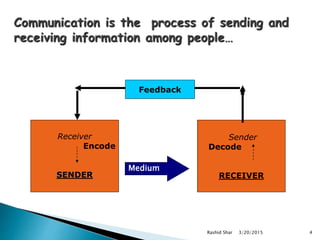
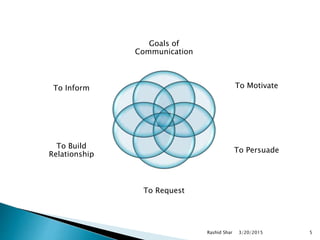
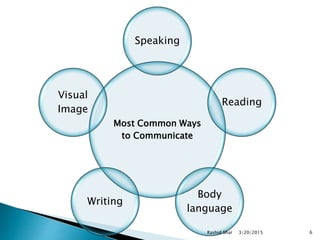
The document discusses communication and its key elements. It defines communication as the exchange of thoughts, messages, or information between a sender and receiver through various means such as speech, signals, writing or behavior. It notes communication requires a source, message, channel, receiver, and encoding and decoding processes. It also discusses the goals and most common forms of communication such as speaking, writing, and body language.