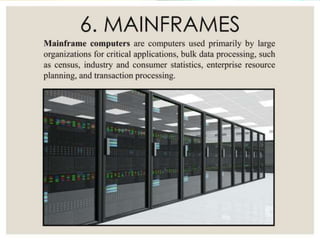
The document outlines the classification of computers, defining them as electronic devices that process data into output information. It describes three main types: digital computers that work with binary data, analog computers that utilize continuous physical quantities, and hybrid computers that incorporate features of both analog and digital systems.