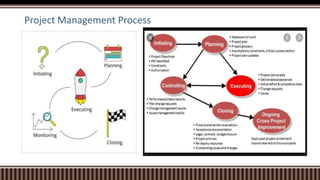
This document provides guidance for a graded unit in computer science. It outlines the aims, recommended prior knowledge, and instructions for designing the assessment task. The assessment involves a project with three stages: analysis and planning, developing, and evaluating. Candidates must demonstrate skills in project planning, implementation, testing, and evaluation to receive a passing grade.