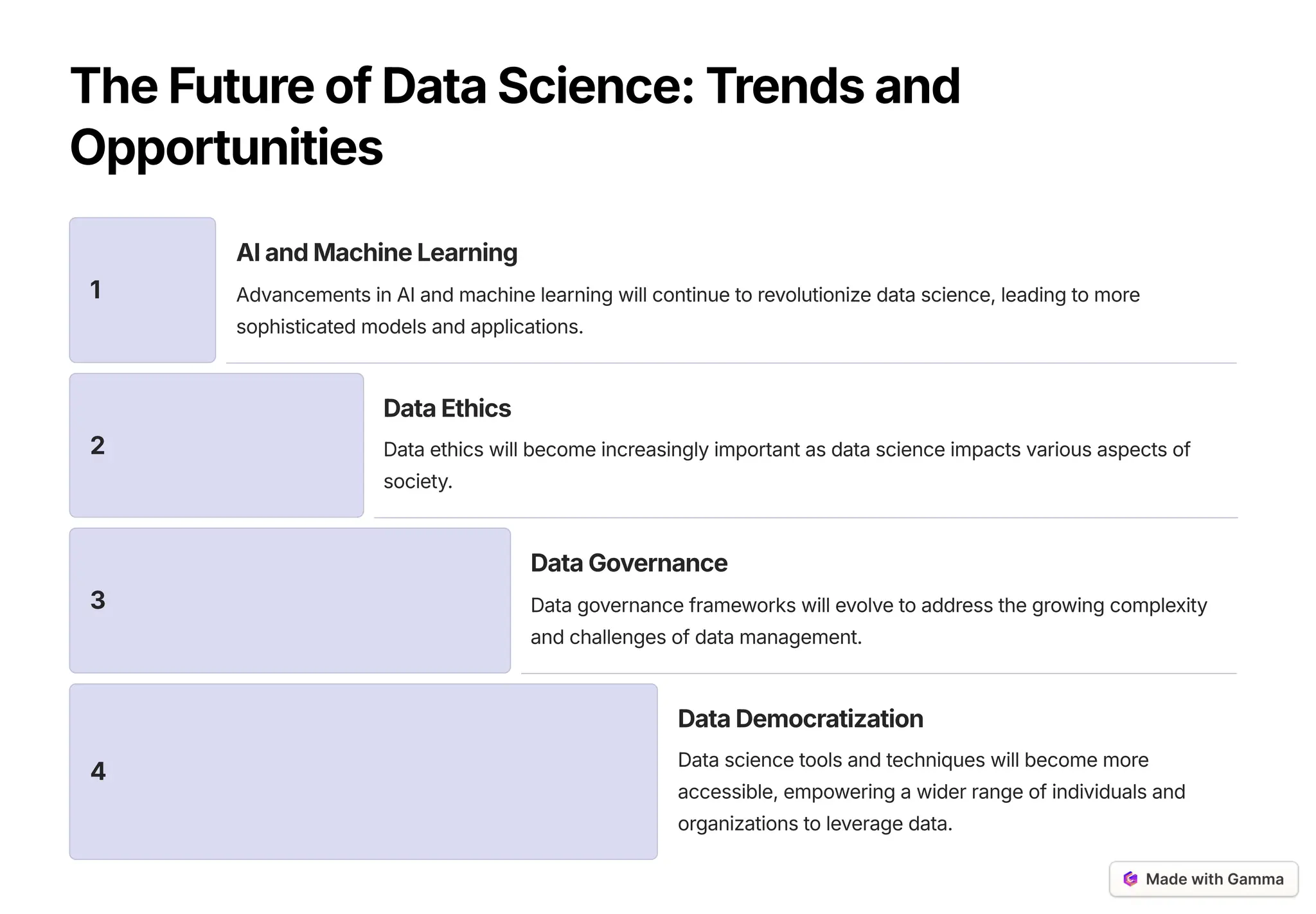
The document provides an overview of data science as a multidisciplinary field focused on analyzing data to unlock insights and drive innovation. It covers the data science lifecycle, including data acquisition, cleaning, analysis, model building, and evaluation, as well as various machine learning techniques. Additionally, it addresses challenges in big data, emphasizes the importance of ethical considerations, and highlights future trends such as advancements in AI and data democratization.