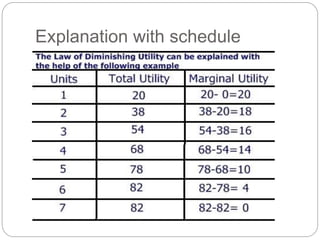
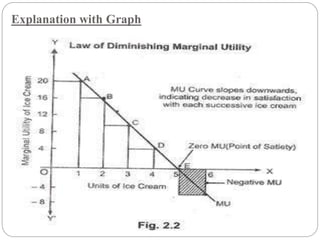
This document discusses consumer behavior and the law of diminishing marginal utility. It defines utility as the power of a commodity to satisfy human wants. The law of diminishing marginal utility states that the additional benefit a person derives from consuming incremental units of a good diminishes with each additional unit. This is illustrated with schedules and graphs showing that marginal utility declines as consumption increases. There are assumptions and exceptions to the law, such as homogeneity of goods and cases where marginal utility may not diminish such as with hobbies or collecting.