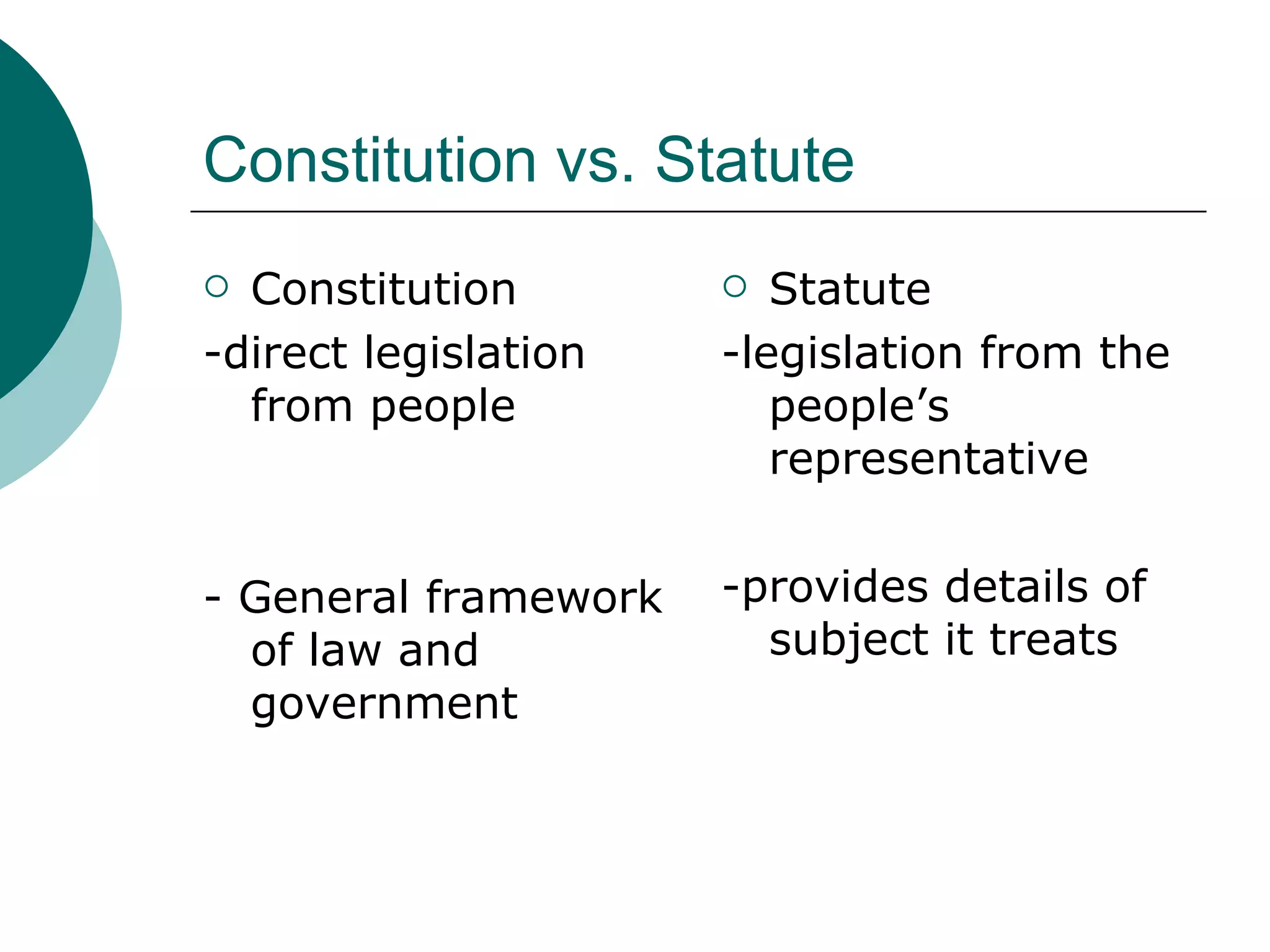
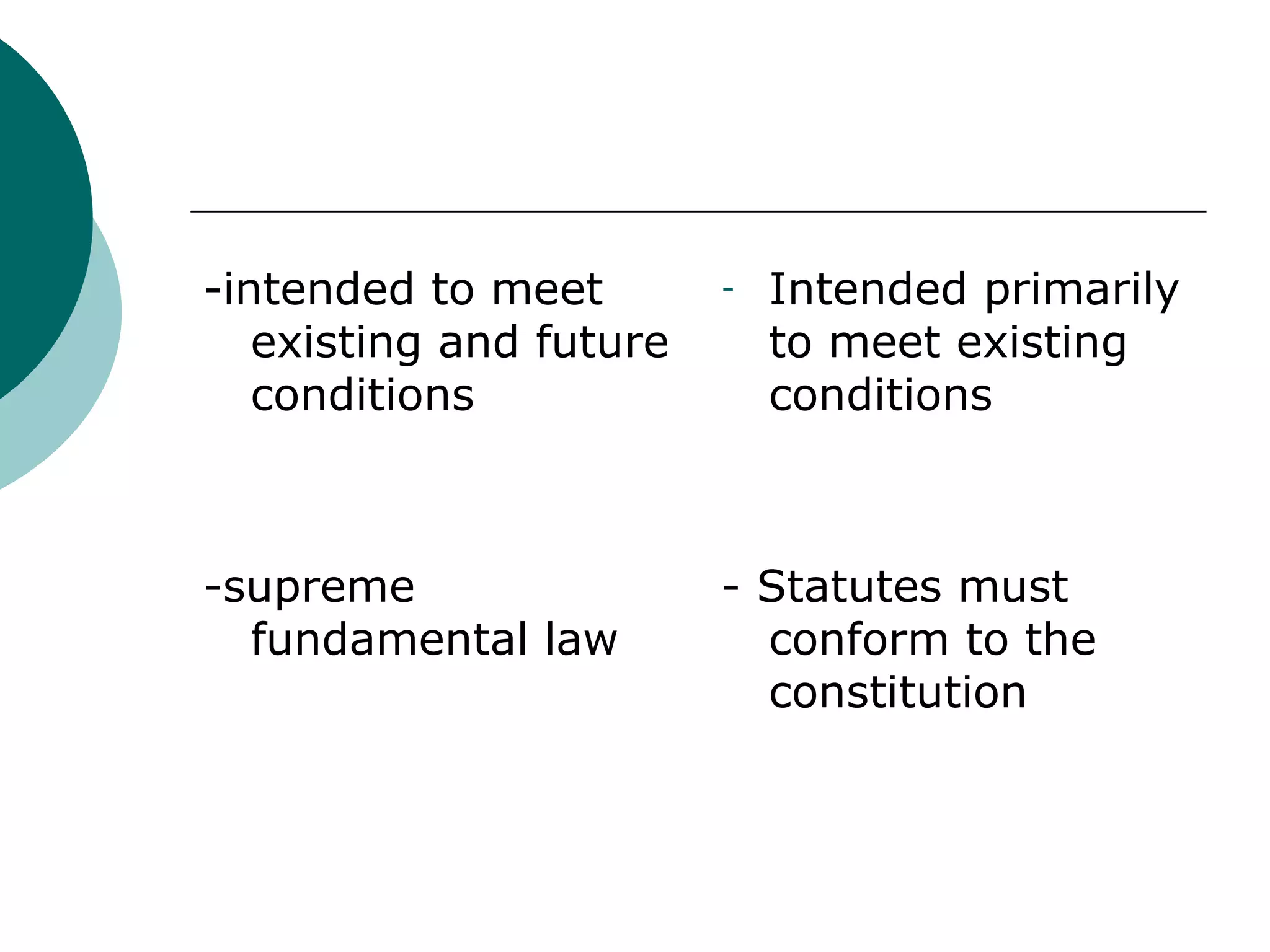
The document discusses key concepts about constitutions including:
1. A constitution establishes the fundamental rules and principles by which a government exercises its sovereignty and defines the basic framework of government.
2. Constitutions can be written or unwritten and are intended to both meet existing conditions and be flexible enough to address future needs.
3. The power to interpret the constitution primarily rests with the courts, whose goal is to ascertain the original intent of the framers and people who adopted the constitution.