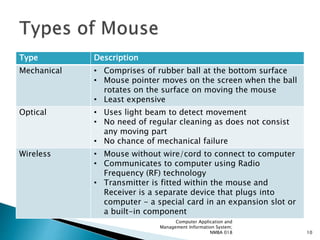
The document discusses various input devices used in computer systems, including keyboards, pointing devices, voice input, and scanners. Keyboards are the most common input device and use standard QWERTY layout. Pointing devices like mice, trackballs, and touchscreens allow users to control the cursor position and make selections on screen without typing. Voice recognition systems allow oral commands and dictation but have limited vocabularies. Scanners digitally convert text, images, barcodes and other data into formats readable by computers.