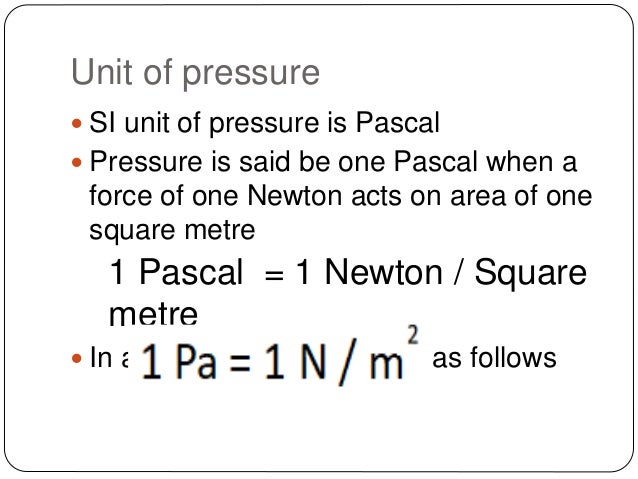
Pressure is defined as the force applied per unit area. The formula for pressure is P=F/A, where P is pressure, F is force, and A is area. Pressure is directly proportional to force and inversely proportional to area. The shorter the area over which a given force is applied, the greater the pressure will be. The SI unit for pressure is the pascal, which is equal to one newton per square meter. Examples of how pressure applies in daily life include a sharp knife cutting better due to greater pressure from its small surface area and porters decreasing pressure on their heads by increasing the area over which heavy loads are supported.