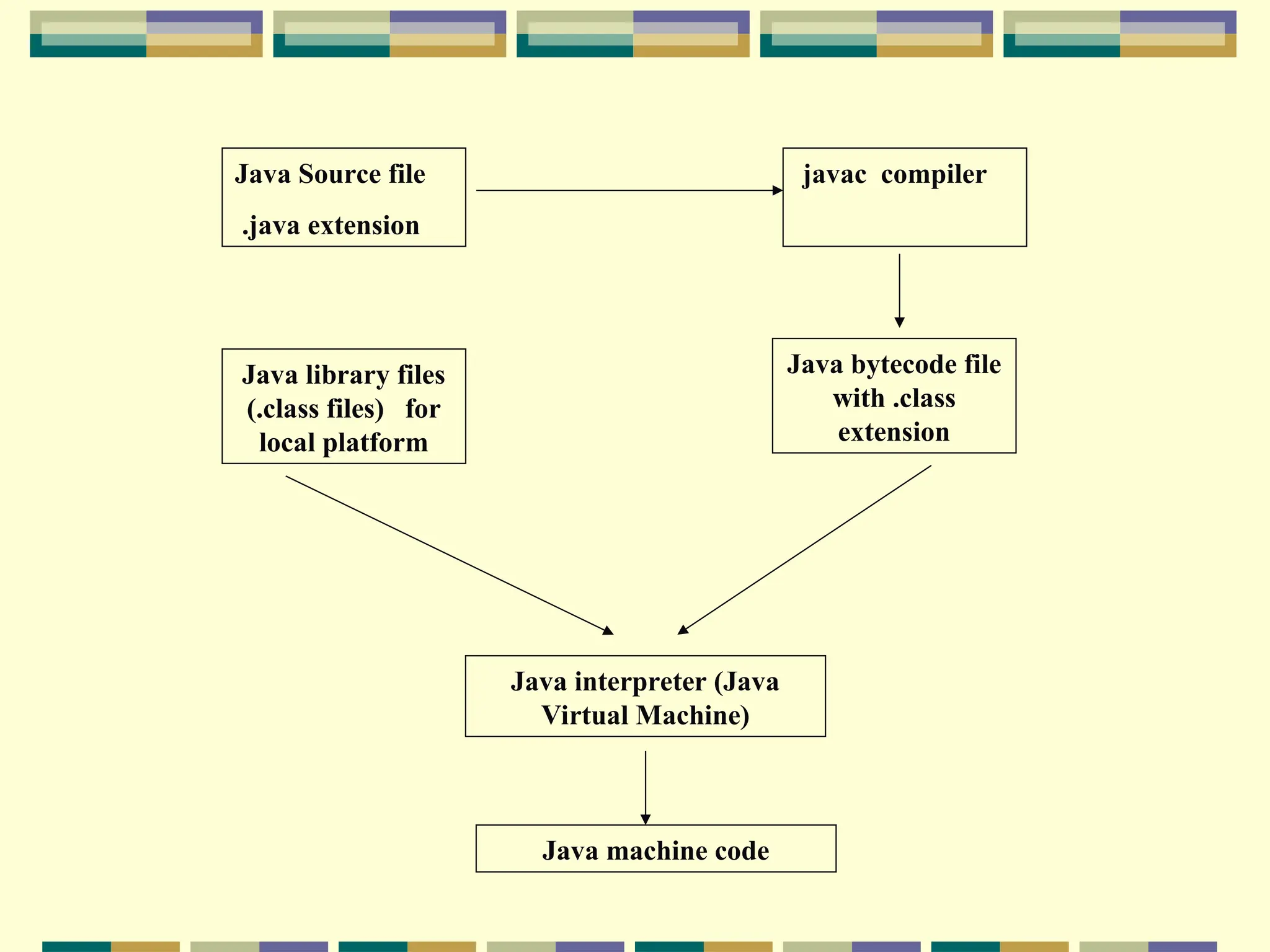
The document discusses the distinction between syntax and semantics in programming languages, explaining how syntax refers to the rules for constructing statements, while semantics pertains to the meaning of these statements. It covers the evolution from low-level languages to high-level languages, highlighting the role of compilers and interpreters in translating source code into executable machine code. Additionally, it details the compilation process, the function of Integrated Development Environments (IDEs), and the specific case of Java's bytecode and execution through the Java Virtual Machine (JVM).