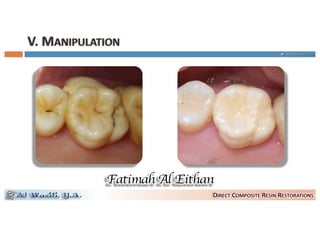
This document discusses dental composite materials, including their chemical and light activation methods, filler types, and shrinkage properties. It provides information on methyl methacrylate and Bis-GMA as common resins, as well as camphoroquinone and tertiary aromatic amines as typical photoinitiators and light absorbers. Details are given on densified and microfine composites, with filler particles less than 3 micrometers. The concepts of C-factor and methods to reduce composite shrinkage stresses at the tooth restoration interface are also summarized.