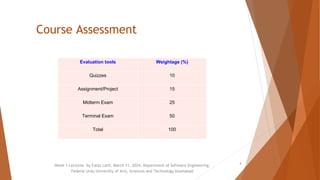
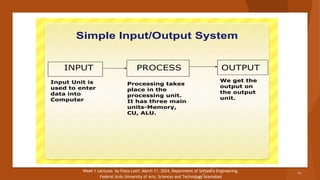
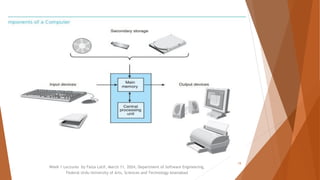
The document outlines the syllabus and structure of the Programming Fundamentals (SE111) course taught by Faiza Latif at the Federal Urdu University of Arts, Sciences and Technology. It covers key topics including basic programming concepts, data types, algorithms, and the role of hardware and software in computing. The course assessment includes quizzes, assignments, a midterm, and a terminal exam, along with specific attendance policies and required reading materials.