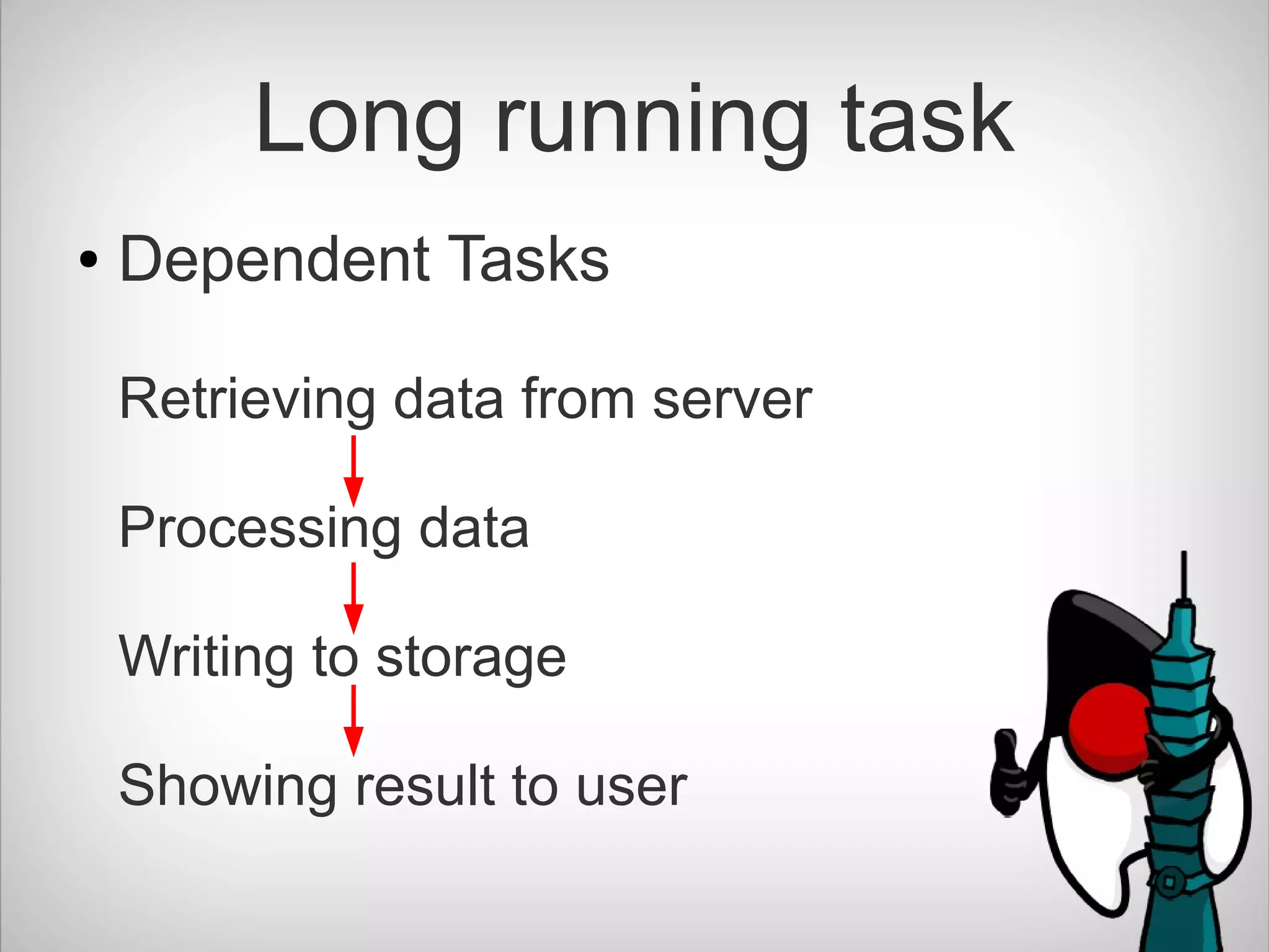
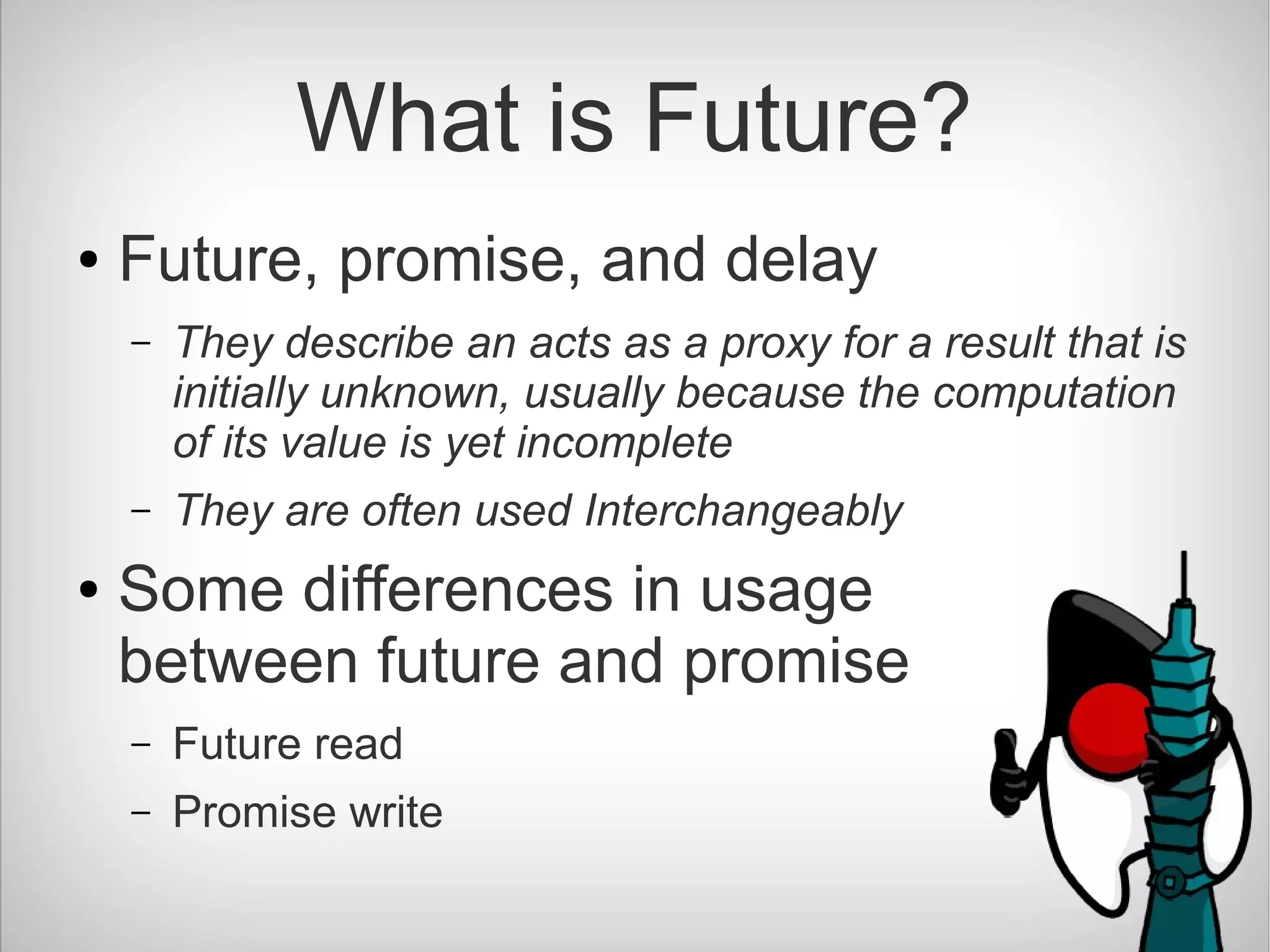
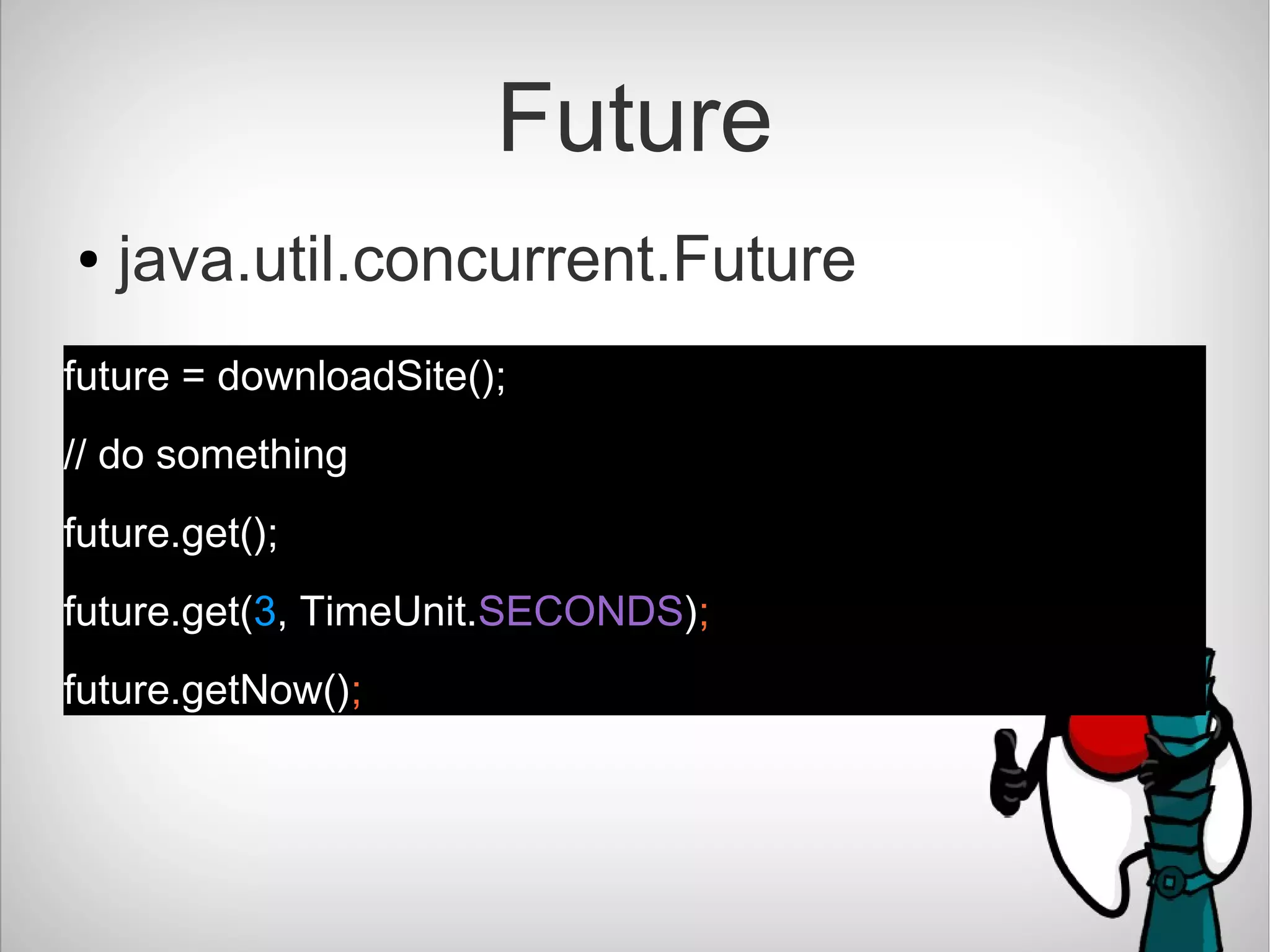
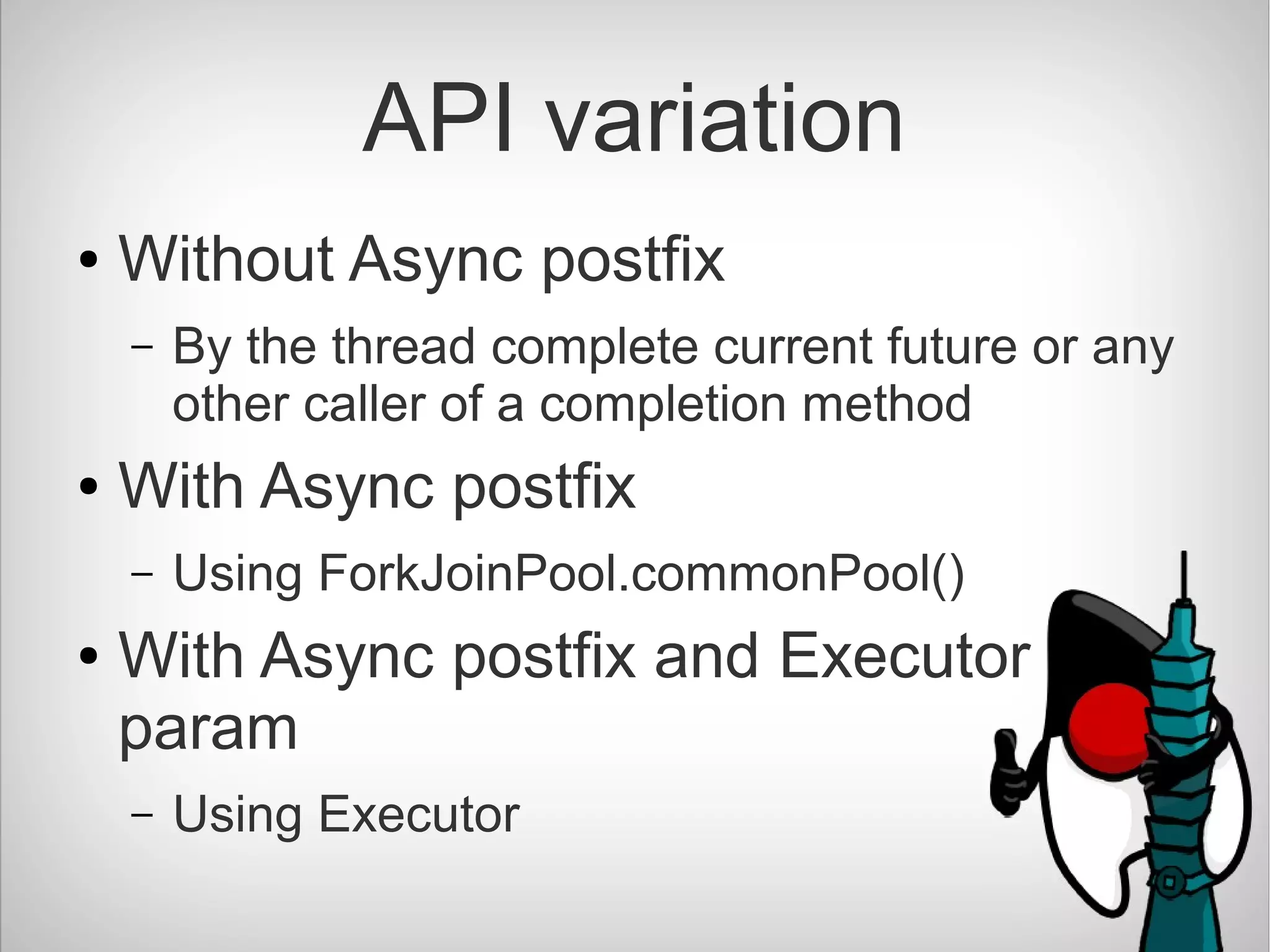
The document introduces CompletableFuture in Java, which is a library that allows asynchronous and non-blocking operations to be performed and chained together. It provides methods to chain dependent tasks together without blocking or callback hell. CompletableFuture implements Future and CompletionStage interfaces and provides various methods to handle results, errors, chaining and composition of asynchronous operations.








































![參考資料
● Java Concurrency in Practice
● The way of the Future, Futures in .NET, Java
and JavaScript
– http://blog.softmemes.com/2012/06/18/the-way-of-the-fu
● [concurrency-interest] Interface
CompletionStage
– http://cs.oswego.edu/pipermail/concurrency-interest/201](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/completablefuture-130907024900-/75/CompletableFuture-45-2048.jpg)
