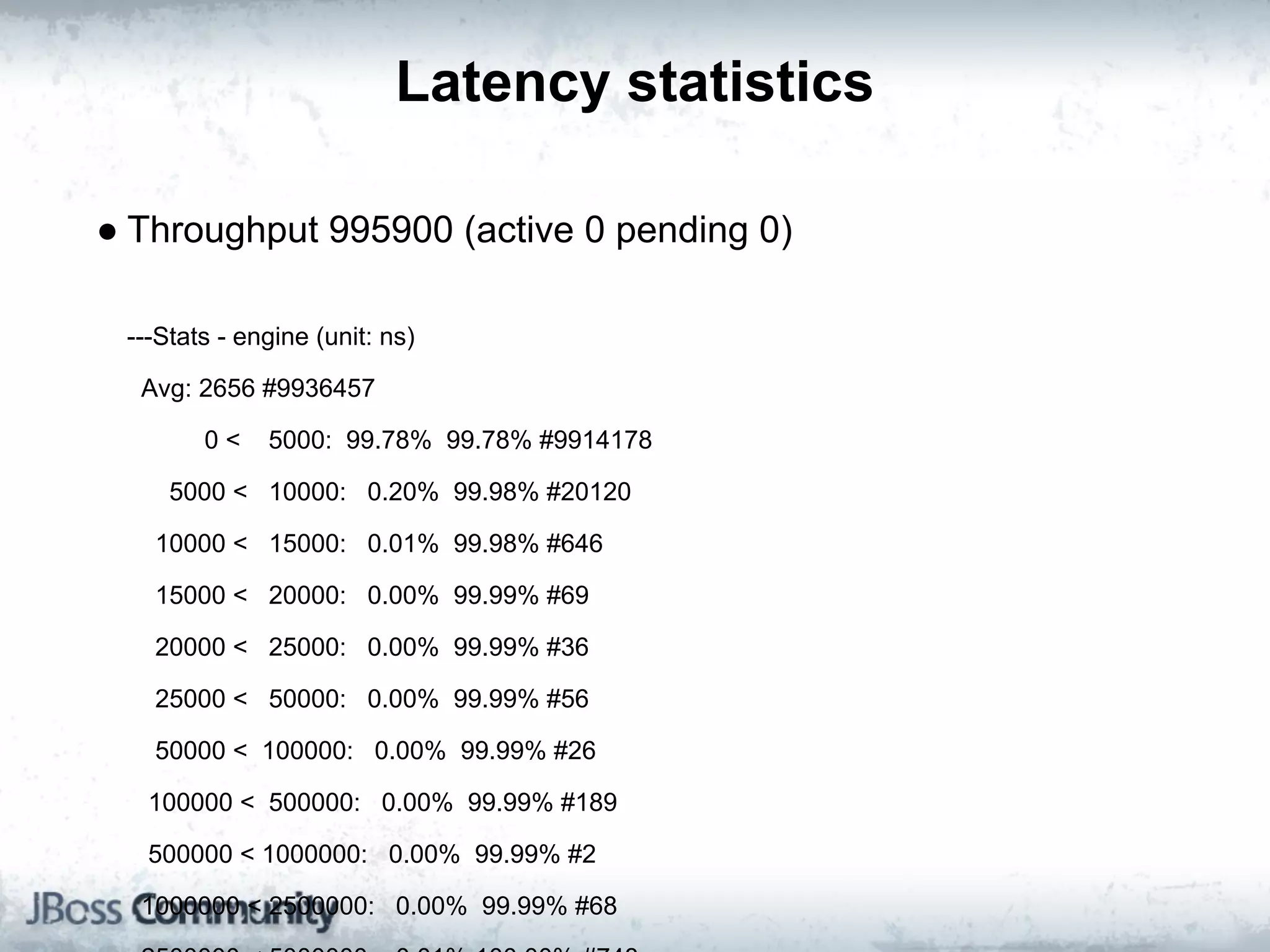
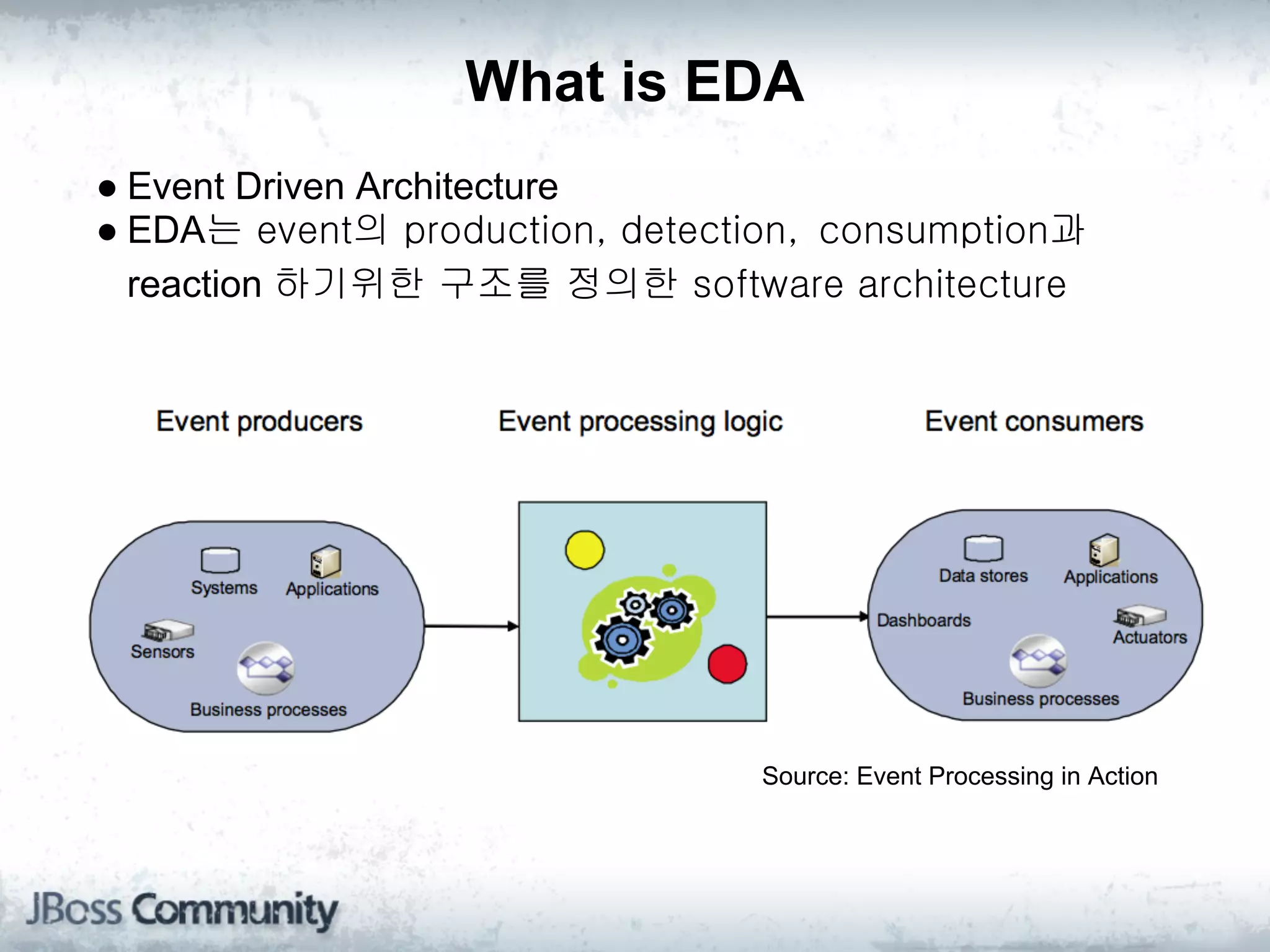
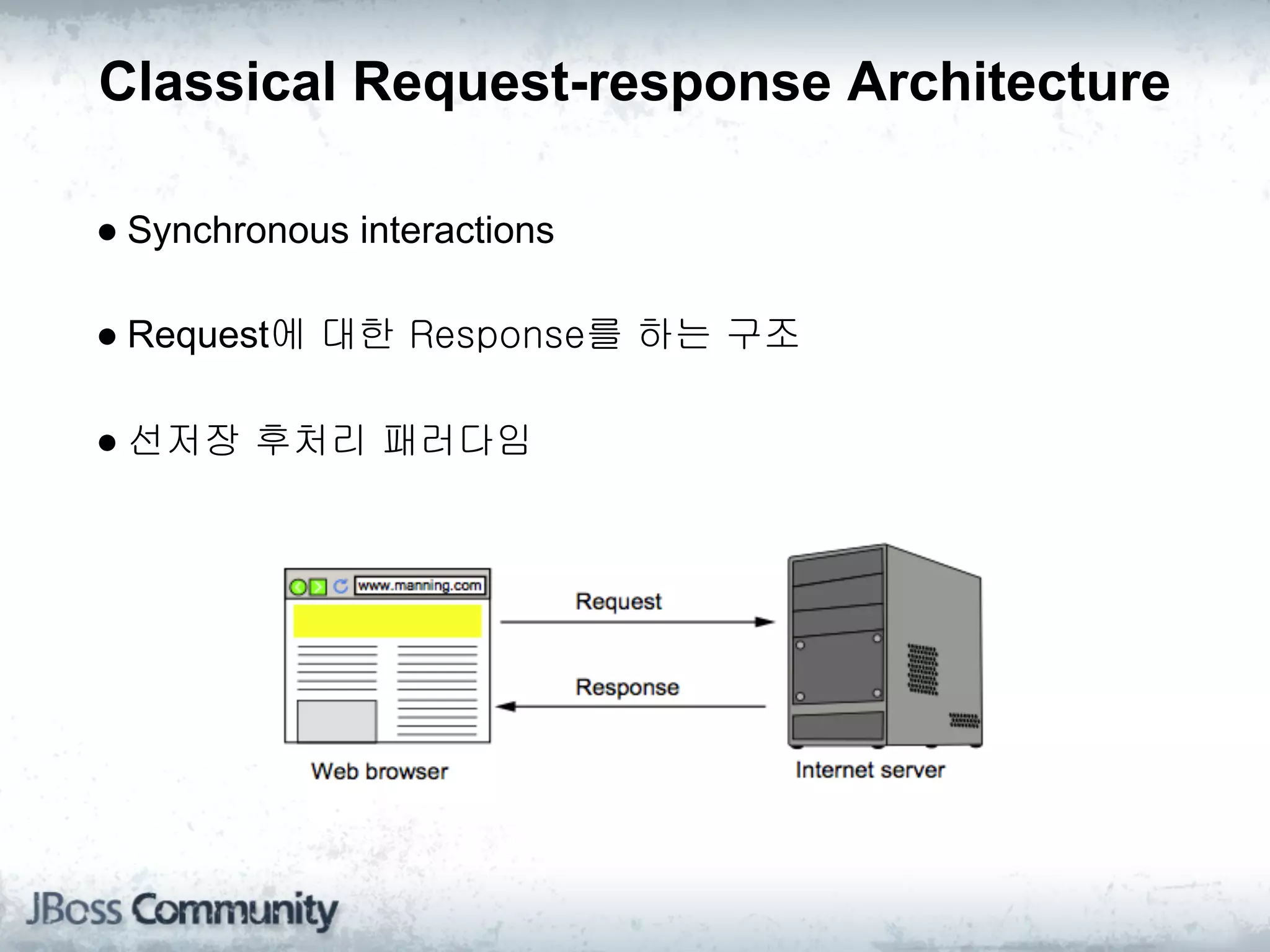
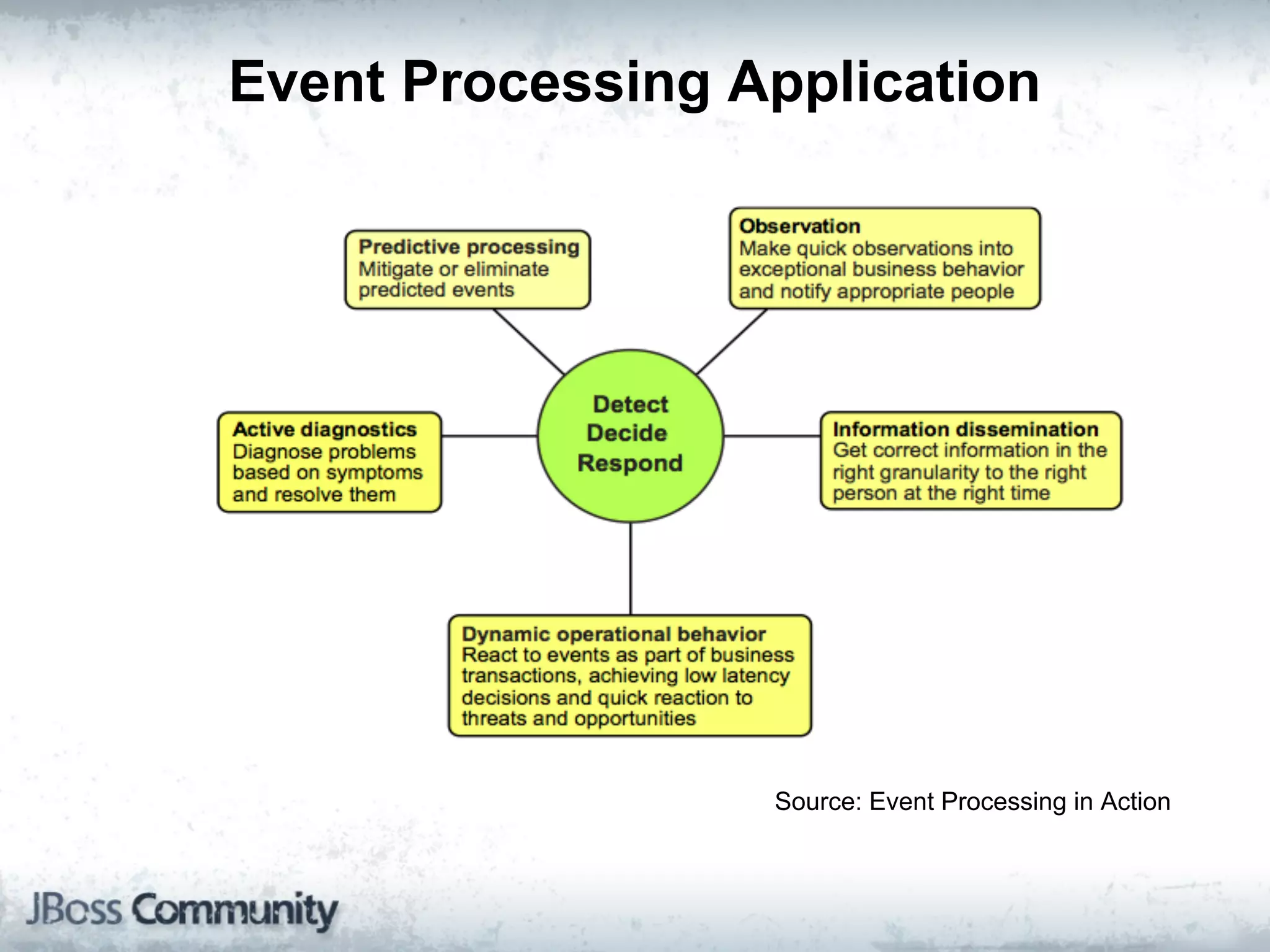
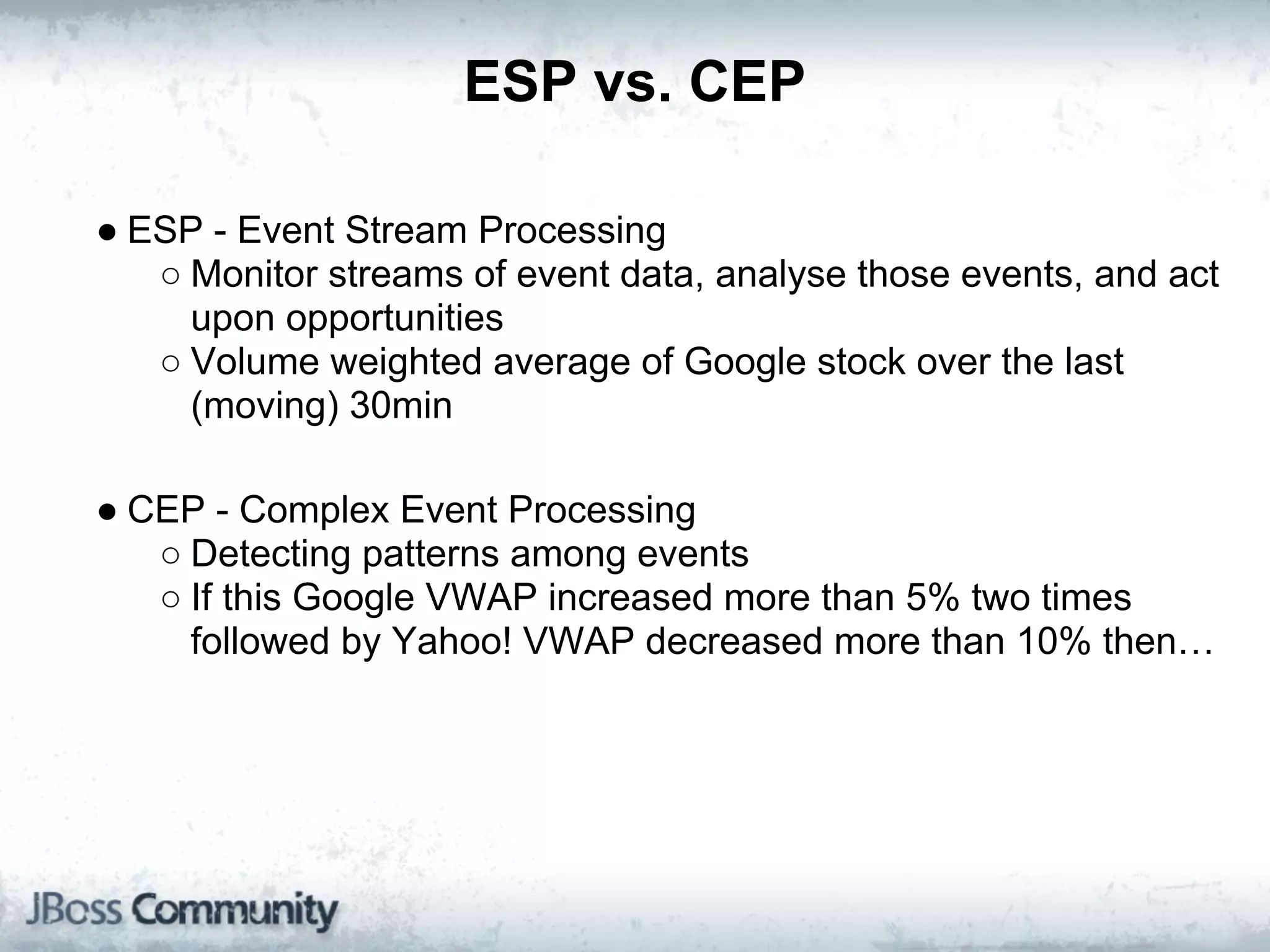
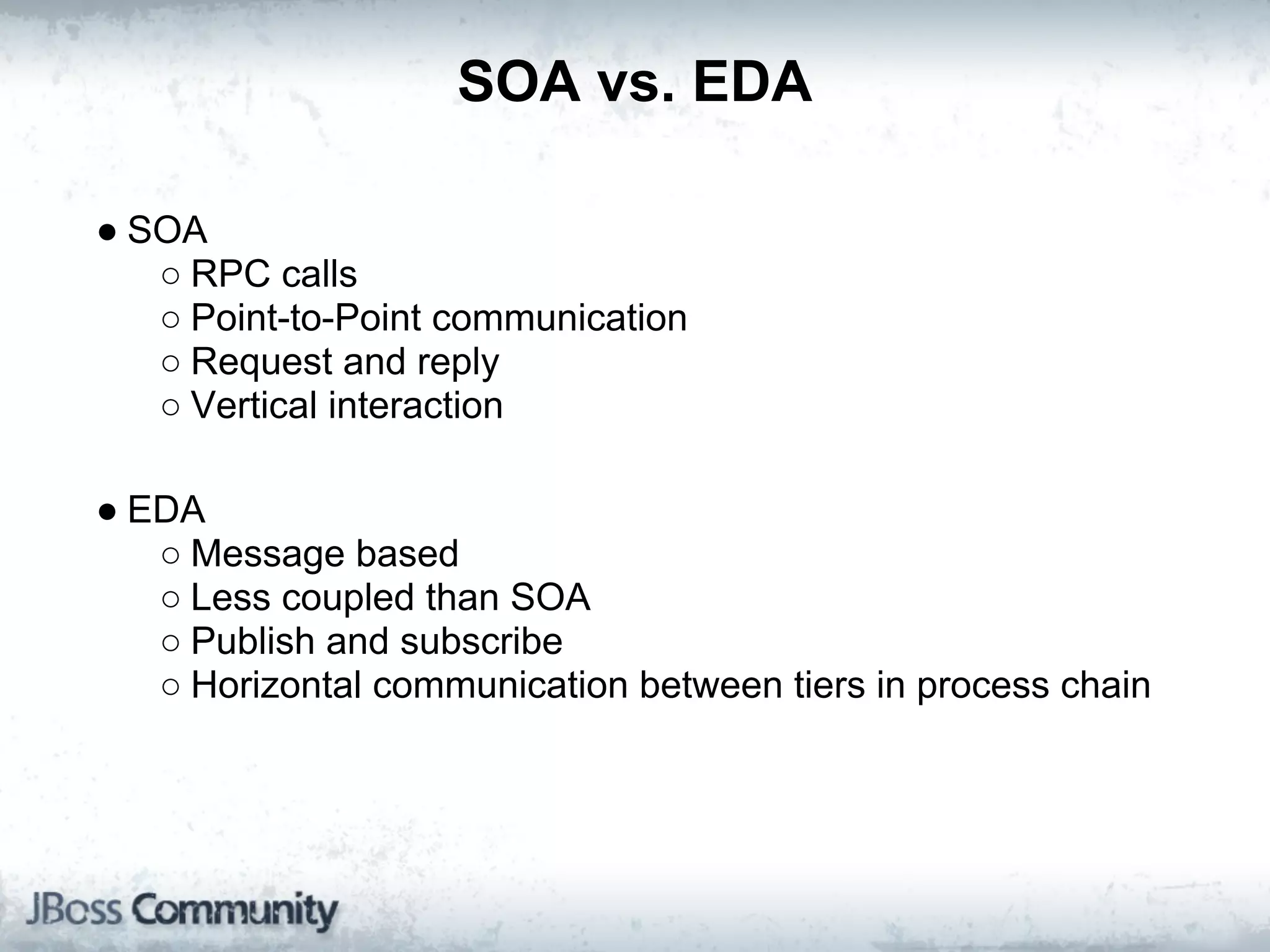
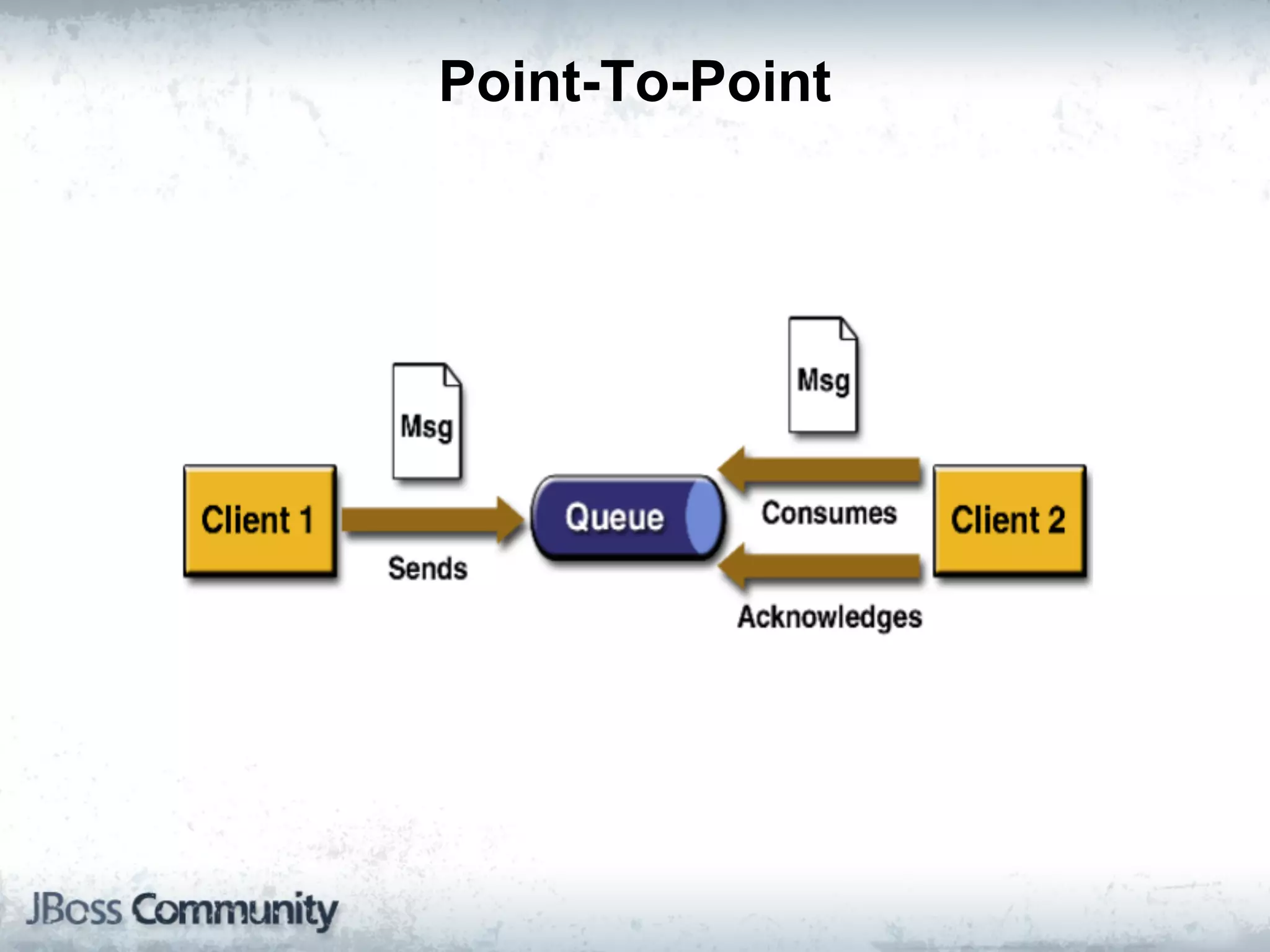
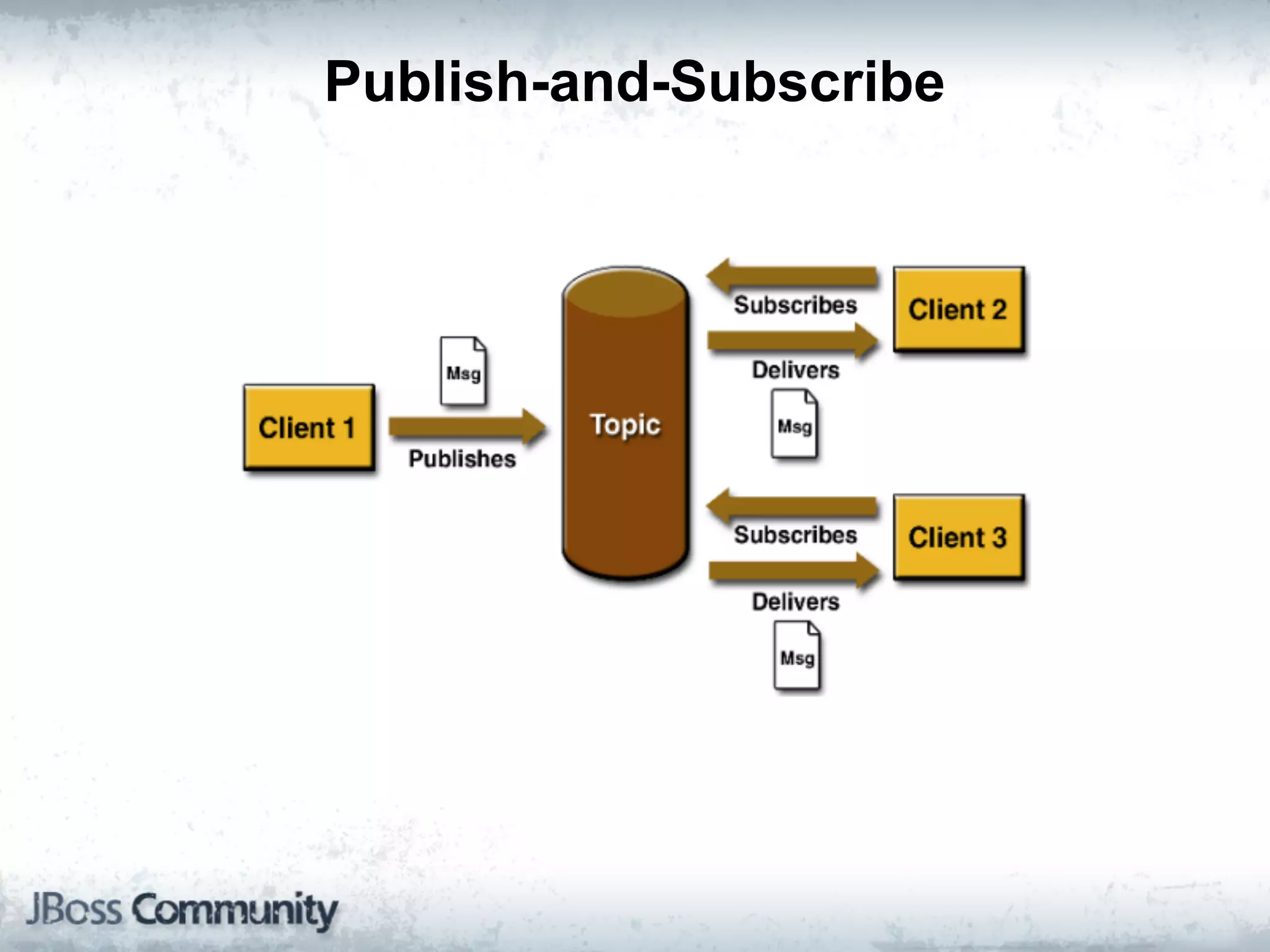
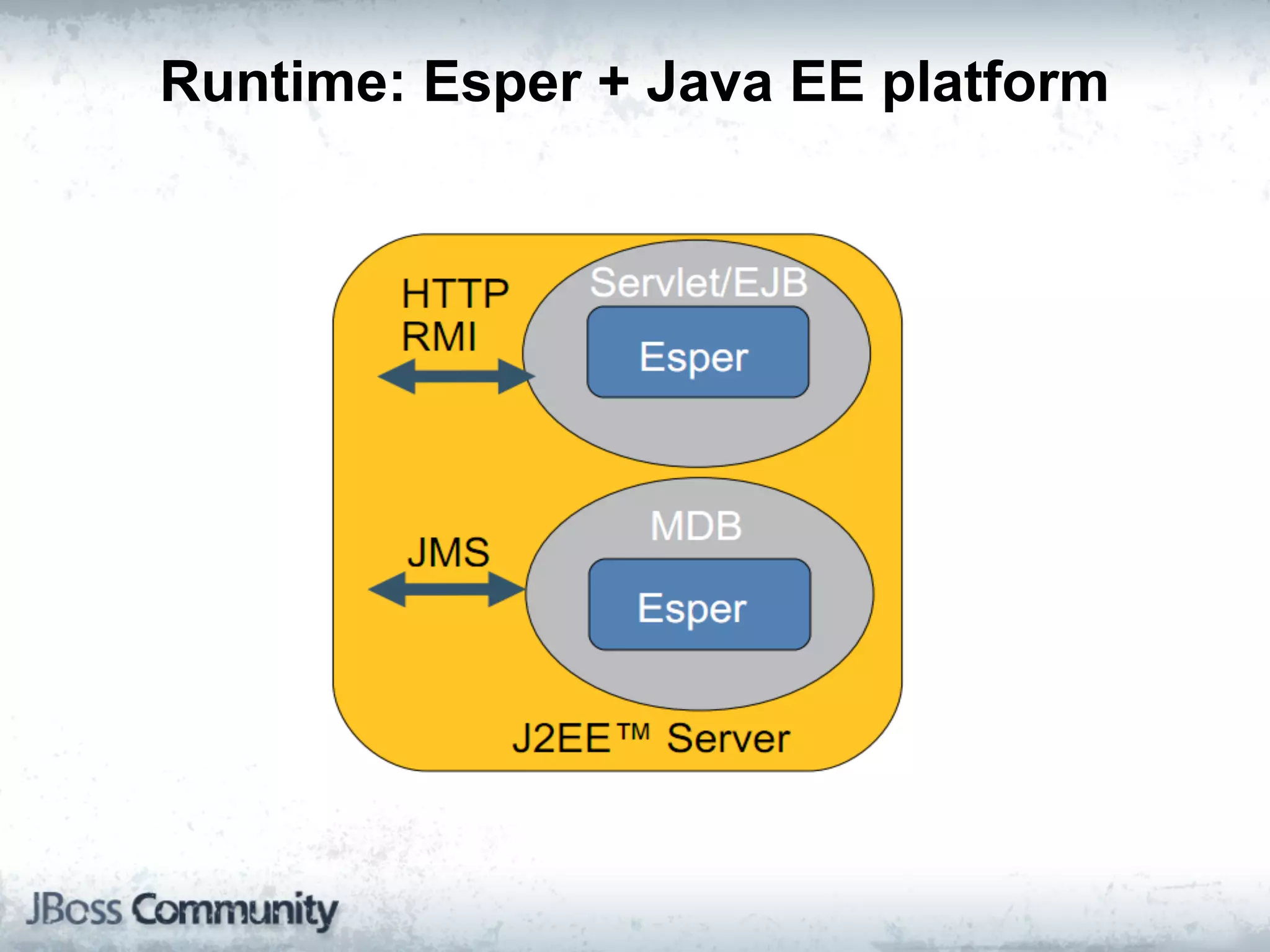
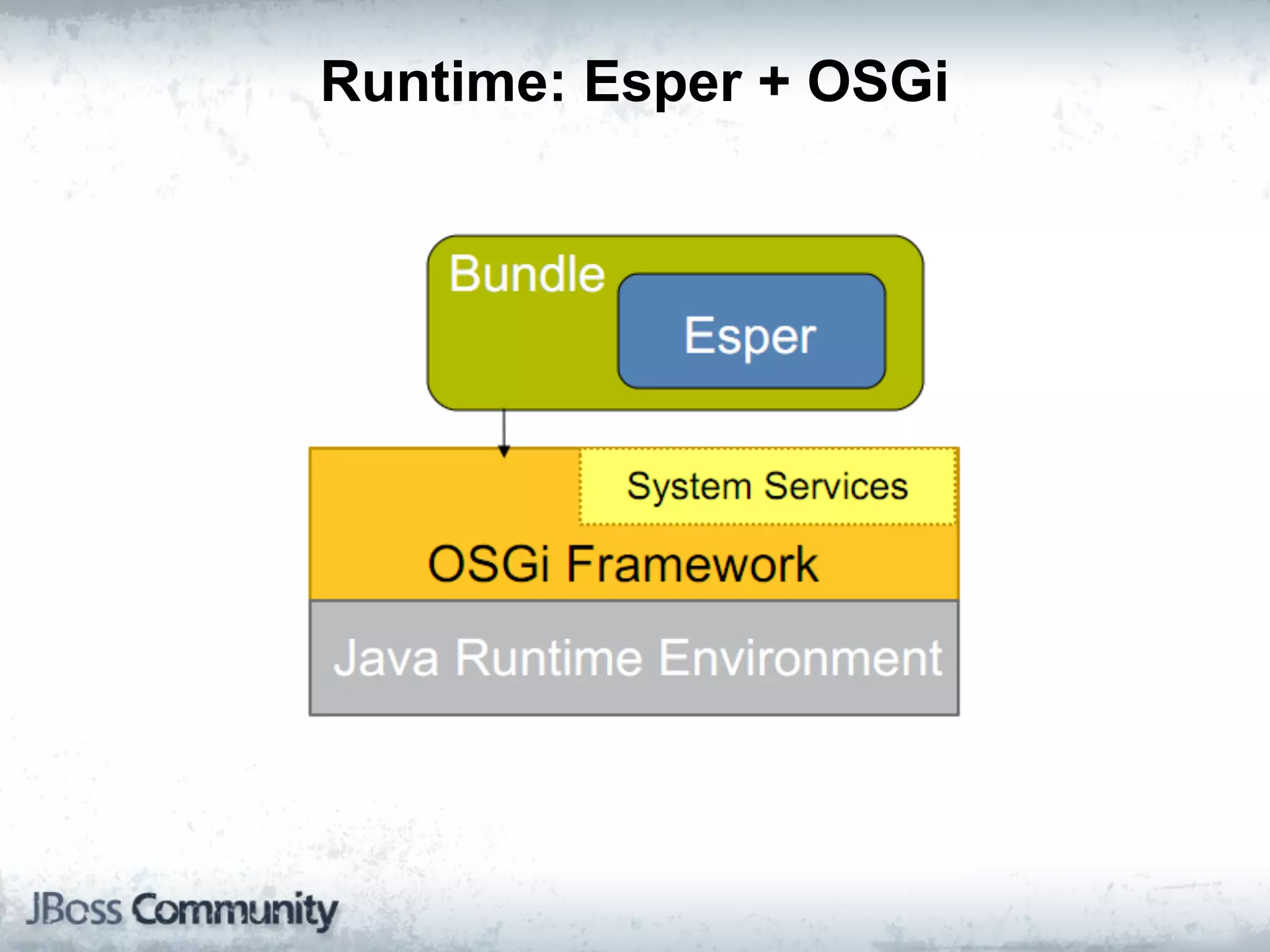
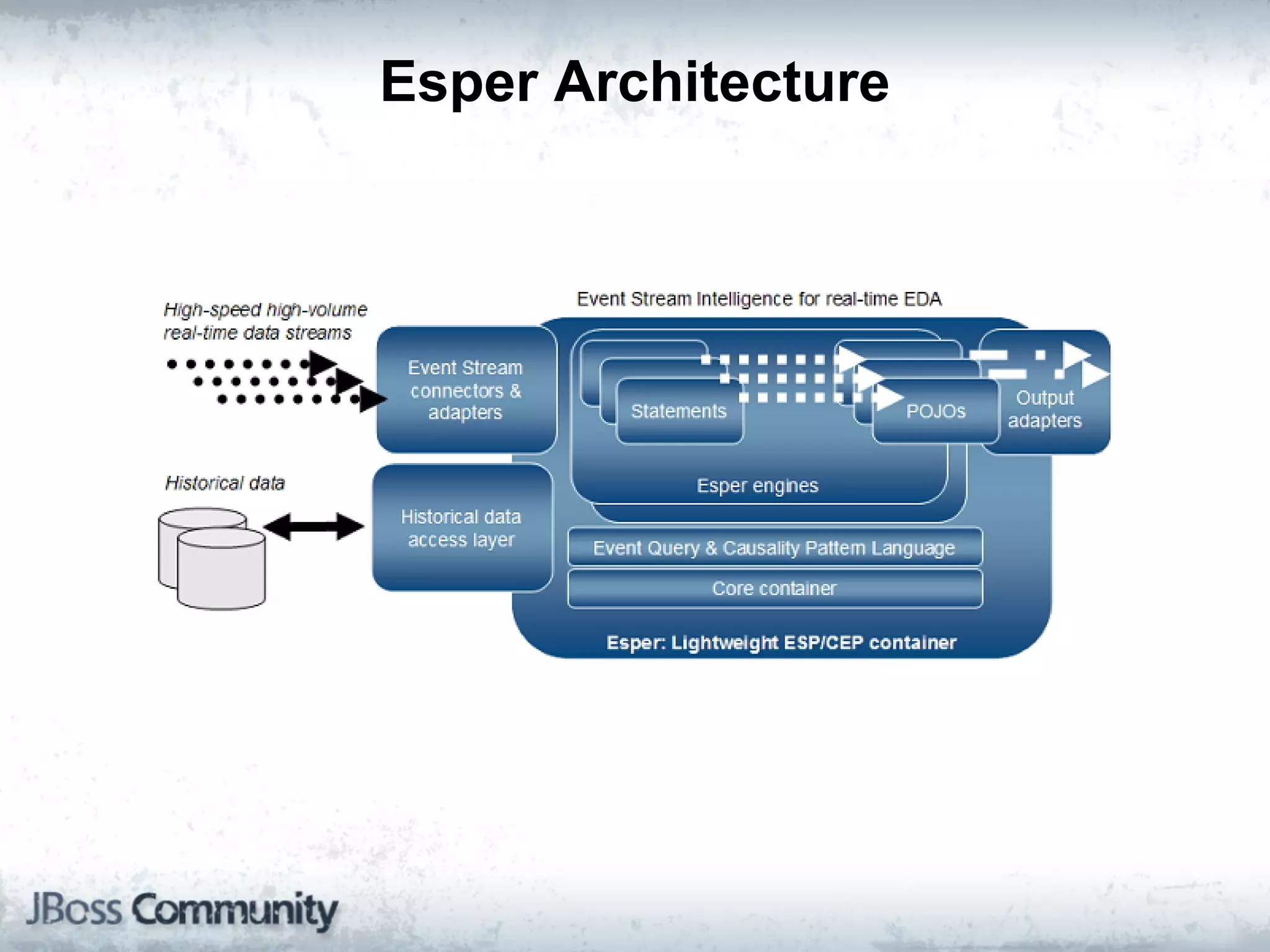
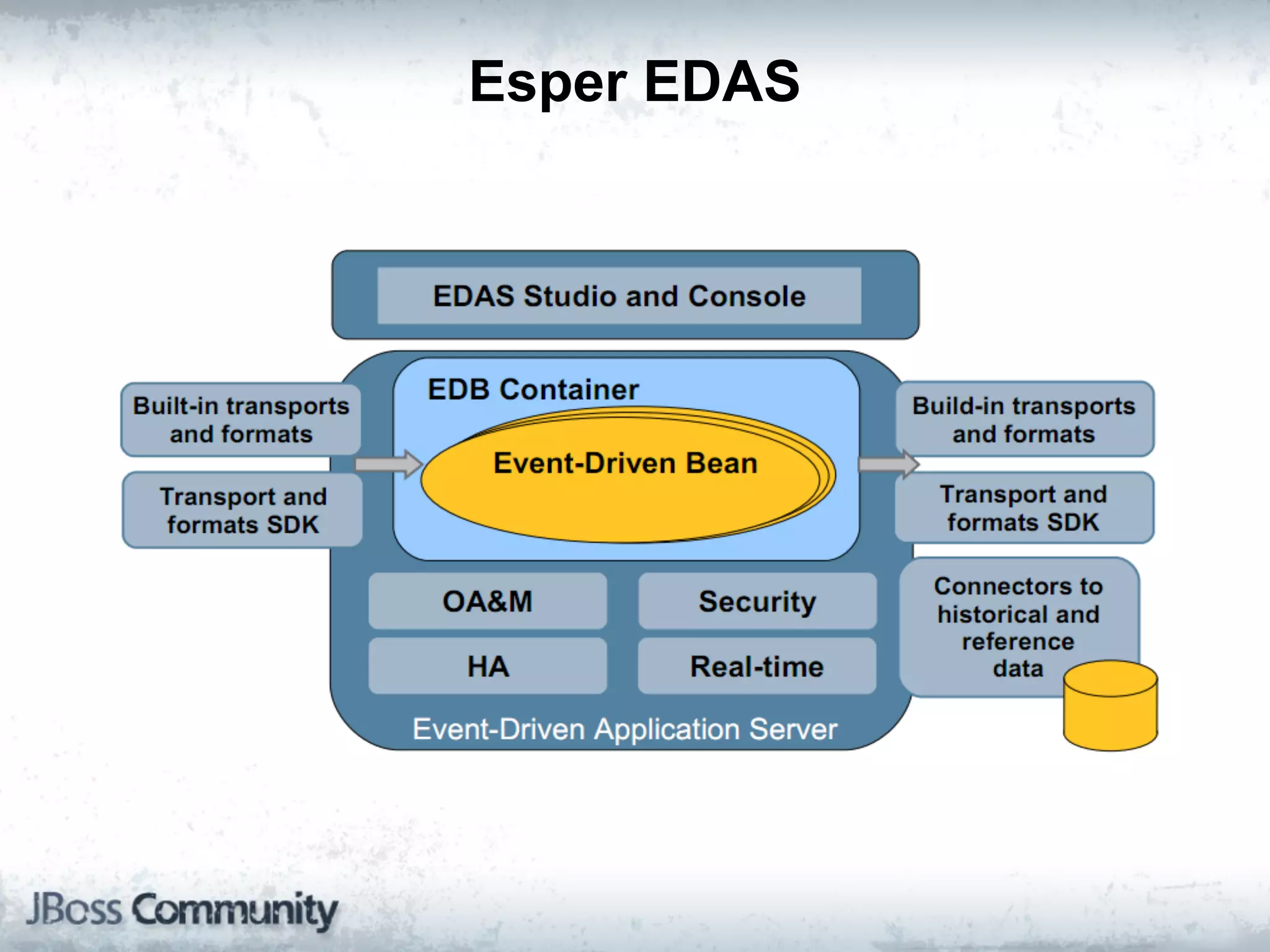
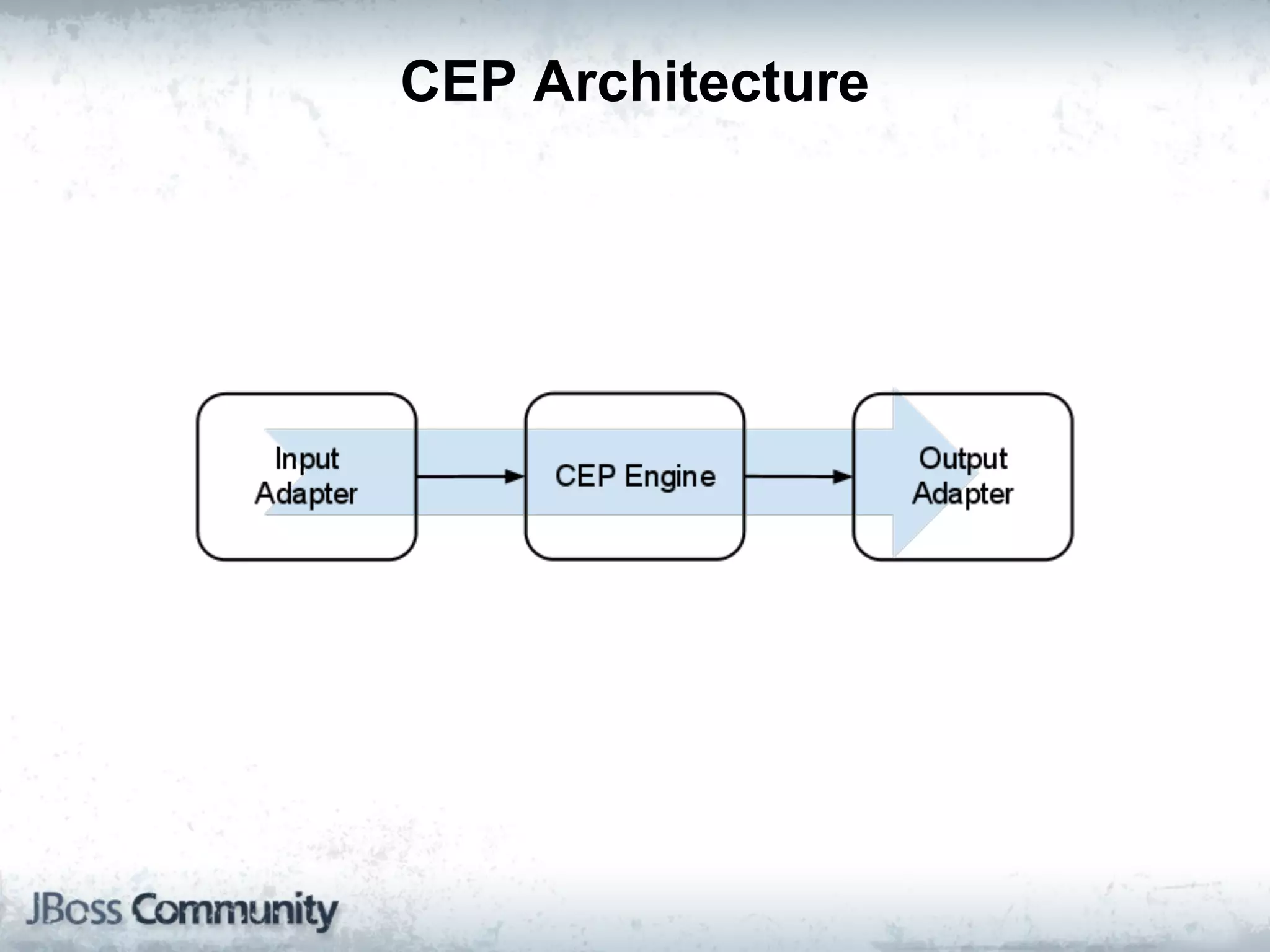
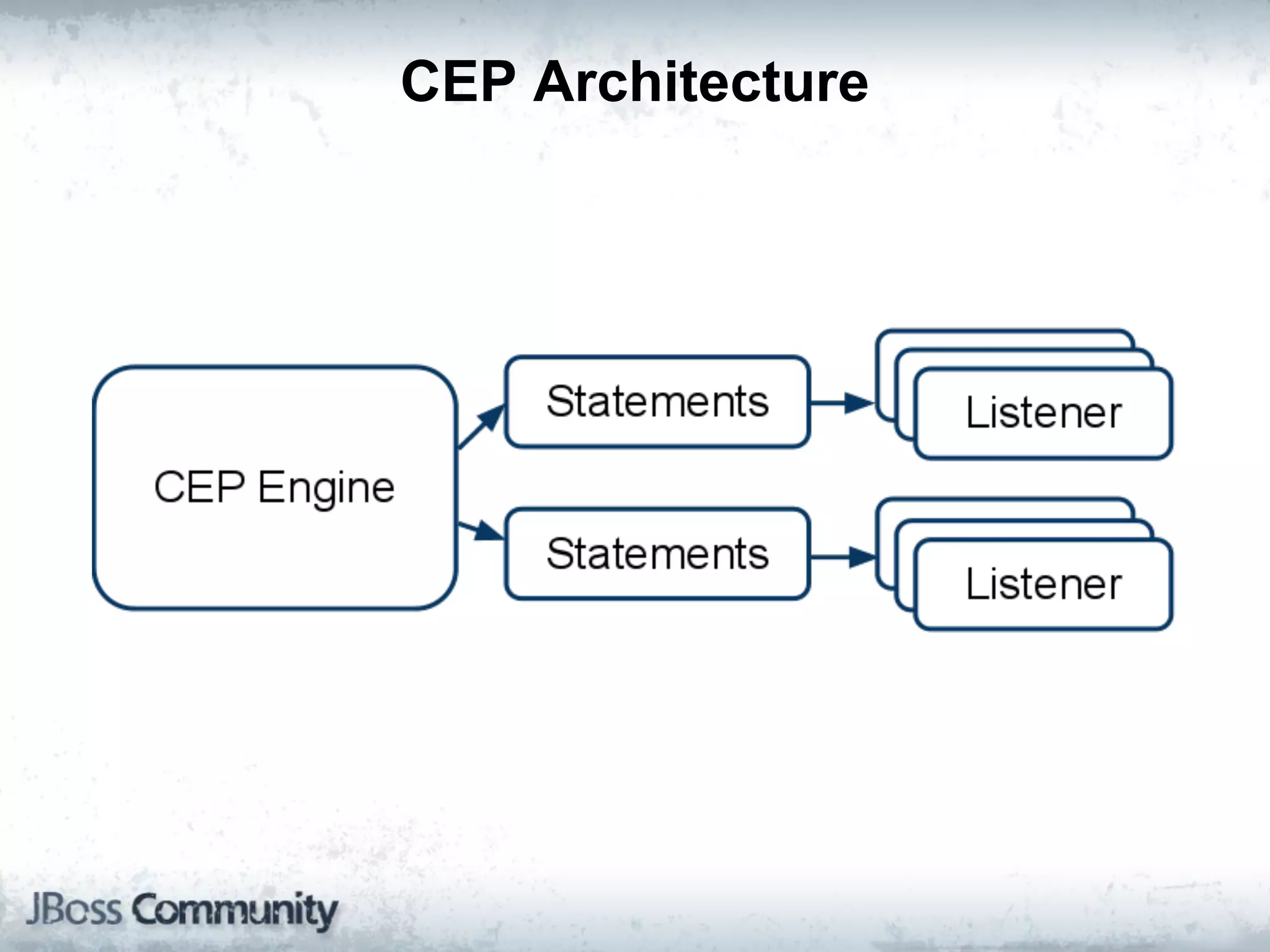
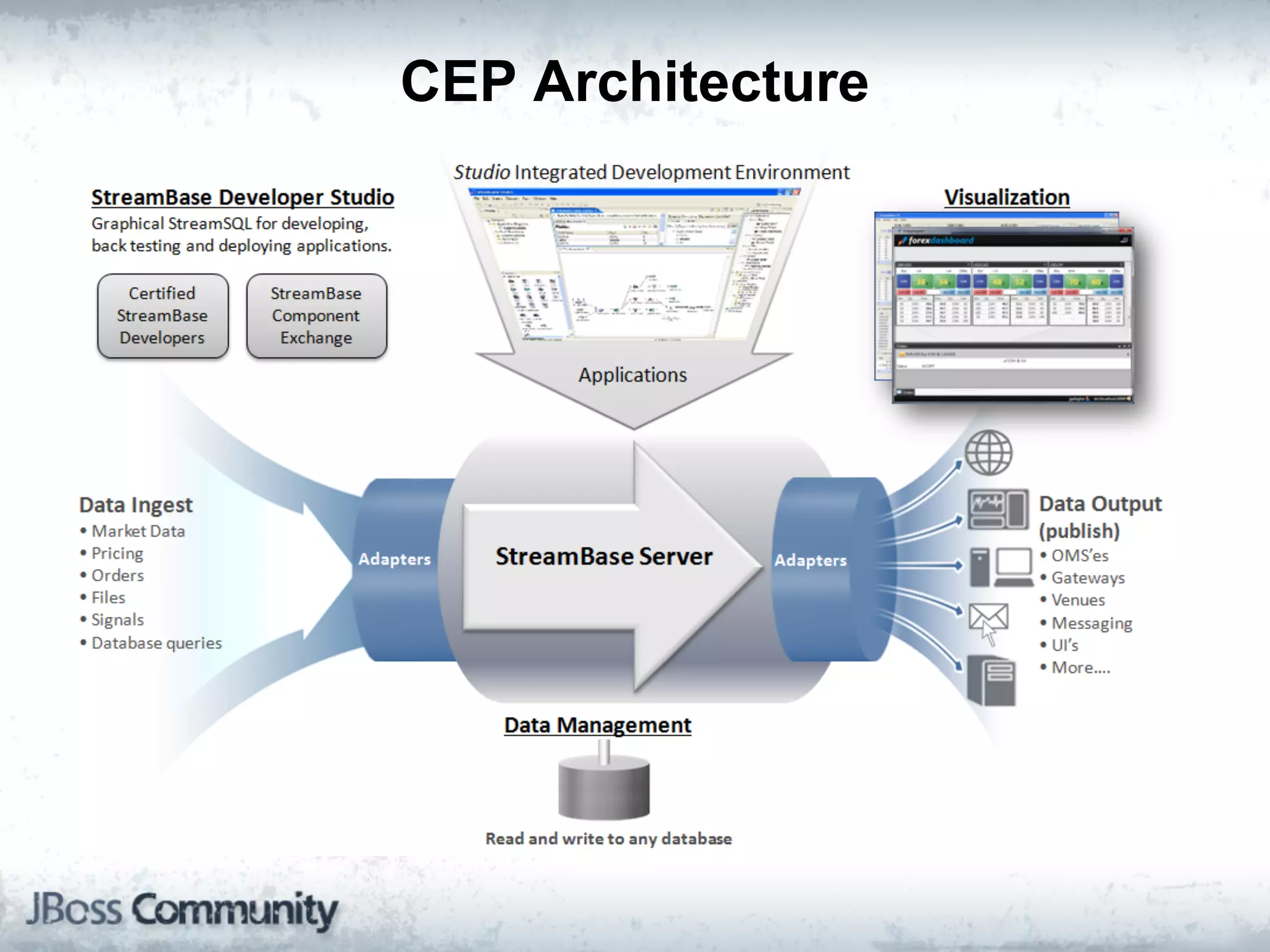
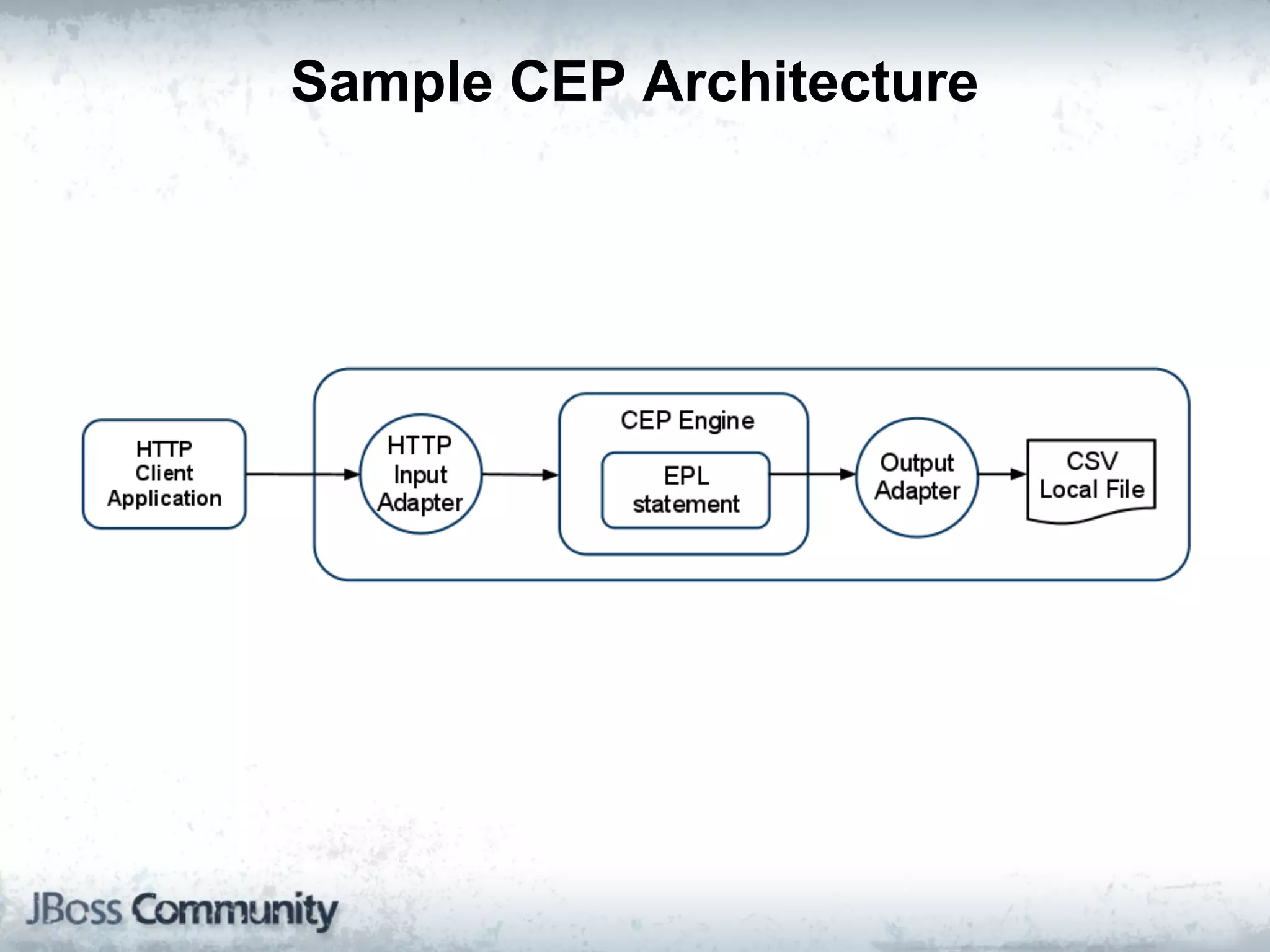
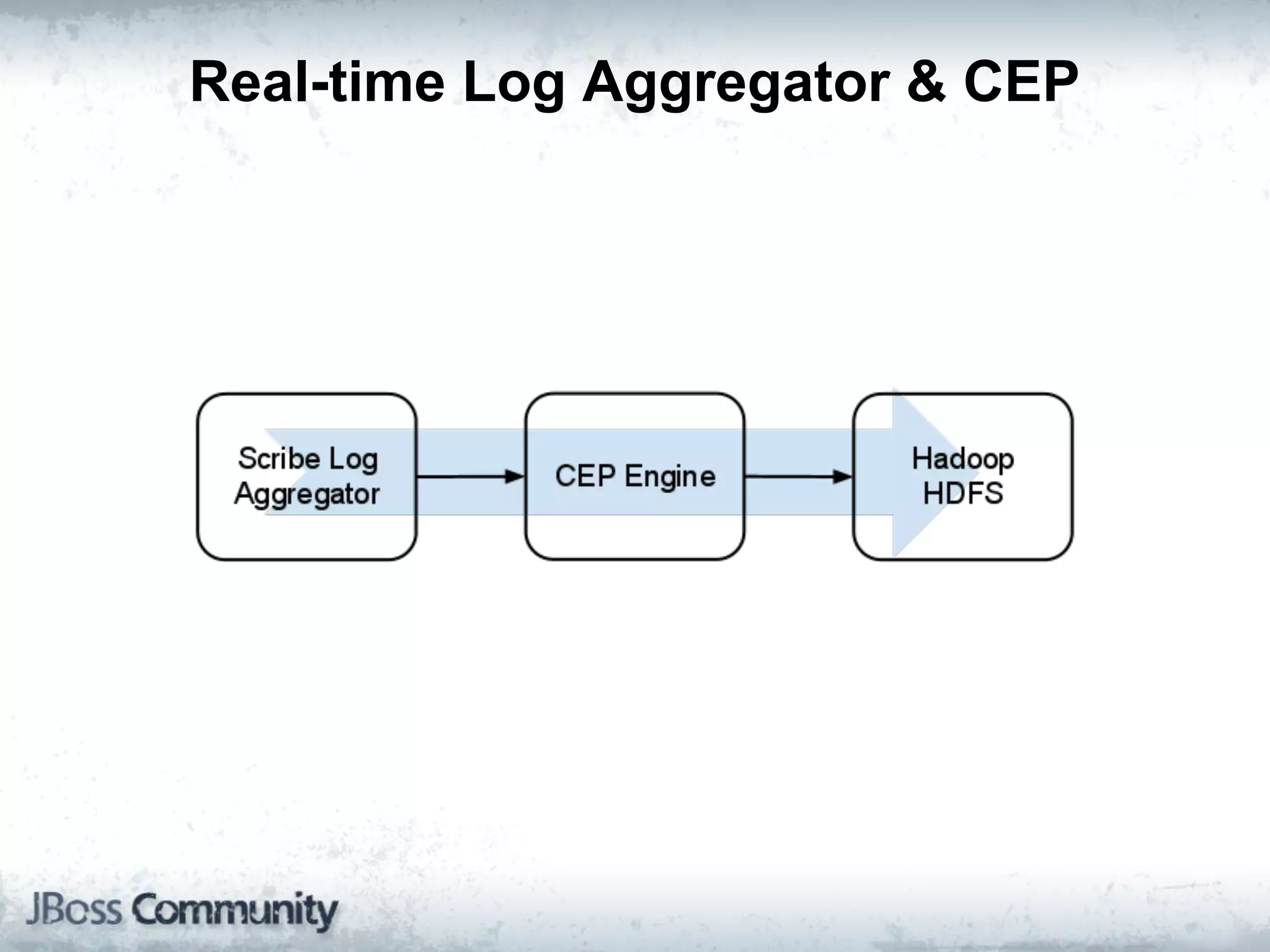
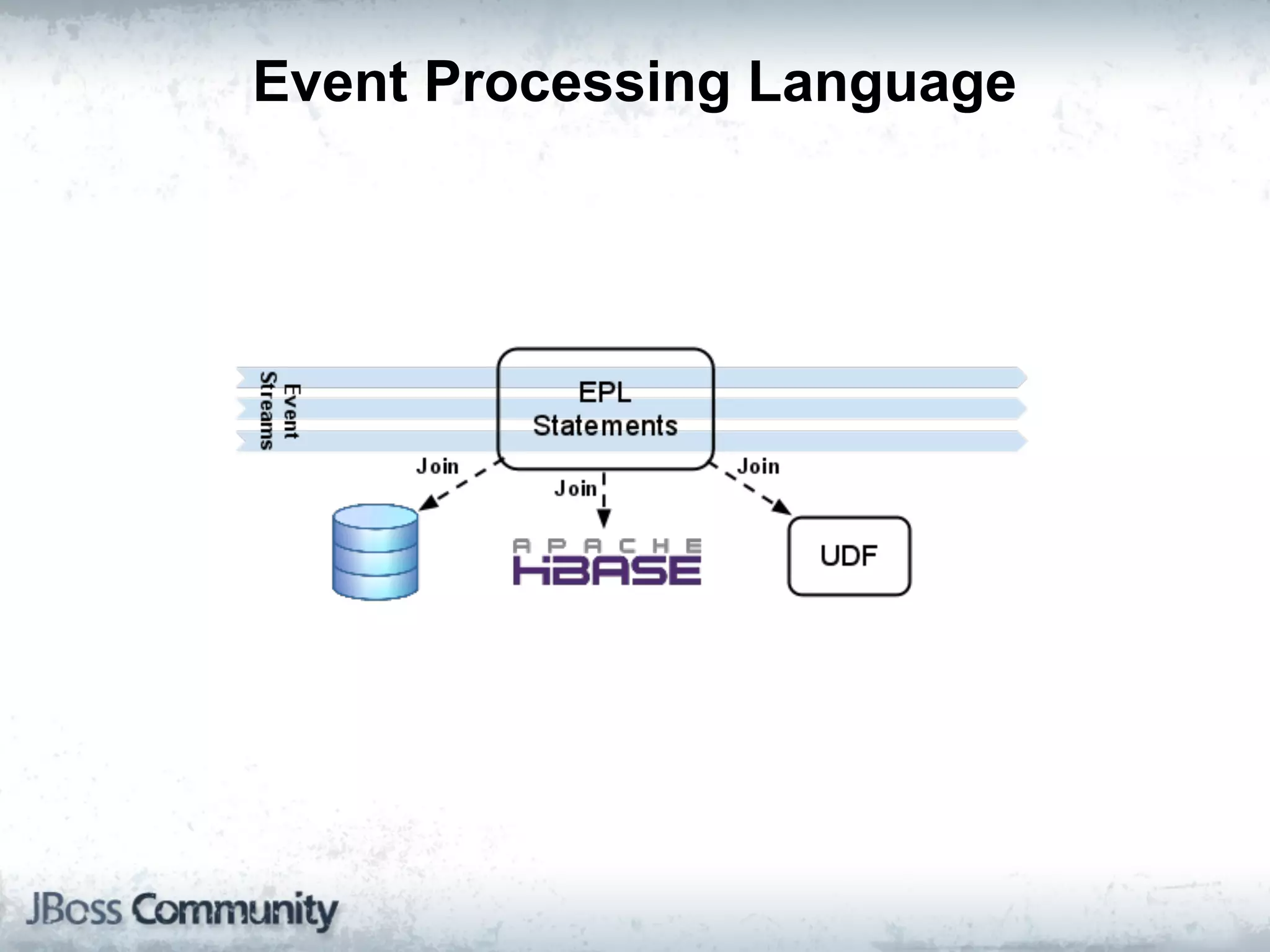
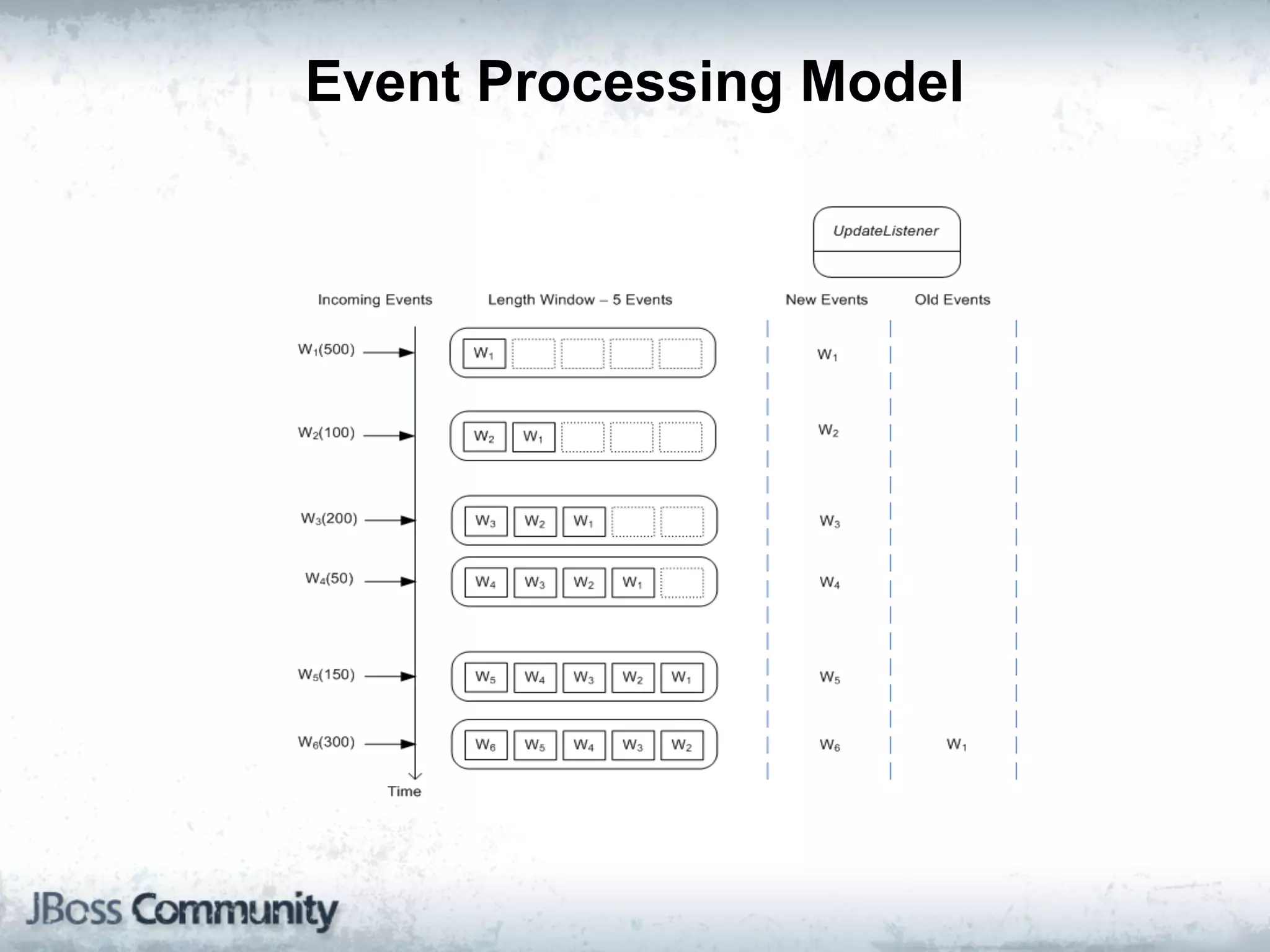
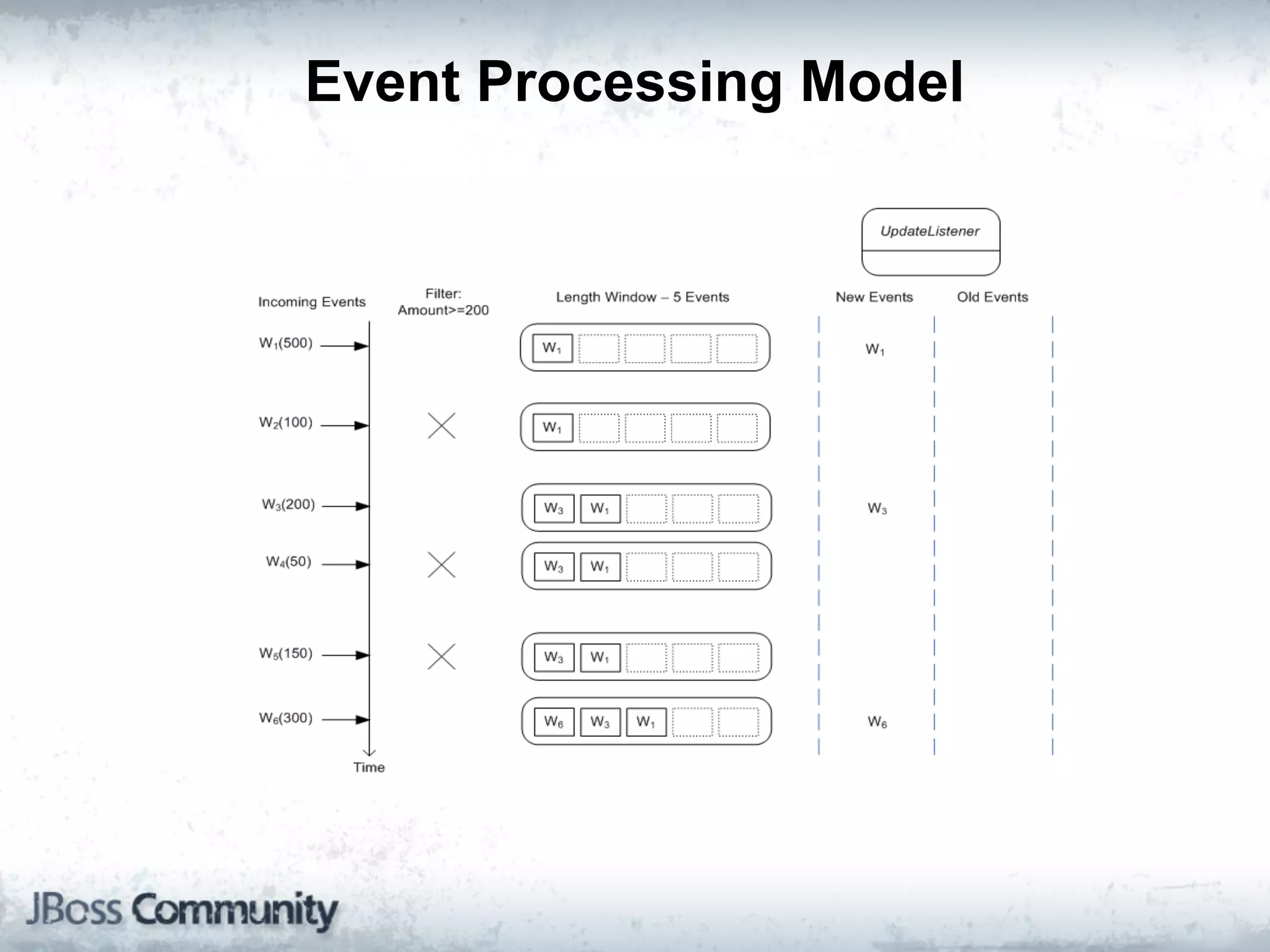
The document explains complex event processing (CEP), emphasizing its ability to analyze and respond to real-time data streams, often measured in nanoseconds. It highlights various application use cases across industries such as retail and finance, and differentiates between terminology like event stream processing (ESP) and simple event processing (SEP). Additionally, it outlines CEP architecture, event types, processing languages, and key considerations for developing high-performance CEP applications.














































![EPL Statement Sample
select Part.zone from pattern [
every Part=CountZone(cnt in (1, 2)) ->
( timer:interval(1 min) and not
CountZone(zone=Part.zone, cnt in (0, 3))
)
]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/complexeventprocessingwithesper-120117064536-phpapp01/75/Complex-Event-Processing-with-Esper-77-2048.jpg)
![Listener and Engine
// Get engine instance and register statement
EPServiceProvider engine = EPServiceProviderManager.getDefaultProvider();
EPStatement statement = engine.getEPAdministrator().createEQL("...");
// Attach a listener
statement.addListener(new UpdateListener() {
public void update(EventBean[] newEvents, EventBean[] oldEvents) {
// Handle complex event
...
}
});](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/complexeventprocessingwithesper-120117064536-phpapp01/75/Complex-Event-Processing-with-Esper-78-2048.jpg)

![Event filtering
// Filter for location report by location rectangle
select * from LR(x in [4:10], y in [6:12])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/complexeventprocessingwithesper-120117064536-phpapp01/75/Complex-Event-Processing-with-Esper-80-2048.jpg)



![Historical or reference data
// Alert when we hit the minimum inventory
// for a given zone
select zone, count(*)
from LR.std:unique(assetId) as lr,
sql:db[select mini from Minimum where zone=${lr.zone}]
having mini < count(*)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/complexeventprocessingwithesper-120117064536-phpapp01/75/Complex-Event-Processing-with-Esper-84-2048.jpg)