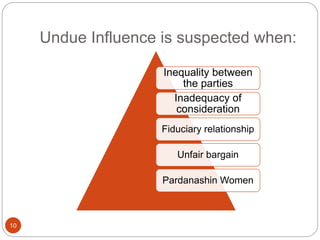
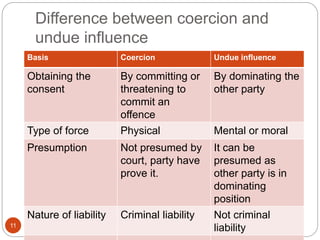
Free consent is essential for a valid contract. Consent is not free when obtained through coercion, undue influence, fraud, misrepresentation, or mistake. Coercion involves threats to compel consent. Undue influence involves exploiting power imbalances. Fraud involves intentional deception. Misrepresentation involves unintentional false statements. Mistakes void a contract if both parties are mistaken about an essential fact or one party exploits the other's unilateral mistake about a fundamental issue. Consent obtained without free will can void a contract.