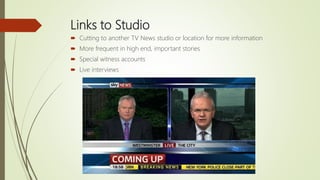
This document outlines several conventions of factual television programs and documentaries. It discusses the roles of anchor/newsreaders and field reporters in factual programs, as well as conventions like linking to other studios, addressing the viewer, and using interviews and footage. For documentaries specifically, it notes the use of handheld cameras, narrative voiceovers, vox pops, archive materials, and creative editing. Overall, the document provides an overview of common techniques used in factual television programming to inform audiences and tell true stories.